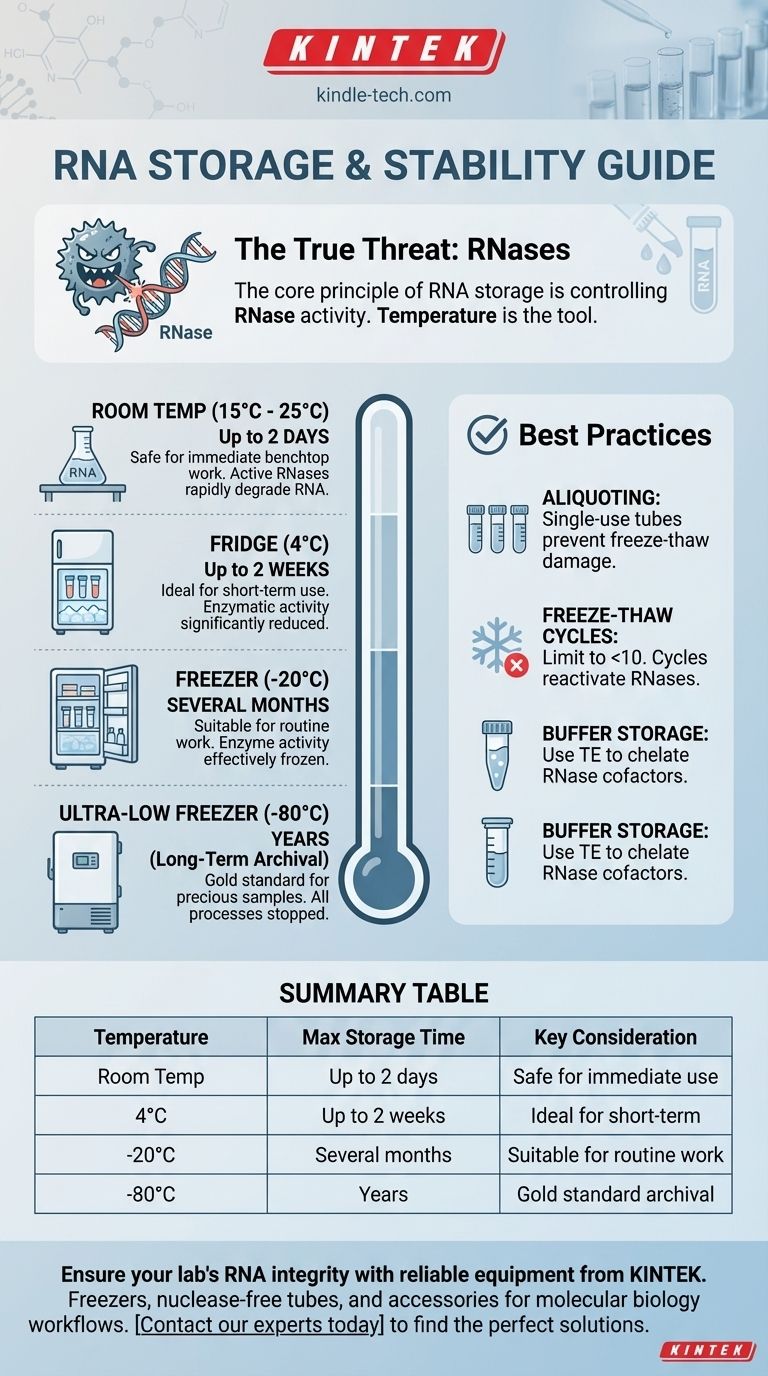
At a glance, properly purified RNA is significantly more stable than its reputation suggests. If free from enzymatic contamination, extracted RNA can be stored at room temperature for up to two days, at 4°C for two weeks, and can withstand up to ten freeze-thaw cycles when stored at -20°C or -80°C without measurable degradation.
The core principle of RNA storage is not about the inherent fragility of the RNA molecule itself, but about the effective inactivation of RNase enzymes. Temperature is simply the tool we use to control the activity of these destructive enzymes.

The True Threat to RNA Integrity: RNases
The common wisdom that RNA is exceptionally fragile is a practical truth rooted in a single cause: ribonucleases (RNases). Understanding how to control them is the key to preserving your samples.
What Are RNases?
