In the pharmaceutical industry, freeze-drying, known formally as lyophilization, is the definitive method for preserving delicate drugs and biologicals. It is used to enhance the stability and extend the shelf life of products that are sensitive to heat or moisture, such as vaccines, enzymes, antibiotics, and injectable protein-based therapies. This process is critical for ensuring these sensitive medications remain effective from manufacturing to patient administration.
The core challenge with many modern medicines, especially biologics, is their inherent instability in liquid form. Lyophilization solves this by removing water at low temperatures, essentially placing the drug in a state of suspended animation to prevent degradation and preserve its therapeutic activity.
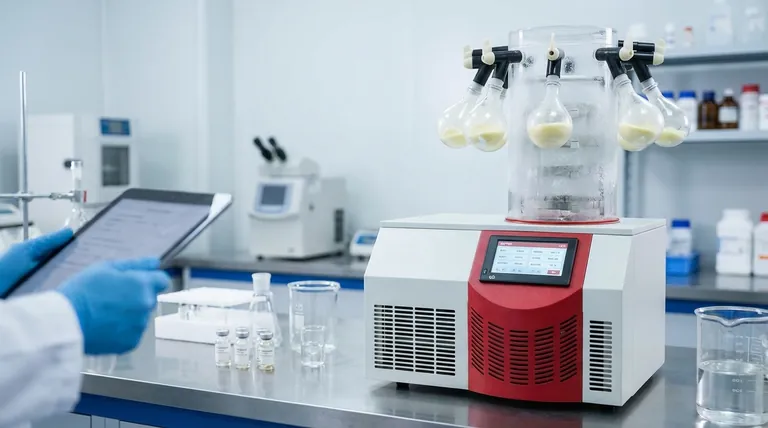

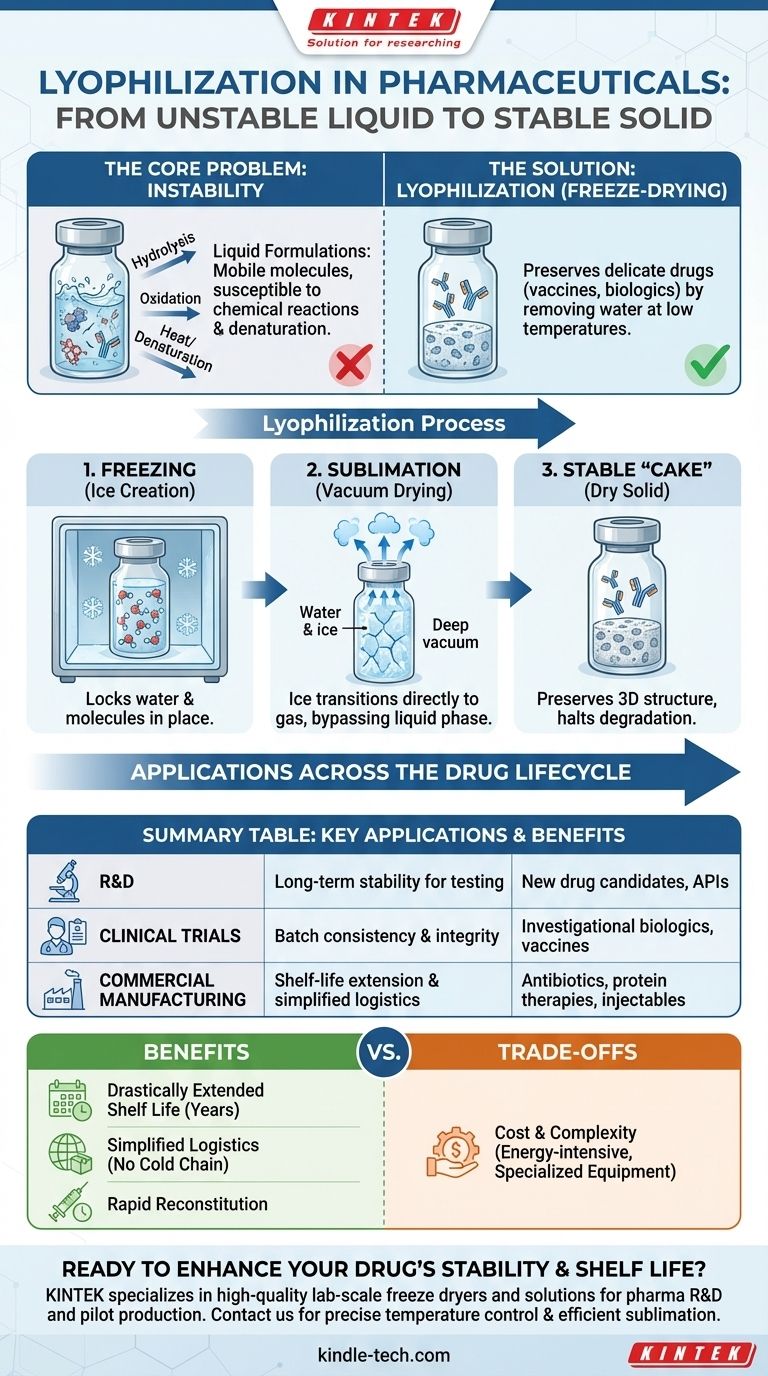
The Core Problem: Instability in Drug Formulations
Many of today's most advanced medicines are large, complex molecules that are highly fragile. Their structure is key to their function, and this structure can be easily damaged.
