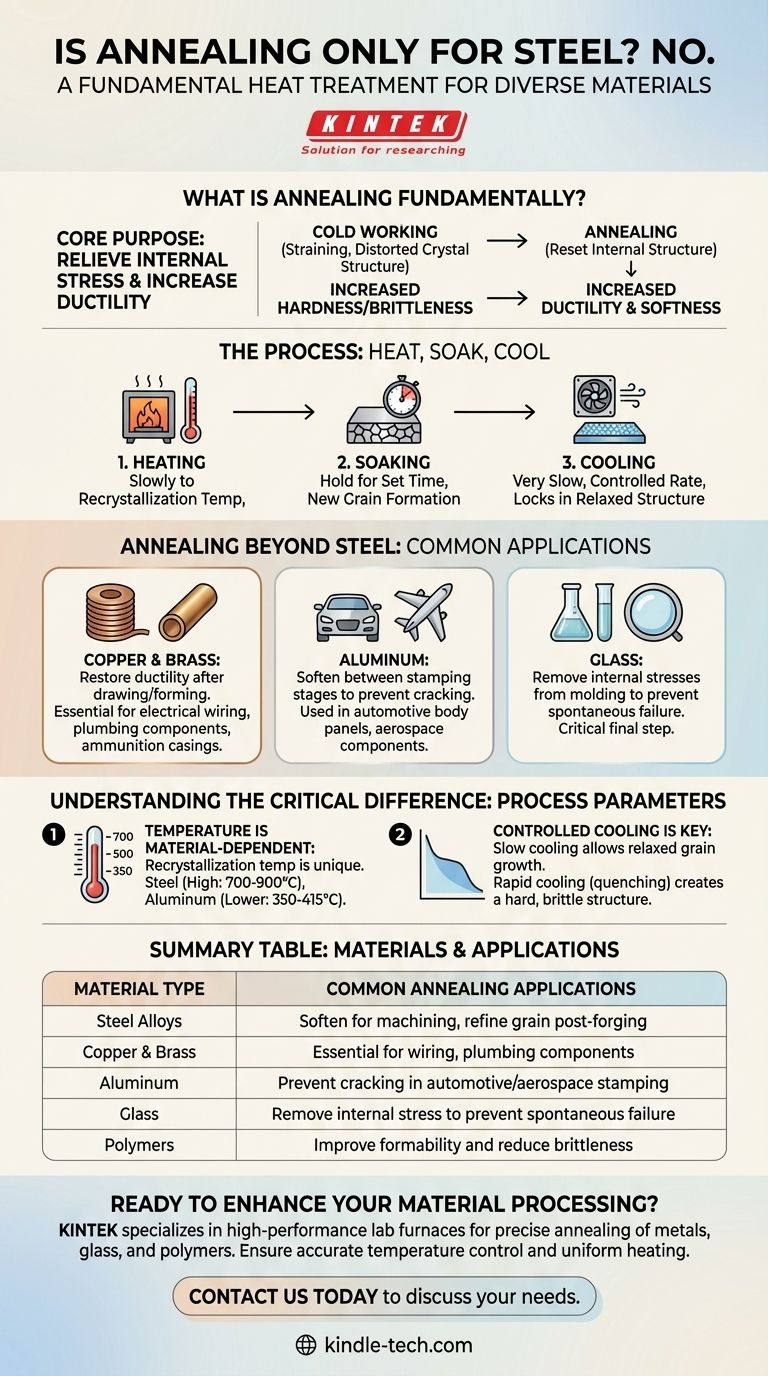
No, annealing is a fundamental heat treatment process applied to a wide range of materials, not just steel. While it is most commonly associated with steel and its alloys, other metals like copper, aluminum, and brass are frequently annealed to improve their properties. The process is also used for materials like glass and even certain polymers.
The core purpose of annealing is not tied to a specific material, but to a specific goal: relieving internal stresses and increasing ductility. The process is simply adapted to the unique recrystallization temperature and properties of each material.

What is Annealing Fundamentally?
To understand why annealing is so versatile, you must first understand its core purpose. It is a process designed to "reset" a material's internal structure, making it softer and easier to work with.
The Goal: Relieving Internal Stress
When a metal is bent, stretched, stamped, or hammered (a process known as cold working), its internal crystal structure becomes strained and distorted. This makes the material harder and more brittle, increasing the risk of cracking during subsequent forming operations.
