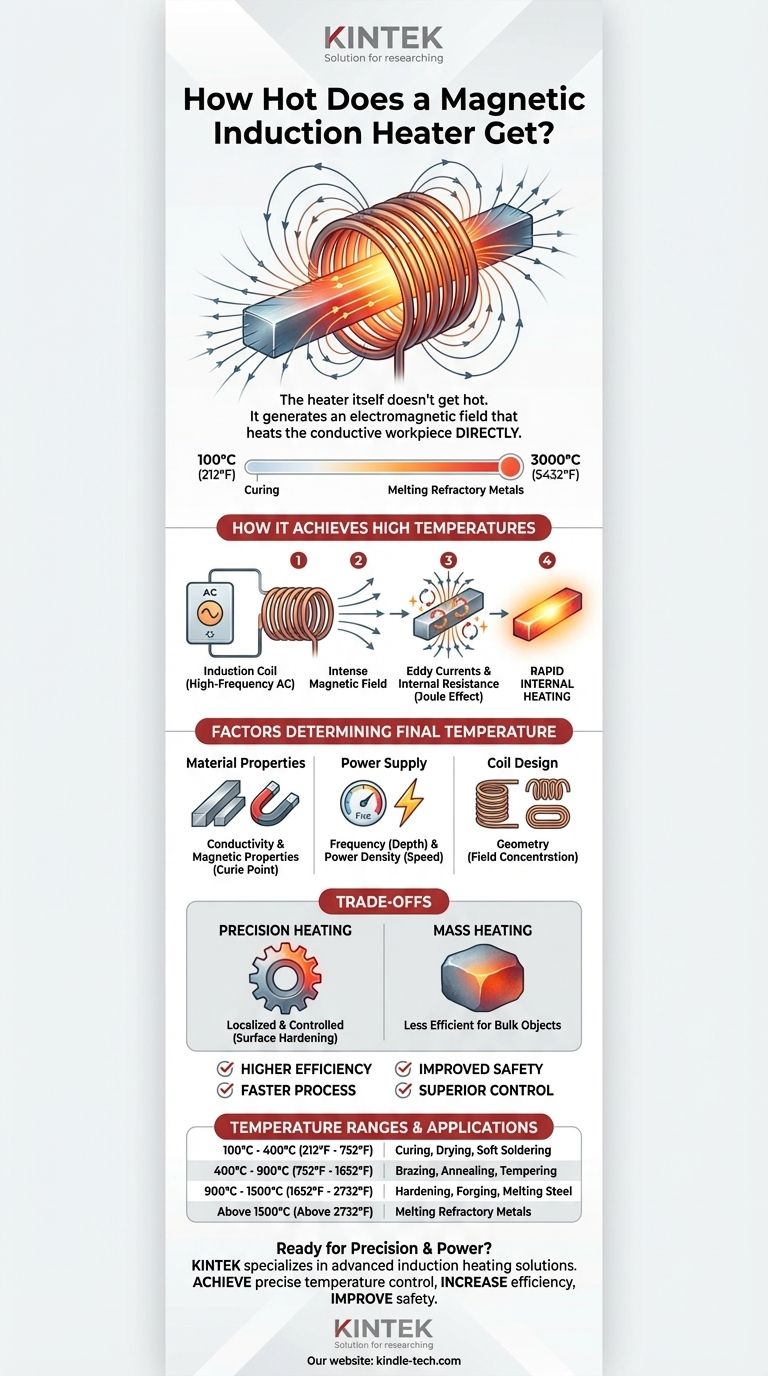
An induction heater itself doesn't "get hot" in the traditional sense; instead, it generates an electromagnetic field that heats a conductive workpiece placed within it. This process allows the workpiece to reach temperatures ranging from a low of 100°C (212°F) for applications like curing, all the way up to 3000°C (5432°F) for melting refractory metals.
The core principle to understand is that induction heating doesn't rely on external heat transfer. The heat is generated directly inside the target material, which means the potential temperature is limited primarily by the material's own melting point, not by the heating device itself.