Why Liquid Formulations Degrade
In a liquid solution, molecules are mobile. This mobility allows for chemical reactions, like hydrolysis or oxidation, that can break down the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API). The presence of water can directly accelerate this degradation, while heat can cause proteins to unfold and lose their function, a process called denaturation.
The Challenge of Biologics
Biologics—such as vaccines, antibodies, and therapeutic proteins—are particularly susceptible to degradation. Unlike simple chemical drugs, their complex, three-dimensional shapes are essential for their efficacy. Even minor changes to this structure can render them ineffective or, in some cases, cause an adverse immune response.
How Lyophilization Creates Stability
Lyophilization is a sophisticated drying process that works by freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water to transition directly from a solid to a gas. This process is called sublimation.
The Principle of Sublimation
By freezing the product first, the process locks water molecules in place as ice. The subsequent application of a deep vacuum allows this ice to turn directly into water vapor, which is then collected. This bypasses the liquid phase entirely, avoiding the damaging effects of liquid water on the drug's structure.
Preserving Molecular Integrity
Because sublimation occurs at very low temperatures, it is an exceptionally gentle process. It preserves the delicate three-dimensional structure of proteins and other large molecules, ensuring the final product retains its full biological activity and therapeutic effect.
Creating a Stable, Porous Structure
The final lyophilized product is a dry, porous solid often referred to as a "cake." In this water-free, solid state, molecules are immobilized, effectively halting degradation. This can extend a product's shelf life from a few days in liquid form to several years at room temperature.
Applications Across the Drug Lifecycle
Lyophilization is not just a manufacturing step; it is a critical tool used throughout the entire journey of drug development and delivery.
Research & Development
In early-stage R&D, scientists use lab-scale freeze dryers to create stable batches of new drug candidates. This allows for long-term storage and testing without the risk of the compound degrading before it can be fully evaluated.
Clinical Trials
For clinical trials, producing stable, consistent batches of an investigational drug is paramount. Lyophilization ensures that the drug administered to patients in different locations and at different times is identical, guaranteeing the integrity of the trial data.
Commercial Manufacturing
In large-scale manufacturing, freeze-drying is used to produce final commercial products. This includes a vast range of injectables, from life-saving vaccines and antibiotics to cutting-edge cancer therapies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Benefits
While lyophilization is a powerful technology, its application is a strategic decision based on a clear set of benefits and inherent complexities.
Benefit: Drastically Extended Shelf Life
The primary advantage is transforming an unstable liquid into a solid that is stable for years. This reduces waste and ensures product availability, which is especially critical for national stockpiles of vaccines or emergency medicines.
Benefit: Simplified Logistics
Lyophilized products are lightweight and often do not require a strict cold chain (continuous refrigeration). This dramatically simplifies storage and global distribution, making it easier to get vital medicines to remote or resource-limited areas.
Benefit: Rapid Reconstitution
The porous cake structure allows the dried drug to be quickly and easily dissolved back into a liquid (a sterile solvent) just before administration. This is crucial in hospital and emergency settings where speed is essential.
The Primary Trade-off: Cost and Complexity
Lyophilization is a slow, energy-intensive, and expensive process. It requires significant capital investment in specialized equipment and is a complex process to develop and validate. For drugs that are inherently stable, simpler and more cost-effective methods are preferred.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Lyophilization is a purpose-driven tool, not a universal solution. Its use is determined by the specific properties of the drug and the strategic goals of the product.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability for a fragile biologic: Lyophilization is often the only viable method to create a commercially successful product.
- If your primary focus is simplifying global distribution and storage: The removal of cold-chain requirements makes lyophilization a powerful strategic choice.
- If your primary focus is a drug that must be administered quickly: The rapid reconstitution of a lyophilized cake is a key clinical advantage for injectables.
- If your primary focus is cost-minimization for an inherently stable molecule: Traditional formulation methods like tablets or simple liquid solutions are far more economical.
Ultimately, freeze-drying empowers the creation and delivery of life-saving medicines that would otherwise be too fragile to survive the journey from lab to patient.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Products |
|---|---|---|
| Research & Development | Long-term stability for testing | New drug candidates, APIs |
| Clinical Trials | Batch consistency and integrity | Investigational biologics, vaccines |
| Commercial Manufacturing | Shelf-life extension & simplified logistics | Antibiotics, protein therapies, injectables |
Ready to enhance your drug's stability and shelf life? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab-scale freeze dryers and lyophilization solutions tailored for pharmaceutical R&D and pilot production. Our equipment ensures precise temperature control and efficient sublimation, helping you preserve the integrity of sensitive biologics, vaccines, and APIs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your drug development and manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- Why does the manufacturer affect the price of a lab freeze dryer? Invest in Reliability, Innovation & Support
- What are the benefits of freeze-drying for sensitive samples? Preserve Delicate Materials with Unmatched Quality
- What role do freeze dryers play in biotechnology and research? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reproducibility
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability



















