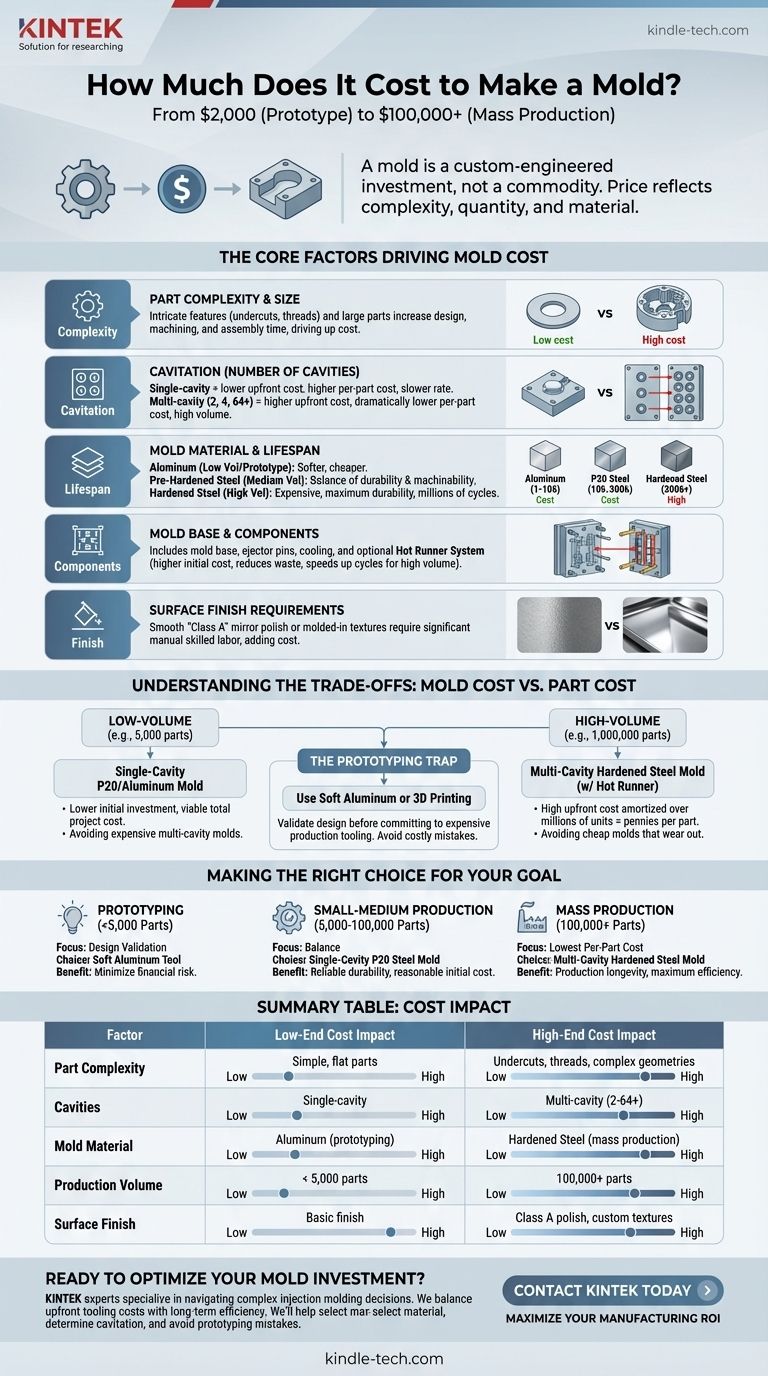
The cost to make an injection mold varies dramatically, ranging from as little as $2,000 for a simple prototype tool to well over $100,000 for a complex, multi-cavity mold designed for mass production. This wide range exists because a mold is not a commodity; it is a custom-engineered piece of industrial equipment. The final price is a direct reflection of your part's design complexity, the total quantity of parts you need to produce, and the material you are molding.
The question isn't just "How much does a mold cost?" but rather, "What is the right tooling investment for my specific production goals?" The cost of the mold is a strategic decision that directly impacts your per-part price and overall project profitability.

The Core Factors Driving Mold Cost
A mold's price tag is the sum of design time, raw materials, precision machining, and skilled labor. Understanding where the money goes is the first step in managing your tooling budget effectively.
Part Complexity and Size
The single greatest cost driver is the complexity of your part. A simple, open-and-shut mold for a flat washer is cheap to produce.
Conversely, parts with intricate features like undercuts, threads, or internal geometries require complex mold actions, such as side-actions (cams) or lifters. These mechanisms add significant design, machining, and assembly time, driving up the cost.
Larger parts naturally require larger molds, which consume more steel and require more time on larger machines, increasing the price.
