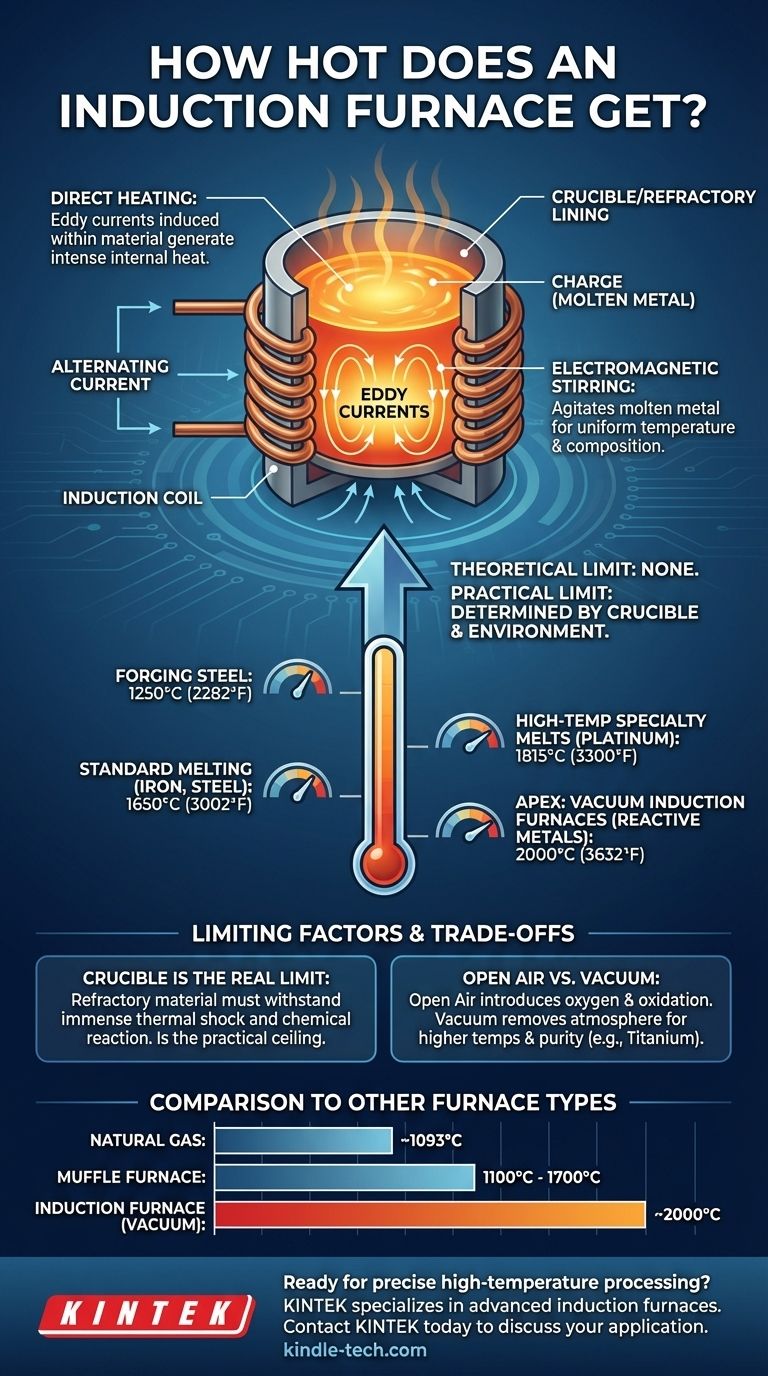
In principle, an induction furnace has no upper temperature limit. The heating process works by inducing an electric current directly within the material, known as the charge. In practice, however, the maximum achievable temperature is dictated by the physical limits of the crucible or refractory lining used to contain the molten metal. For most industrial applications, this means operating temperatures up to 1650°C (3002°F), with specialized systems reaching even higher.
