At its core, extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that transforms raw material, typically plastic pellets or granules, into a finished product with a fixed cross-sectional profile. The process involves feeding the raw material into a heated barrel, where a rotating screw melts and pressurizes it, before forcing the molten material through a shaping tool known as a die.
The fundamental principle of extrusion is the conversion of solid raw material into a continuous, molten stream that is then shaped and solidified. The entire process is a carefully controlled balance of heat, pressure, and movement to create a uniform, finished profile.
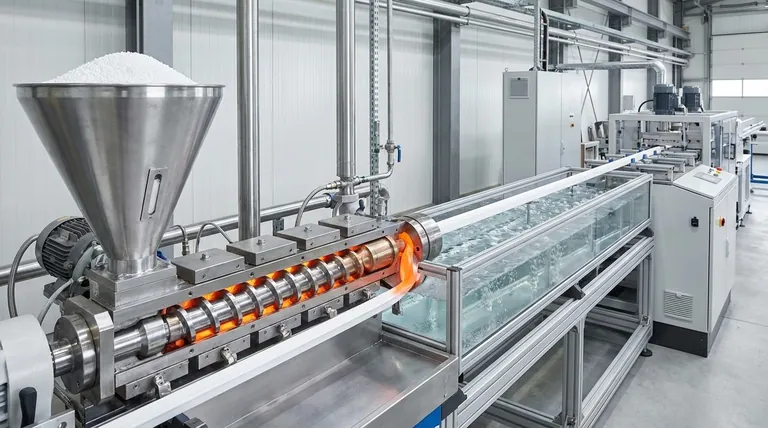

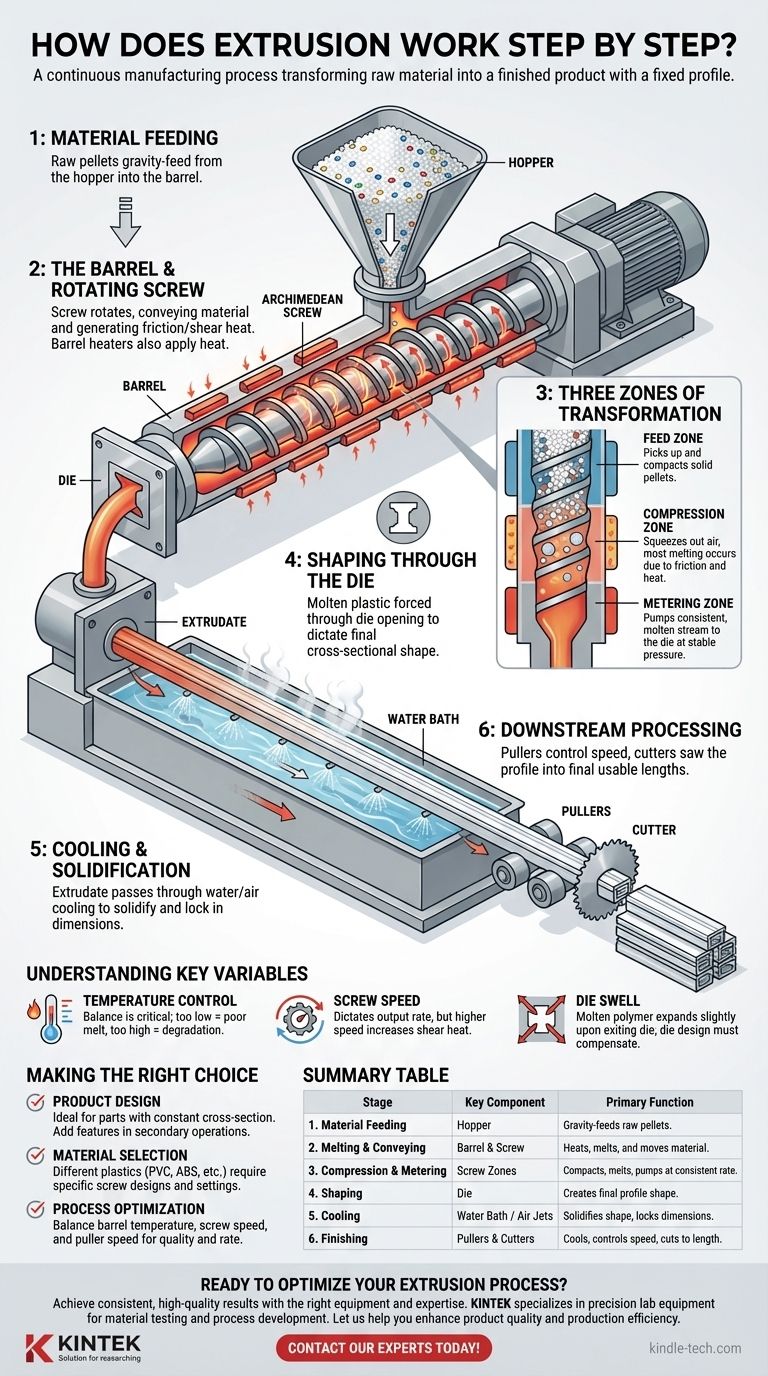
The Anatomy of an Extruder: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly understand how extrusion works, we must look at the mechanical stages that transform simple pellets into a precisely shaped final product.