RNases are enzymes that specialize in breaking down RNA. They are notoriously stable, require no cofactors, and are present on almost every surface, including our hands, dust particles, and non-certified lab equipment.
The presence of even trace amounts of RNase in a purified RNA sample is the primary cause of degradation.
How Temperature Controls RNase Activity
Storing RNA at low temperatures does not destroy RNases; it merely slows them down or renders them dormant.
- At room temperature, active RNases will rapidly degrade RNA.
- At 4°C, enzymatic activity is significantly reduced, but not halted.
- At -20°C and -80°C, enzymatic activity is effectively frozen, preserving the RNA indefinitely as long as it remains frozen.
This is why the stability timelines are directly linked to temperature—they are a measure of how long it takes for any potential, contaminating RNases to inflict significant damage.
A Practical Guide to RNA Storage
The stability of your RNA depends entirely on using the correct temperature for your intended timeline, assuming you have followed nuclease-free handling procedures during extraction.
Long-Term Archival (-80°C)
For storage longer than a few months or for highly precious samples, -80°C is the gold standard. At this temperature, all enzymatic and nearly all chemical processes are stopped, ensuring sample integrity for years.
Medium-Term Storage (-20°C)
For routine work and storage up to several months, -20°C is perfectly adequate. The stability is comparable to -80°C for this timeframe, making it a practical choice for most working labs.
Short-Term Experimental Use (4°C)
You can confidently keep your RNA on ice or in a 4°C refrigerator for up to 14 days without degradation. This is ideal for when you are actively using a sample for a series of experiments over a week or two. Be sure to use sealed tubes to prevent evaporation.
Immediate Benchtop Work (Room Temperature)
Pure RNA is stable enough to sit on a clean lab bench at room temperature for up to two days. This provides a safe window to perform downstream applications like reverse transcription or setting up a qPCR plate without needing to constantly keep the samples on ice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Simply choosing a temperature is not enough. Proper handling strategy is essential to maintain the quality established by your extraction protocol.
The Danger of Freeze-Thaw Cycles
The most significant risk to frozen RNA is not the storage itself, but the process of thawing and refreezing. The reference to 10 freeze-thaw cycles is a critical limit.
Each cycle presents a brief window where dormant RNases can become active. While one or two cycles are unlikely to cause issues, repeated cycles will inevitably lead to sample degradation.
The Critical Importance of Aliquoting
The single best practice to protect your RNA is to aliquot your sample immediately after extraction.
Storing your master sample in multiple small, single-use tubes prevents the need to thaw the entire stock for every experiment. This completely avoids the damage caused by freeze-thaw cycles and preserves the integrity of your main sample.
Water vs. Buffer Storage
While nuclease-free water is common, storing RNA in a weak buffer like TE (Tris-EDTA) can provide extra protection. The EDTA in the buffer chelates divalent cations that some RNases require for activity, adding another layer of security against residual contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your storage strategy should be dictated by your experimental plan and the value of your sample.
- If your primary focus is long-term archiving or creating an invaluable reference sample: Store your RNA in a buffered solution, aliquoted into single-use tubes at -80°C.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis over several weeks or months: Storing aliquots at -20°C provides a practical balance of security and accessibility.
- If your primary focus is immediate processing within a few days: Storing your sample at 4°C or even at room temperature is safe, provided your initial extraction yielded a pure, nuclease-free product.
Ultimately, your handling technique and a rigorous nuclease-free workflow are far more critical to preserving your RNA than the specific temperature of your freezer.
Summary Table:
| Temperature | Maximum Recommended Storage Time | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temp | Up to 2 days | Safe for immediate benchtop work |
| 4°C | Up to 2 weeks | Ideal for short-term experimental use |
| -20°C | Several months | Suitable for routine work and medium-term storage |
| -80°C | Years (long-term archival) | Gold standard for precious samples |
Ensure your lab's RNA integrity with reliable equipment from KINTEK. Proper storage is just one part of successful RNA work. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables—including freezers, nuclease-free tubes, and accessories—to support your molecular biology workflows. Protect your valuable samples and improve your results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the process of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Parts
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- What are the advantages of using a Cold Isostatic Press for perovskite solar cells? Unlock High-Pressure Performance
- What is CIP in powder metallurgy? Unlock Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- What temperature is cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Room-Temperature Powder Compaction



















