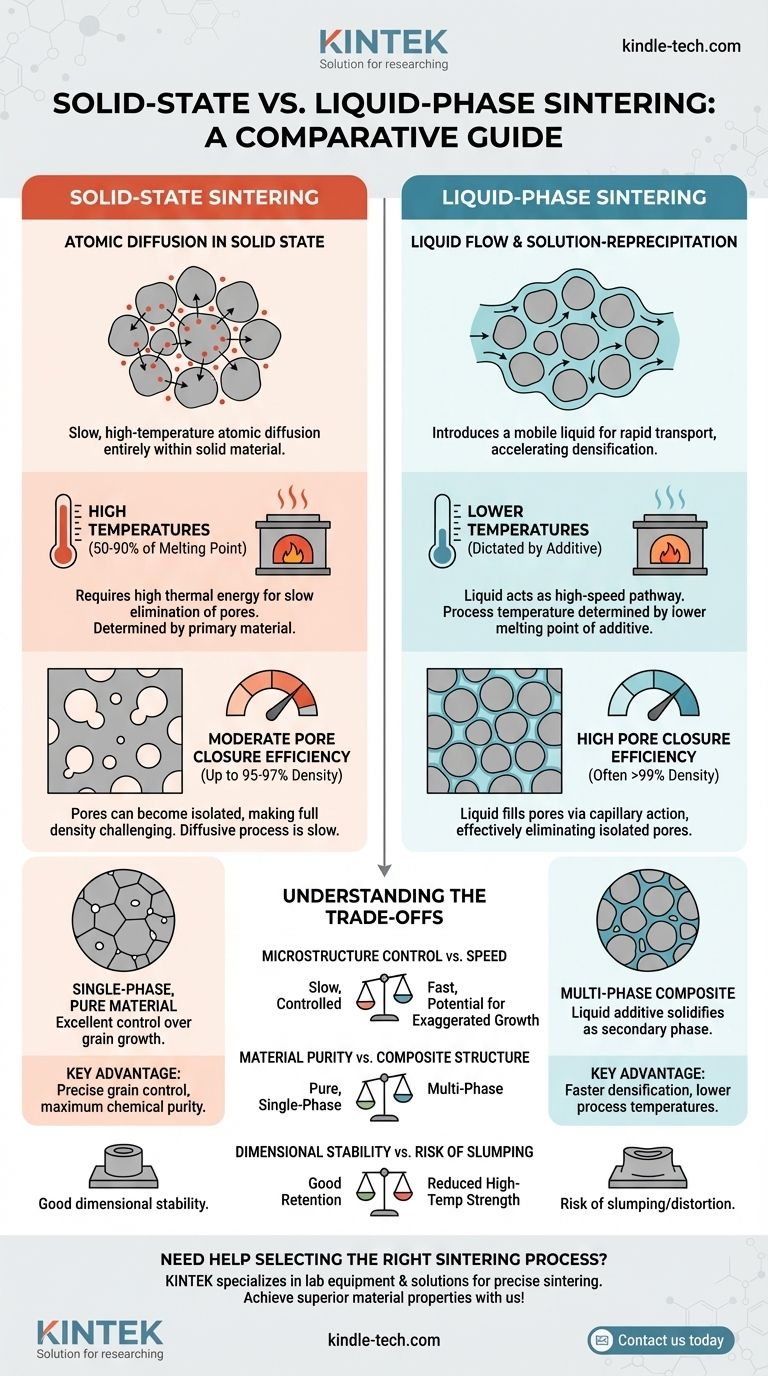
The fundamental difference between solid-state and liquid-phase sintering is the medium through which atoms move to densify the material. Solid-state sintering relies on slow, high-temperature atomic diffusion entirely within the solid material. In contrast, liquid-phase sintering introduces a small amount of liquid that acts as a rapid transport path, allowing for densification at lower temperatures and achieving more complete pore closure.
The core distinction is one of mechanism and efficiency. Solid-state sintering is a diffusion-driven process requiring high thermal energy to slowly eliminate pores. Liquid-phase sintering uses a mobile liquid to fundamentally accelerate particle rearrangement and densification, making it more effective at achieving full density at lower process temperatures.

Understanding the Core Mechanisms
To grasp the differences in temperature and pore closure, we must first understand how each process works at the particle level.
Solid-State Sintering: A Process of Atomic Diffusion
In this process, a compacted powder (a "green body") is heated to a high temperature, typically 50% to 90% of its absolute melting point.
No melting occurs. Instead, atoms migrate from areas of high stress (the contact points between particles) to areas of low stress (the pores or "necks" between particles).