Stage 1: Material Feeding
The process begins at the hopper, a large, funnel-shaped container mounted at one end of the extruder.
Raw plastic pellets, granules, or powders are loaded into the hopper. From here, gravity feeds the material through an opening at the bottom (the feed throat) into the extruder's barrel.
Stage 2: The Barrel and Rotating Screw
This is the heart of the extruder, where the primary transformation occurs. The material enters a long, heated cylinder known as the barrel.
Inside the barrel is a large, rotating Archimedean screw. This screw is the critical component that performs two jobs simultaneously: it conveys the material forward along the barrel and generates intense heat through friction (shear).
Stage 3: The Three Zones of Transformation
The journey along the barrel and screw is not uniform. It is divided into three distinct zones, each with a specific purpose.
- The Feed Zone: In this first section, the screw's channels are deep. Its primary role is to simply pick up the solid pellets from the feed throat and convey them forward, compacting them slightly.
- The Compression Zone: Here, the depth of the screw channel gradually decreases. This physically squeezes the material, forcing out trapped air and pressing it against the heated barrel wall. This is where most of the melting occurs, driven by both the barrel heaters and the intense shear heat from the screw's rotation.
- The Metering Zone: In this final section, the screw channel is very shallow. The material should be fully molten and homogenized here. The purpose of this zone is to act as a pump, ensuring a consistent, surge-free flow of molten plastic is delivered to the die at a stable pressure.
Stage 4: Shaping Through the Die
At the end of the barrel, the molten plastic is forced through a specialized tool called a die.
The die is a hardened steel plate with a precisely machined opening. This opening dictates the final cross-sectional shape of the product, whether it's a simple pipe, a complex window frame profile, or a flat sheet.
Stage 5: Cooling and Solidification
The process does not end when the material exits the die. The hot, pliable shape, now called the extrudate, must be cooled to solidify and lock in its dimensions.
This is typically achieved by pulling the extrudate through a water bath, spraying it with cool water, or passing it through cooling air jets. The rate of cooling is critical for controlling the final properties of the material.
Stage 6: Downstream Processing
Once cooled and solid, the continuous profile moves to the final stage.
Equipment such as pullers (which control the speed of the line) and cutters or saws are used to cut the profile into its final, usable lengths.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
The quality of an extruded product depends on a delicate balance of several factors. Misunderstanding these can lead to defects and inefficiencies.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature control is paramount. The barrel is typically fitted with multiple independent heating and cooling zones.
If the temperature is too low, the plastic won't melt completely, resulting in a poor surface finish and internal stress. If it's too high, the material can degrade, losing its structural properties.
The Impact of Screw Speed
The rotational speed of the screw dictates the output rate. However, a higher screw speed also generates more frictional shear heat.
Engineers must balance the desired production speed against the risk of overheating and degrading the material.
The Challenge of Die Swell
As the molten polymer is released from the pressure of the die, it has a tendency to expand slightly. This phenomenon is known as die swell.
Die designers must anticipate this effect and machine the die opening to be slightly smaller than the desired final dimensions to compensate for this expansion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the steps of extrusion allows you to make more informed decisions, whether you are designing a part or managing a production line.
- If your primary focus is product design: Recognize that the process is ideal for parts with a constant cross-section. Features like holes or tabs perpendicular to the extrusion direction must be added in a secondary operation.
- If your primary focus is material selection: Know that different plastics (e.g., PVC, ABS, Polycarbonate) have unique melt temperatures and flow characteristics that demand specific screw designs and process settings.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Concentrate on the interplay between barrel temperature, screw speed, and puller speed, as this triad governs both the production rate and the final quality of the part.
By mastering these fundamental stages, you can effectively leverage the power of extrusion to create consistent, high-quality products efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Feeding | Hopper | Gravity-feeds raw plastic pellets into the extruder. |
| 2. Melting & Conveying | Barrel & Rotating Screw | Heats and melts the plastic while moving it forward. |
| 3. Compression & Metering | Screw Zones (Feed, Compression, Metering) | Compacts, melts, and pumps the plastic at a consistent rate. |
| 4. Shaping | Die | Forces molten plastic through an opening to create the final profile. |
| 5. Cooling | Water Bath / Air Jets | Solidifies the extruded shape to lock in dimensions. |
| 6. Finishing | Pullers & Cutters | Cools the continuous profile and cuts it to the desired length. |
Ready to Optimize Your Extrusion Process?
Understanding the mechanics is the first step; achieving consistent, high-quality results requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for material testing and process development, helping R&D teams and production facilities like yours validate materials and perfect extrusion parameters.
Let us help you enhance product quality and production efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of the extrusion process? High Costs and Geometric Limits Explained
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling
- What machine is used to make pellets? The Complete Guide to Pellet Mills & Production Systems
- What is the difference between extrusion and co-extrusion? Engineer Multi-Material Parts
- What are the advantages of coextrusion? Achieve Multi-Material Efficiency and Superior Performance



















