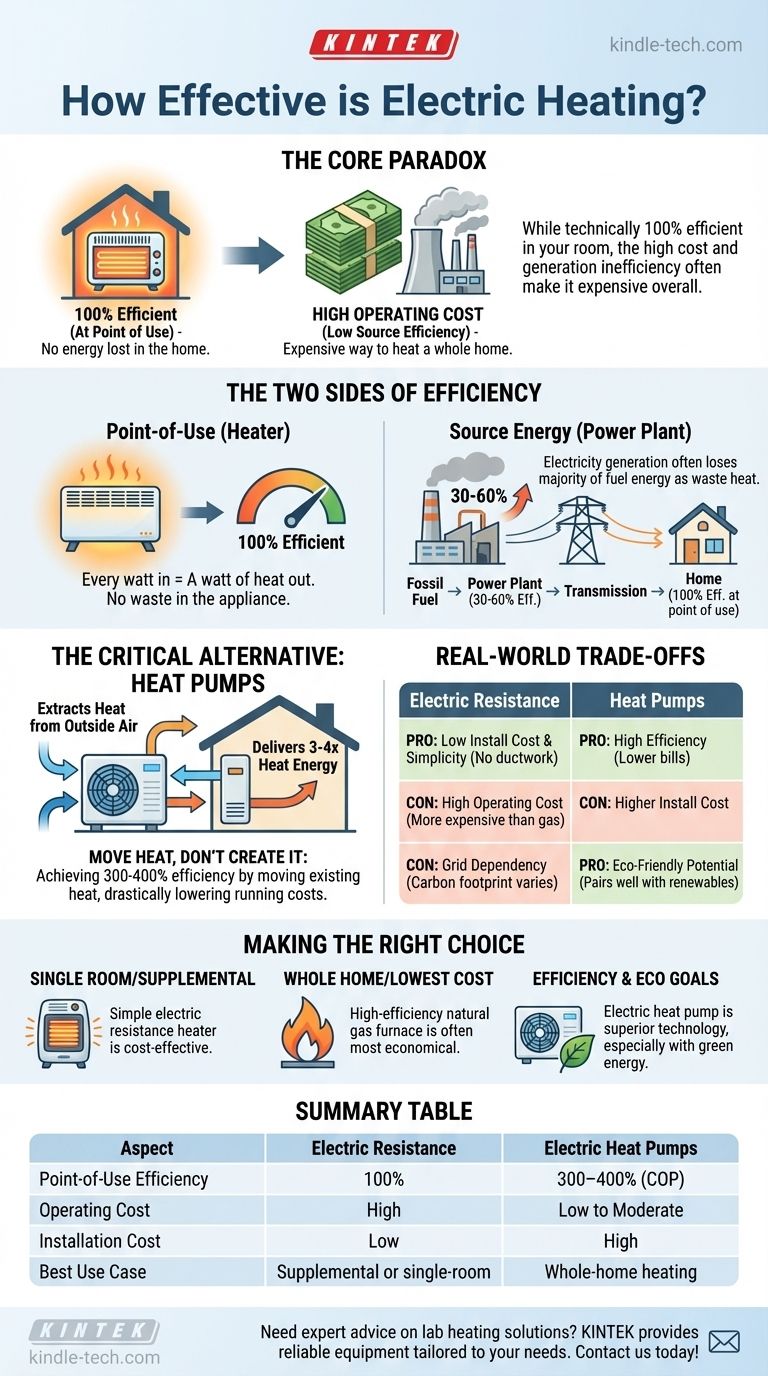
In one specific sense, electric heating is exceptionally effective. An electric resistance heater converts virtually 100% of the electricity it consumes directly into heat energy at the point of use. This means no energy is lost through chimneys or pipes within your home, unlike some traditional combustion furnaces.
The core issue is not the efficiency of the heater itself, but the high cost and generation inefficiency of the electricity it consumes. While technically 100% efficient in your room, electric resistance heating is often one of the most expensive ways to heat an entire home.

The Two Sides of "Efficiency"
The term "100% efficient" is technically accurate for electric resistance heaters, but it can be misleading. To understand its true effectiveness, we must distinguish between efficiency at the point of use and the total efficiency of the system.
Point-of-Use Efficiency: The Heater in Your Room
Every watt of electricity that flows into a simple electric heater (like a baseboard heater or portable space heater) is converted into a watt of heat. There is no waste product.
This direct conversion is why it's considered 100% efficient at the point of use. Nothing is lost in the conversion process within the appliance itself.
Source Energy Efficiency: The Power Plant to Your Home
The story changes when you look at the entire energy journey. Electricity doesn't appear magically in your wall outlet.
It is most often generated at a power plant by burning fossil fuels like natural gas or coal. This process is typically only 30-60% efficient, with the majority of the fuel's energy lost as waste heat at the plant. Further energy is lost during transmission over power lines.
Therefore, the total system efficiency of electric resistance heat—from the power plant to your living room—is often far lower than a modern natural gas furnace operating directly in your home.
The Critical Alternative: Heat Pumps
Not all electric heating works by resistance. Heat pumps are a fundamentally different and far more efficient technology.
Moving Heat vs. Creating Heat
Instead of using electricity to generate heat, a heat pump uses electricity to move existing heat from one place to another. In winter, it extracts heat from the outside air (even when it's cold) and transfers it inside.
Efficiency Ratings Over 100%
Because they are moving heat rather than creating it, heat pumps can achieve efficiency ratings of 300% to 400%. For every one unit of electricity they consume, they can deliver three to four units of heat.
This makes them dramatically more cost-effective to run than electric resistance heaters, often competing with or even beating the running costs of natural gas.
Understanding the Real-World Trade-offs
Choosing a heating system involves balancing installation cost, running cost, and performance.
Pro: Low Installation Cost & Simplicity
Electric resistance heaters are simple devices. They are inexpensive to purchase and easy to install, requiring no ductwork, vents, or fuel lines. This makes them a great choice for supplemental heat or for small, specific applications.
Con: High Operating Cost
The primary drawback is the cost of the fuel. Per unit of energy delivered, electricity is almost always more expensive than natural gas. Using resistance heaters as the primary source for an entire home will typically result in very high utility bills.
Con: Grid Dependency and Emissions
The environmental friendliness of electric heat is tied directly to your electricity grid. If your power comes from coal, your heating system has a significant carbon footprint. If it comes from renewables like solar, wind, or hydro, it can be a very clean option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if electric heat is effective for you, match the technology to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is heating a single room or supplementing a weak spot: A simple electric resistance heater is a cost-effective and practical solution.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible running cost for a whole home: A high-efficiency natural gas furnace is typically the most economical choice where available.
- If your primary focus is combining efficiency and environmental goals: An electric heat pump is the superior technology, especially when paired with solar panels or a green electricity plan.
Ultimately, judging effectiveness requires you to look past the single metric of efficiency and consider the entire cost and impact of the system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Electric Resistance Heating | Electric Heat Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| Point-of-Use Efficiency | 100% | 300–400% (COP) |
| Operating Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Installation Cost | Low | High |
| Best Use Case | Supplemental or single-room heat | Whole-home heating |
Need expert advice on selecting the right heating solution for your lab or facility? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require precise temperature control for experiments or efficient environmental systems, our solutions ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic floor press used for? A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Lab Applications
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries



