Cavitation (The Number of Cavities)
A mold can be built with one cavity (producing one part per cycle) or multiple cavities (producing 2, 4, 8, or even 64+ parts per cycle).
A single-cavity mold has the lowest upfront cost but the highest per-part cost and a slower production rate.
A multi-cavity mold is significantly more expensive to build but dramatically lowers the per-part cost by increasing production output. This is the standard for high-volume manufacturing.
Mold Material and Lifespan
The material used to construct the mold is chosen based on the required production volume.
- Aluminum (e.g., 7075): Used for prototyping and low-volume runs (typically 1,000 to 10,000 parts). It's softer, easier to machine, and therefore less expensive.
- Pre-Hardened Steel (e.g., P20): The workhorse of the industry. It offers a good balance of durability and machinability, suitable for production runs up to a few hundred thousand parts.
- Hardened Steel (e.g., H13, S7): Used for high-volume, abrasive materials, or parts with very tight tolerances. These molds are heat-treated for maximum durability and can last for millions of cycles, but they are the most expensive to machine and finish.
Mold Base and Components
The mold isn't just the cavity; it's a complex assembly. The cost includes the steel mold base, ejector pins, cooling channels, and potentially a hot runner system.
A hot runner system keeps the plastic molten all the way to the part cavity, reducing waste and often shortening cycle times. While it adds thousands of dollars to the mold's initial cost, it can pay for itself in material savings and efficiency gains on high-volume projects.
Surface Finish Requirements
If your part requires a perfectly smooth, "Class A" mirror polish, or a specific molded-in texture, this adds significant cost. These finishes are achieved through hours of skilled manual labor, as technicians meticulously polish the steel cavity surfaces by hand.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Mold Cost vs. Part Cost
Choosing a mold is an exercise in balancing upfront investment against long-term production efficiency. A mistake here can cripple a project's budget.
The Low-Volume Scenario
For a run of 5,000 parts, investing $80,000 in a multi-cavity hardened steel mold makes no financial sense. The tooling cost would never be recouped.
The correct choice here is a less expensive single-cavity P20 steel or aluminum mold. While the molding time per part is higher, the low initial tooling investment makes the total project cost viable.
The High-Volume Equation
For a run of 1,000,000 parts, using a cheap, single-cavity aluminum mold would be a disaster. The mold would wear out long before the run is complete, and the slow cycle time would make the per-part labor and machine time costs astronomical.
Here, the high initial investment in a multi-cavity, hardened steel mold with a hot runner system is the only logical path. The high upfront cost is amortized over a million units, resulting in a per-part cost of mere pennies.
The Prototyping Trap
A common mistake is to create an expensive production-quality mold for a first-generation product. If a design flaw is discovered, the costly mold becomes a worthless piece of steel.
Always use lower-cost tooling (like aluminum) or even 3D printing to validate your design before committing to expensive, "hard" production tooling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine your ideal tooling budget, align your choice directly with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is prototyping and design validation (under 5,000 parts): Choose a soft aluminum tool to minimize your financial risk while you finalize the part design.
- If your primary focus is a small to medium production run (5,000 - 100,000 parts): A single-cavity mold made from P20 steel offers the best balance of initial cost and reliable durability.
- If your primary focus is mass production (100,000+ parts): A multi-cavity, hardened steel mold is a necessary investment to achieve the lowest possible per-part cost and ensure production longevity.
Understanding these drivers transforms the cost of a mold from an unknown expense into a strategic tool for manufacturing success.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Low-End Cost Impact | High-End Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Part Complexity | Simple, flat parts | Undercuts, threads, complex geometries |
| Cavities | Single-cavity | Multi-cavity (2-64+) |
| Mold Material | Aluminum (prototyping) | Hardened Steel (mass production) |
| Production Volume | < 5,000 parts | 100,000+ parts |
| Surface Finish | Basic finish | Class A polish, custom textures |
Ready to Optimize Your Mold Investment?
Choosing the right mold is critical to your project's success and profitability. The experts at KINTEK specialize in helping laboratories and manufacturers navigate the complex decisions around injection molding. We provide tailored solutions that balance upfront tooling costs with long-term production efficiency.
We'll help you:
- Select the ideal mold material (aluminum, P20, or hardened steel) for your production volume
- Determine optimal cavitation to minimize your per-part cost
- Avoid costly prototyping mistakes with strategic tooling advice
Don't leave your mold investment to chance. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us help you make the strategic choice that maximizes your manufacturing ROI.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why are high-strength graphite molds essential for vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Your Diamond/Copper Composites
- What role do customized metal molds play in solid-state battery densification? Achieving Precision at 500 MPa
- What technical characteristics are required for specialty pressure molds used in the compaction of Li10GeP2S12? Expert Tips
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity



