How Induction Heating Achieves High Temperatures
Induction heating is a non-contact process. It works by using a powerful, high-frequency electromagnet to induce electrical currents within a conductive target object.
The Role of the Induction Coil
The primary component is the induction coil, typically made of copper tubing. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
This current generates a rapidly changing and intense magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Generating Heat Within the Workpiece
When a conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed in this field, two things happen to generate heat:
- Eddy Currents: The magnetic field induces circular electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal.
- Internal Resistance: The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents results in rapid and precise heating due to the Joule effect.
The coil itself stays cool because it is not resisting the magnetic field in the same way, and it is often internally water-cooled to manage its own electrical resistance.
Factors Determining the Final Temperature
The maximum temperature a workpiece can reach is not a single number. It is a function of the equipment's design, the material being heated, and the process parameters.
Material Properties
The conductivity and magnetic properties of the workpiece are critical. Ferrous metals like iron and steel heat very efficiently below a certain temperature (the Curie point) due to magnetic hysteresis losses, which generate additional heat.
Power Supply Frequency and Density
The frequency of the alternating current determines the depth of heat penetration. Higher frequencies result in shallower, more concentrated surface heating, ideal for case hardening.
Power density—the amount of power delivered per unit of surface area—directly influences how quickly the workpiece heats up. Higher power density leads to faster temperature rise.
Coil Design
The geometry of the induction coil is engineered to match the workpiece. A well-designed coil ensures the magnetic field is concentrated precisely where the heat is needed, maximizing efficiency and controlling the final temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Induction heating is a powerful technology, but its application requires understanding its specific characteristics and limitations.
Precision vs. Mass Heating
Induction is exceptionally precise, allowing for localized heating of specific areas without altering the rest of the part. This is a significant advantage over furnace heating, which heats the entire object.
However, this precision means it is less efficient for bulk heating of very large or irregularly shaped objects compared to a simple furnace.
Equipment and Setup Costs
The initial investment in induction heating equipment—the power supply and custom coils—is typically higher than for conventional resistance or flame heaters.
The trade-off is significantly higher energy efficiency, faster process times, improved safety (no open flame), and superior process control, which often lead to a lower total cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The temperature an induction system can achieve is a variable you control based on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or tempering: You will use high frequencies to heat the surface of a steel part to around 800-1000°C (1472-1832°F) very quickly, followed by a quench.
- If your primary focus is brazing or soldering: You need a lower temperature, precisely controlled between 200-900°C (392-1652°F), to melt the filler alloy without melting the parent metals.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for casting: You will need a system capable of delivering high power for a sustained period to bring materials like steel or silicon to well above their melting points, potentially exceeding 1500°C (2732°F).
Ultimately, the temperature capability of an induction heater is defined by the needs of your application and the properties of the material you intend to heat.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|
| 100°C - 400°C (212°F - 752°F) | Curing, Drying, Soft Soldering |
| 400°C - 900°C (752°F - 1652°F) | Brazing, Annealing, Tempering |
| 900°C - 1500°C (1652°F - 2732°F) | Hardening, Forging, Melting Steel |
| Above 1500°C (Above 2732°F) | Melting Refractory Metals (e.g., Tungsten) |
Ready to harness the precision and power of induction heating for your lab or production process?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for research, quality control, and specialized manufacturing. Our solutions offer unmatched temperature control, energy efficiency, and process repeatability.
We help you:
- Achieve precise temperature control for applications from brazing to metal melting.
- Increase energy efficiency and reduce processing times.
- Improve safety with non-contact, flameless heating.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific heating requirements and discover how our expertise in laboratory equipment can optimize your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize WC/Cu-Zr-Ti Composite Consolidation
- What is the purpose of introducing hydrogen or argon gas into a vacuum hot pressing furnace during sintering or cooling?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
