This movement, or diffusion, slowly closes the gaps between particles, causing the component to shrink and densify. It is a kinetically limited process that depends heavily on providing enough thermal energy for a long enough time.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: Leveraging a Mobile Liquid
Liquid-phase sintering (LPS) is used for composite materials or when a small amount of a second material with a lower melting point is added.
The component is heated to a temperature above the melting point of the additive but below the melting point of the primary material.
This creates a small amount of liquid that wets the solid particles. The process then occurs in stages: particle rearrangement due to liquid flow, followed by a solution-reprecipitation mechanism where smaller particles dissolve into the liquid and reprecipitate onto larger ones, further densifying the part.
Differentiating by Sintering Temperature
The required temperature is a direct consequence of the transport mechanism.
Why Solid-State Sintering Requires Higher Temperatures
Atomic diffusion through a solid crystal lattice is an energetically demanding process. A high temperature is essential to give atoms enough thermal energy to break their bonds, move through the lattice, and fill vacancies.
Without this high thermal energy, the rate of diffusion is impractically slow, and significant densification would not occur. The temperature is therefore dictated by the intrinsic properties of the primary material.
How Liquid-Phase Sintering Lowers the Temperature
LPS bypasses the need for slow solid-state diffusion. The liquid phase acts as a high-speed pathway for material transport.
The process temperature is determined not by the primary material's high melting point, but by the lower melting point of the additive. This often allows for significant energy savings and the use of furnaces with lower temperature ratings.
Differentiating by Pore Closure and Densification
The ability to eliminate porosity is arguably the most significant practical difference between the two methods.
The Challenge of Pore Closure in Solid-State Sintering
In solid-state sintering, densification slows dramatically in the final stage. Pores can become isolated and trapped within growing grains, making them extremely difficult to remove.
Achieving a relative density greater than 95-97% is often challenging and requires precise control over temperature and time. Final-stage pore closure relies on the slowest diffusion mechanisms.
The Advantage of Liquid in Eliminating Porosity
The liquid in LPS has two powerful effects. First, it fills the pores through capillary action, pulling the solid particles together with immense force and leading to rapid initial densification.
Second, the liquid provides a medium that can eliminate isolated pores that would be trapped in a solid-state process. This makes it far more effective at achieving near-full density (>99%) consistently and efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method involves more than just temperature and density; it requires balancing key material and process characteristics.
Microstructure Control vs. Speed
Solid-state sintering is slow, but it offers excellent control over grain growth, which is critical for many mechanical properties.
Liquid-phase sintering is much faster, but the presence of a liquid can lead to rapid, exaggerated grain growth (known as Ostwald ripening), which can be detrimental if not properly controlled.
Material Purity vs. Composite Structure
By its nature, solid-state sintering maintains the chemical purity of the initial powder, resulting in a single-phase material.
LPS inherently creates a multi-phase material. The liquid additive solidifies upon cooling, becoming a permanent secondary phase in the final microstructure. This must be acceptable for the final application.
Dimensional Stability vs. Risk of Slumping
Because a solid-state part remains entirely solid, it has good shape retention throughout the process.
The presence of a liquid phase reduces the high-temperature strength of the component. This introduces a risk of slumping or distortion under its own weight, especially for larger or complex geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of sintering method should be driven by the end-goal for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and a fine, single-phase grain structure: Solid-state sintering is the superior choice, despite its higher temperature and slower speed.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-full density quickly and at lower energy cost: Liquid-phase sintering is the more effective method, provided a composite microstructure is acceptable for your application.
- If you are working with materials that are very difficult to densify (e.g., covalent ceramics, refractory metals): Liquid-phase sintering often enables a level of densification that is simply not practical via solid-state methods.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental differences in mechanism is the key to selecting and optimizing the sintering process to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Solid-State Sintering | Liquid-Phase Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering Temperature | High (50-90% of melting point) | Lower (dictated by additive) |
| Pore Closure Efficiency | Moderate (up to 95-97% density) | High (often >99% density) |
| Mechanism | Atomic diffusion in solid state | Liquid flow and solution-reprecipitation |
| Final Microstructure | Single-phase, pure material | Multi-phase composite |
| Key Advantage | Precise grain control, purity | Faster densification, lower temperature |
Need help selecting the right sintering process for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions that ensure precise temperature control and optimal densification for your sintering needs. Whether you're working with high-purity ceramics or complex composites, our expertise can help you achieve superior material properties. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness



















