The standard rule of thumb for annealing steel is to soak the material for one hour for every inch of its thickest cross-section. However, this is only a starting point. The correct duration is inseparable from the target temperature and the specific alloy being treated, as the ultimate goal is not just to heat the steel, but to fundamentally change its internal structure.
The most common mistake in annealing is focusing only on time. True success depends on the precise interplay of three factors: reaching the correct temperature, holding for sufficient time to ensure a complete internal transformation, and then executing a very slow cool-down.
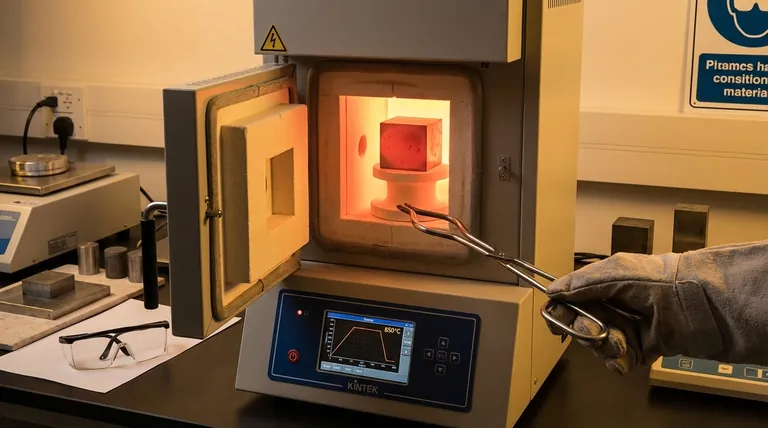
The Three Pillars of a Successful Anneal
Annealing is a process designed to achieve one primary goal: make steel as soft and ductile as possible. This is accomplished by creating a very specific internal microstructure called coarse pearlite. Each stage of the process is a deliberate step toward forming that structure.
1. Heating to the Austenitizing Temperature
The first step is to heat the steel above its critical transformation temperature. This dissolves the hard, brittle structures (like cementite or martensite) into a new, uniform crystal structure called austenite.
The exact temperature is crucial and depends on the carbon content.
- For most carbon and low-alloy steels (hypo-eutectoid): Heat to approximately 30-50°C (50-90°F) above the upper critical temperature, known as the Ac3.
- For high-carbon steels (hyper-eutectoid): You typically heat to just above the lower critical temperature (Ac1) to avoid forming a brittle network of carbides upon cooling.
Getting this temperature right is non-negotiable. Too low, and the transformation to austenite won't be complete. Too high, and you risk excessive grain growth.
2. Soaking (Holding at Temperature)
This is the "how long" part of the question. The primary purpose of the soaking period is to ensure two things happen:
- The entire part, including its core, reaches a uniform austenitizing temperature.
- The transformation to a homogenous austenite structure is fully completed.
The "one hour per inch of thickness" rule is a safe guideline to guarantee this thermal and microstructural equilibrium. For a part that is 2 inches thick, you would soak for 2 hours after the entire part has reached the target temperature.
3. The Critical Cooling Phase
This is arguably the most important stage for achieving maximum softness. After soaking, the steel must be cooled as slowly as possible.
This slow cooling allows the austenite to transform into the desired large, soft structure of coarse pearlite. A fast cool would produce harder structures like martensite (hardening), while a moderate cool would produce finer, tougher structures (normalizing).
Common slow-cooling methods include leaving the part inside the furnace and shutting it off (furnace cooling) or burying the hot part in an insulating material like vermiculite, ash, or dry sand.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
The "one hour per inch" rule is a baseline. Real-world applications require adjusting the recipe based on several factors.
Steel Composition (Alloying)
Alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, or tungsten significantly slow down the transformation process. For these alloy steels, both the soaking time and the austenitizing temperature often need to be increased beyond the standard for plain carbon steel. Always consult the datasheet for the specific alloy.
Part Thickness and Geometry
Thermal mass is the key driver here. A thick, blocky part requires a much longer soak than a thin sheet of the same material to ensure the core is fully heated. The "per inch of thickness" rule applies to the thickest section of the part.
The Danger of Insufficient Soaking
If the soaking time is too short, the transformation to austenite will be incomplete. The resulting material will have hard spots and inconsistent machinability, defeating the entire purpose of the anneal.
The Danger of Excessive Time or Temperature
Holding the steel at temperature for too long, or at too high a temperature, causes the individual grains of the steel to grow. This grain growth can reduce toughness and lead to a poor "orange peel" surface finish after machining.
Another significant risk is decarburization, where carbon leaches out of the surface of the steel, leaving a soft, weak skin that may need to be machined off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the core principles to guide your process. Time is a tool to ensure a complete transformation, not a goal in itself.
- If you are annealing a simple carbon steel part: Heat to just above the Ac3, soak for one hour per inch of thickness, and let it cool down slowly inside the furnace overnight.
- If you are annealing an alloy steel (e.g., tool steel): Always consult the manufacturer's datasheet. Expect to use higher temperatures and potentially longer soak times.
- If you are working with limited equipment: Heat the part to the correct temperature, then bury it in a large container of dry vermiculite or sand to ensure a slow, controlled cool-down.
- If you are re-annealing a previously hardened part: A full soak time is critical to ensure all the hard martensite structure is fully dissolved and transformed.
By understanding that annealing is a process of controlled transformation, you move from following a recipe to intelligently engineering the properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Annealing | Guideline |
|---|---|---|
| Soaking Time | Ensures uniform heating & complete transformation | 1 hour per inch of thickness (starting point) |
| Temperature | Dissolves hard structures into austenite | 30-50°C above Ac3 for most steels |
| Cooling Rate | Forms soft, coarse pearlite structure | As slow as possible (e.g., furnace cooling) |
Achieve precise and consistent annealing results for your laboratory samples.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables that provide the exact temperature control and uniform heating required for reliable annealing processes. Whether you are working with carbon steels or complex alloys, our equipment ensures complete microstructural transformation for maximum softness and machinability.
Contact us today to find the perfect annealing solution for your laboratory needs. Our experts are ready to help you optimize your heat treatment protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















