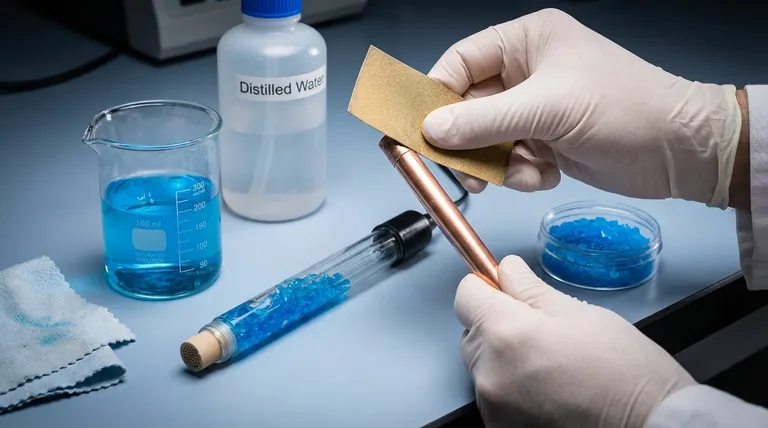
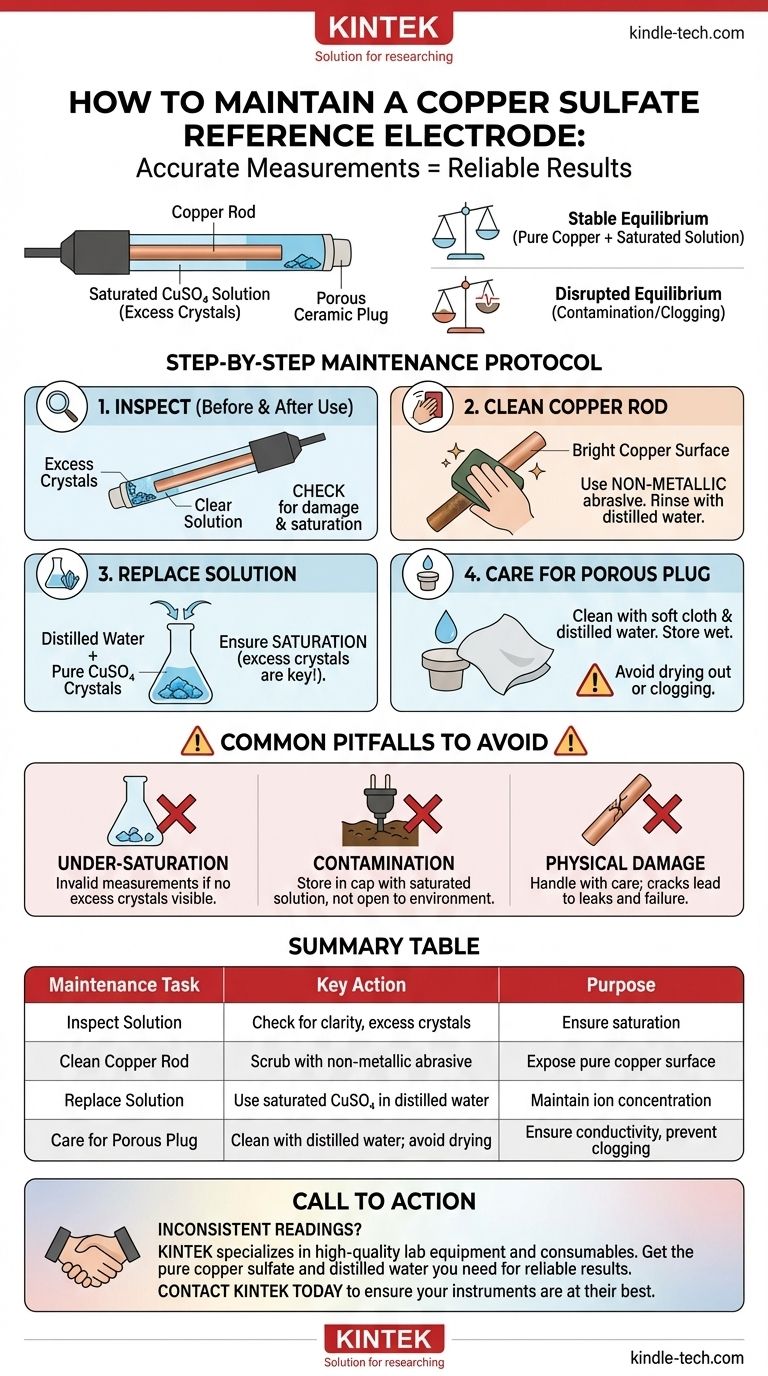
Proper maintenance of a copper sulfate reference electrode is a critical discipline for ensuring measurement accuracy in applications like cathodic protection and electrochemical testing. The core tasks involve periodically replacing the saturated copper sulfate solution, cleaning the copper rod with a non-metallic abrasive until it is bright, and ensuring the porous ceramic plug at the tip remains clean and unclogged. These steps are essential for maintaining the stable potential that makes the electrode a reliable reference point.