The core principle to understand is that the induction heating method itself is not the bottleneck. The true temperature limit of any induction furnace system is determined by the heat tolerance of the crucible holding the material and the environment (open air vs. vacuum) it operates in.

How Induction Achieves Extreme Temperatures
To understand the capabilities of an induction furnace, you must first grasp how it generates heat so efficiently, without any external flame or heating element.
The Principle of Direct Heating
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the metal charge placed inside the coil.
This magnetic field induces powerful secondary currents, known as eddy currents, directly inside the metal. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and intensely as these eddy currents flow through it—the same principle behind resistive heating, but generated internally.
The Benefit of Electromagnetic Stirring
A key advantage of this process is the electromagnetic stirring that occurs. The forces created by the magnetic field naturally agitate the molten metal, ensuring a highly uniform temperature and chemical composition throughout the melt.
Practical Temperature Ranges in Operation
While the theory is limitless, real-world applications operate within specific temperature ranges determined by the furnace type, the material being melted, and the operating environment.
Standard Forging and Melting
For common industrial tasks, temperatures are well-defined. Forging applications typically require heating steel up to 1250°C (2282°F).
For melting metals like iron and steel, coreless induction furnaces routinely operate at temperatures up to 1650°C (3002°F). Small-scale furnaces often have a maximum heating temperature of around 1600°C (2900°F).
High-Temperature Specialty Melts
For metals with very high melting points, specialized induction furnaces are used. Melting platinum in an open-air environment, for example, can be done at temperatures around 1815°C (3300°F).
The Apex: Vacuum Induction Furnaces
When the highest possible purity and temperature are required, a vacuum induction furnace is used. By removing the atmosphere, these systems prevent oxidation and other reactions. This allows them to achieve extreme temperatures, with some systems rated for a maximum of 2000°C (3632°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limiting Factors
The decision to use an induction furnace often comes down to understanding its limitations, which are almost entirely related to the materials science of the components that contain the heat.
The Crucible is the Real Limit
The single most critical limiting factor is the refractory material used to create the crucible or furnace lining. This container must have a melting point significantly higher than the charge material it holds. It also must be ableto withstand immense thermal shock and resist chemical reaction with the molten metal. This is the practical ceiling on temperature.
Open Air vs. Vacuum
Operating in open air introduces oxygen, which can cause oxidation of both the charge material and the crucible itself at extreme temperatures. A vacuum environment removes this limitation, enabling higher temperatures and the processing of reactive metals like titanium.
Comparison to Other Furnace Types
The unique capability of induction heating becomes clear when compared to other methods. A natural gas furnace is typically limited to around 1093°C (2000°F). A muffle furnace, which uses an external heat source to heat a chamber, generally maxes out between 1100°C and 1700°C depending on its design, but it cannot match the direct, rapid heating of induction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is melting standard ferrous and non-ferrous metals like iron, steel, or copper: A standard coreless induction furnace operating up to 1650°C is the ideal, efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is melting high-temperature or reactive metals like platinum, titanium, or specialty alloys: A specialized system, likely a vacuum induction furnace, is necessary to achieve the required temperatures and purity.
- If your primary focus is lower-temperature heat treating or general lab work: A less complex technology like a muffle or resistance furnace may be a more cost-effective solution.
Understanding these factors allows you to select not just a furnace, but the precise heating technology your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Application / Furnace Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Forging | 1250°C (2282°F) | Steel |
| General Melting (Iron, Steel) | 1650°C (3002°F) | Ferrous/Non-ferrous metals |
| High-Temp Melting (Open Air) | 1815°C (3300°F) | Platinum |
| Vacuum Induction Melting | 2000°C (3632°F) | Reactive metals, Titanium, Specialty alloys |
Ready to achieve the precise high-temperature processing your materials demand?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific needs—whether you're melting standard alloys or high-purity reactive metals. Our experts will help you select the right system to ensure efficiency, purity, and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover the ideal heating solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