The Process: Heat, Soak, Cool
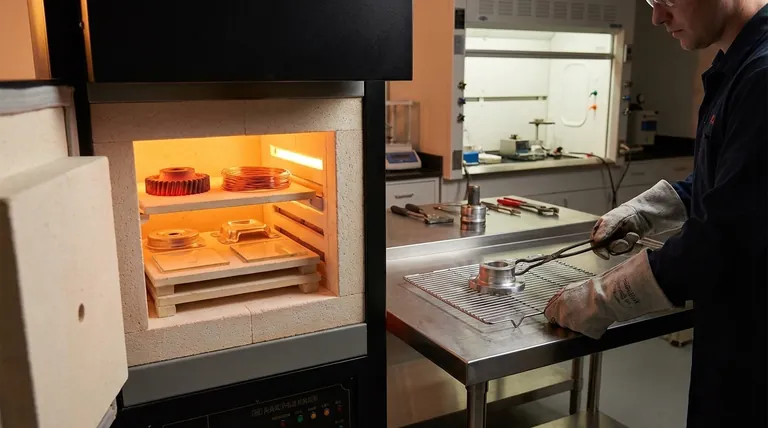
Annealing reverses this by taking the material through three distinct stages:
- Heating: The material is slowly heated to a specific point called its recrystallization temperature.
- Soaking: It is held at this temperature for a set amount of time, allowing new, stress-free grains to form within the material's microstructure.
- Cooling: It is then cooled at a very slow, controlled rate to ensure the relaxed, ductile structure is locked in.
The Result: Increased Ductility
The primary result of annealing is a significant increase in ductility (the ability to be deformed without fracturing) and a reduction in hardness. This makes the material ready for further manufacturing steps.
Annealing Beyond Steel: Common Applications
The principles of annealing are applied wherever internal stress needs to be removed and formability needs to be restored.
Annealing Copper and Brass
Copper and its alloys, like brass, work-harden very quickly. Annealing is essential in manufacturing plumbing components, electrical wiring, and ammunition casings, where the metal is drawn or formed into its final shape in multiple stages.
Annealing Aluminum
In the automotive and aerospace industries, aluminum sheets are stamped into complex body panels or structural components. Annealing is performed between stamping stages to soften the aluminum, preventing it from tearing or cracking as it's forced into the die.
Annealing Glass
Even non-crystalline materials like glass are annealed. After being molded, glass cools at different rates, creating immense internal stress. The annealing process involves reheating the glass and cooling it very slowly for hours or days to remove these stresses, which would otherwise cause it to shatter spontaneously.
Understanding the Critical Difference: Process Parameters
While the principle of annealing is universal, the execution is highly material-specific. You cannot anneal copper using a procedure meant for steel.
Temperature is Material-Dependent
The recrystallization temperature is unique to each material. Steel is annealed at very high temperatures (often 700-900°C / 1300-1650°F), while aluminum is annealed at much lower temperatures (around 350-415°C / 660-780°F). Using the wrong temperature will either have no effect or, in the worst case, melt the material.
Controlled Cooling is Key
The slow cooling rate is what defines annealing. If a material like steel were cooled rapidly (quenched), it would produce a very different result: a much harder and more brittle structure. The controlled cool is what allows the material's internal grains to grow in a relaxed, low-stress state.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
The decision to anneal depends entirely on the material you are using and the state it is in.
- If your primary focus is steel alloys: Annealing is used to soften the material for machining after hardening or to refine the grain structure after a process like forging.
- If your primary focus is non-ferrous metals like copper or aluminum: Annealing is an essential intermediate step to restore ductility after cold working, allowing for further drawing, stamping, or forming.
- If your primary focus is preventing failure in materials like glass: Annealing is a critical final step to remove internal stresses from manufacturing that would otherwise lead to catastrophic failure.
Ultimately, annealing is a versatile tool in materials science, defined not by the material it's applied to, but by the goal of making a material softer and more workable.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Annealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Steel Alloys | Soften for machining, refine grain post-forging |
| Copper & Brass | Essential for electrical wiring, plumbing components |
| Aluminum | Prevent cracking in automotive/aerospace stamping |
| Glass | Remove internal stress to prevent spontaneous failure |
| Polymers | Improve formability and reduce brittleness |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precise heat treatment?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab furnaces and equipment tailored for annealing a wide range of materials. Whether you're working with metals, glass, or polymers, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and uniform heating for optimal results.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve superior material properties and streamline your production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