The ultimate goal of maintenance is not just cleaning components, but preserving the precise electrochemical equilibrium between the copper rod and its saturated solution. Any deviation—whether from contamination, incorrect solution concentration, or physical damage—compromises this balance and directly leads to inaccurate and unreliable potential readings.

Why Maintenance Is Not Optional
A copper sulfate (Cu/CuSO₄) electrode's reliability hinges on a single, stable electrochemical reaction. Understanding this principle clarifies why each maintenance step is critical.
A Stable Electrochemical Reaction
The electrode generates a reference potential through the reversible reaction between the solid copper rod and copper ions (Cu²⁺) in the solution. This equilibrium is only stable under specific conditions: a chemically pure copper rod and a fully saturated copper sulfate solution.
The Impact of Contamination
Any foreign substance, whether impurities on the rod's surface or contamination in the solution, can introduce competing or side reactions. This interference disrupts the primary copper/copper-ion equilibrium, causing the electrode's potential to drift and become unreliable.
The Role of the Porous Plug
The porous plug at the electrode's tip is the bridge to the environment you are measuring. It must allow for ionic conductivity but prevent the bulk mixing of your reference solution and the external environment. If this plug becomes clogged, it increases electrical resistance, which can dramatically skew your measurements or prevent a reading altogether.
A Step-by-Step Maintenance Protocol
Follow this routine to ensure your electrode performs accurately and has a long service life.
1. Inspect Before and After Each Use
Visually inspect the electrode body for cracks or physical damage. Check that the internal solution is clear and that there are visible, undissolved copper sulfate crystals at the bottom, which confirms saturation.
2. Clean the Copper Rod
Over time, the copper rod will develop a deposit. This must be cleaned to expose a pure copper surface.
Gently remove the rod from the electrode body. Using a non-metallic abrasive, such as fine-grit sandpaper or a cleaning pad, scrub the rod until the surface is bright and clean. Rinse it with distilled water before reassembly.
3. Replace the Solution
The internal solution must be a saturated copper sulfate solution. To prepare it, mix pure copper sulfate crystals with distilled or deionized water until no more crystals will dissolve. Always ensure there are excess, undissolved crystals in the electrode to maintain saturation as temperature changes.
This solution should be replaced periodically, or anytime you suspect it has become contaminated.
4. Care for the Porous Plug
After use, gently clean the porous plug and the outer casing with a soft cloth and distilled water to remove dirt. Never use sharp objects on the plug, as scratches or damage can ruin the electrode. Ensure it does not dry out, which can cause crystallization that clogs the pores.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in maintenance are the primary cause of electrode failure. Be aware of these common issues.
The Risk of Under-Saturation
If you do not see excess copper sulfate crystals in your solution, it is not saturated. An unsaturated solution will produce an incorrect and unstable potential, making all your measurements invalid. This is one of the most common and critical errors.
Contamination from the Environment
Never allow the porous plug to come into prolonged contact with soil, air, or other substances when not in use. Store the electrode in its protective cap, which should be filled with a small amount of saturated copper sulfate solution to keep the plug wet and clean.
Physical Damage Is Often Irreparable
The electrode body is often made of transparent plastic or glass and can crack if dropped or handled roughly. A cracked body will lead to leaks and contamination, typically requiring complete replacement of the electrode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your maintenance schedule should align with the demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy lab work: Perform a full maintenance check (rod cleaning, solution check) and calibration against another trusted reference before each critical measurement series.
- If your primary focus is routine field testing: Implement a schedule for periodic solution replacement (e.g., quarterly or annually) and always inspect the electrode's condition and solution level before each day of use.
- If an electrode has been in long-term storage: Always perform a complete maintenance cycle—replace the solution, clean the rod, and check its potential against a known, trusted reference—before putting it back into service.
Consistent maintenance transforms your reference electrode from a potential source of error into a reliable cornerstone of your electrochemical measurements.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Task | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect Solution | Check for clarity and excess crystals | Ensure solution is saturated |
| Clean Copper Rod | Scrub with non-metallic abrasive | Expose pure copper surface for stable potential |
| Replace Solution | Use saturated CuSO4 in distilled water | Maintain correct ion concentration |
| Care for Porous Plug | Clean with distilled water; avoid drying | Ensure proper ionic conductivity and prevent clogging |
Are inconsistent readings affecting your cathodic protection or lab results? Properly maintained equipment is the foundation of accurate data. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the pure copper sulfate and distilled water essential for reliable reference electrode maintenance. Let our experts help you achieve precise and dependable electrochemical measurements. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and ensure your instruments are performing at their best.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of the ceramic core type copper sulfate reference electrode?
- What are the pre-treatment steps before using a portable copper sulfate reference electrode? Ensure Accurate Corrosion Potential Measurements
- Is there a difference in performance between wood plug and ceramic core copper sulfate electrodes? Speed vs. Durability Explained
- What is the operating principle of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Reliable Potential Measurement Explained
- What are the post-treatment procedures after using a copper sulfate reference electrode? Essential Steps for Accuracy & Longevity



















