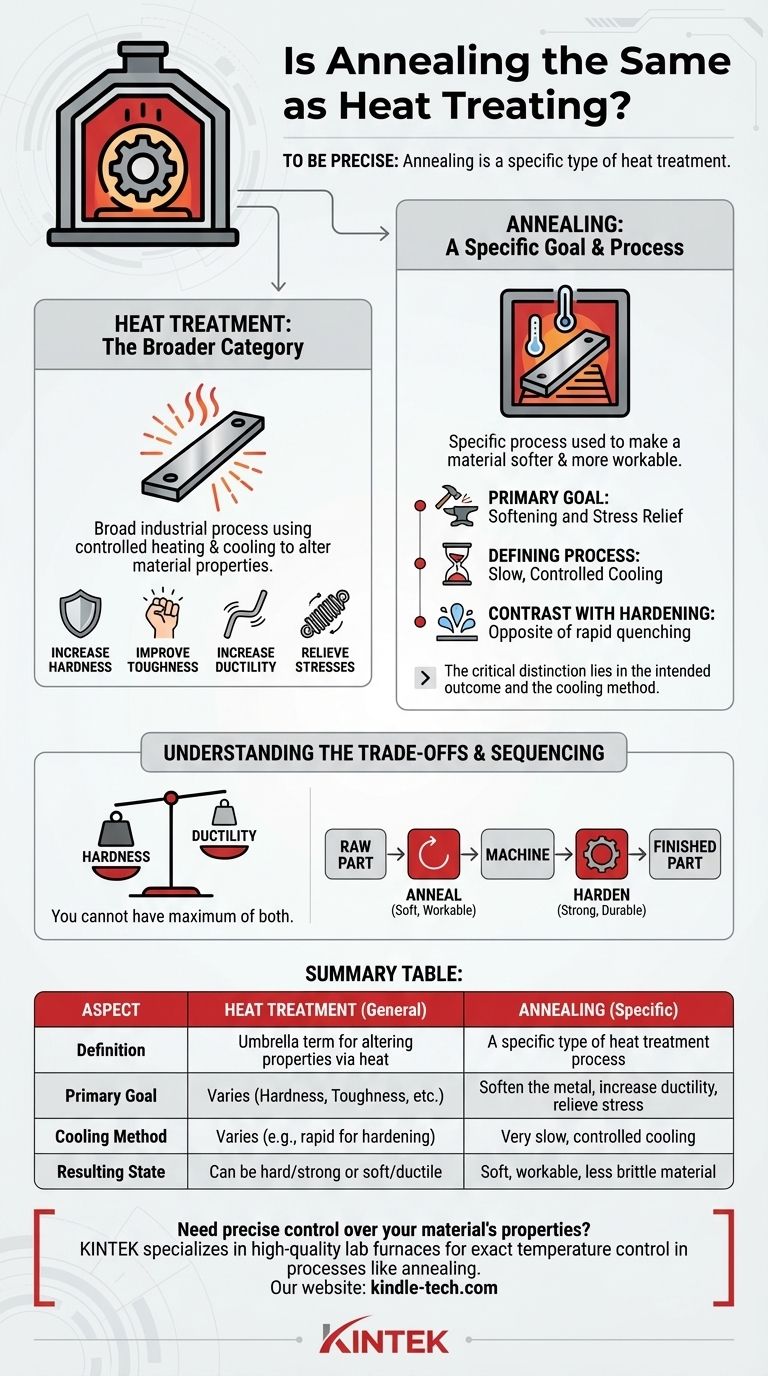
To be precise, annealing is not the same as heat treating; rather, it is a specific type of heat treatment. Heat treating is the broad industrial process of using controlled heating and cooling to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. Annealing is one of the key processes within that category, defined by its specific goal of softening a metal.
The critical distinction lies in the intended outcome and the cooling method. Heat treatment is the umbrella term for changing a material with heat, while annealing is the specific process used to make a material softer and more workable through slow, controlled cooling.

What is Heat Treatment? The Broader Category
Heat treatment is a fundamental process in metallurgy used to manipulate the properties of metals and alloys to suit a specific application. It's a versatile toolset, not a single procedure.
The Core Principle: Changing Microstructure
Nearly all heat treatments work by altering the microstructure, or the internal crystalline arrangement of a material. By carefully controlling the heating temperature, holding time, and cooling rate, you can change the size and composition of these crystals to achieve desired properties.
A Range of Goals
Heat treatment can be used to achieve a variety of goals, often in opposition to one another. These include increasing hardness, improving toughness, increasing ductility (the ability to be deformed without breaking), and relieving internal stresses created during manufacturing.
Where Annealing Fits In: A Specific Goal
Annealing is one of the most common forms of heat treatment, but it has a very specific purpose that sets it apart from hardening processes.
The Primary Goal: Softening and Stress Relief
The sole purpose of annealing is to return a metal to its softest, most workable state. This process increases ductility and reduces hardness, making the material easier to machine, form, or stamp without fracturing. It also removes internal stresses from previous operations like casting or welding.
The Defining Process: Slow, Controlled Cooling
The key to annealing is the slow cooling rate. After being heated to its target temperature, the material is cooled very slowly, often by simply turning off the furnace and letting it cool down over many hours. This slow cooling allows the material's microstructure to re-form into its most stable, low-energy, and therefore softest, state.
Contrast with Hardening
This is the direct opposite of hardening processes like quenching, where the material is cooled as rapidly as possible by submerging it in a liquid like water or oil. This rapid cooling traps the microstructure in a hard, brittle state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right heat treatment is a matter of balancing competing properties. You cannot have a material that is simultaneously at its maximum hardness and maximum ductility.
The Hardness vs. Ductility Dilemma
Annealing makes a material highly ductile but also very soft. A hardened material is strong and wear-resistant but can be brittle. An annealed part is easy to machine but would fail quickly in an application requiring high strength.
The Importance of Sequencing
In many manufacturing workflows, multiple heat treatments are used in sequence. A raw part might first be annealed to make it easy to machine into its final shape. Once machined, the finished part is then put through a hardening process (like quenching and tempering) to give it the strength and durability required for its final use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using the correct terminology is essential for communicating with engineers, machinists, and heat-treating suppliers to ensure you get the material properties you need.
- If your primary focus is to prepare a material for machining or forming: You are asking for an annealing process to maximize softness and relieve stress.
- If your primary focus is to achieve final strength and wear resistance in a finished part: You need a hardening process, such as quenching and tempering.
- When communicating technical specifications: Use "heat treatment" as the general category, but always specify the exact process (e.g., "full anneal" or "quench and temper") to avoid costly errors.
Understanding this distinction is fundamental to controlling the final performance of a metallic component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Heat Treatment (General) | Annealing (Specific) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Umbrella term for altering material properties via controlled heating/cooling | A specific type of heat treatment process |
| Primary Goal | Varies: Can increase hardness, toughness, ductility, or relieve stress | Specifically to soften the metal, increase ductility, and relieve internal stresses |
| Cooling Method | Varies by process (e.g., rapid for hardening) | Characterized by very slow, controlled cooling (e.g., inside a turned-off furnace) |
| Resulting State | Can produce a hard and strong or a soft and ductile material, depending on the process | Produces a soft, workable, and less brittle material |
Need precise control over your material's properties? The right lab equipment is critical for successful heat treatment processes like annealing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment that deliver the exact temperature control and uniform heating your laboratory requires. Whether you are annealing for softness or hardening for strength, our solutions ensure reliable and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific heat treatment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















