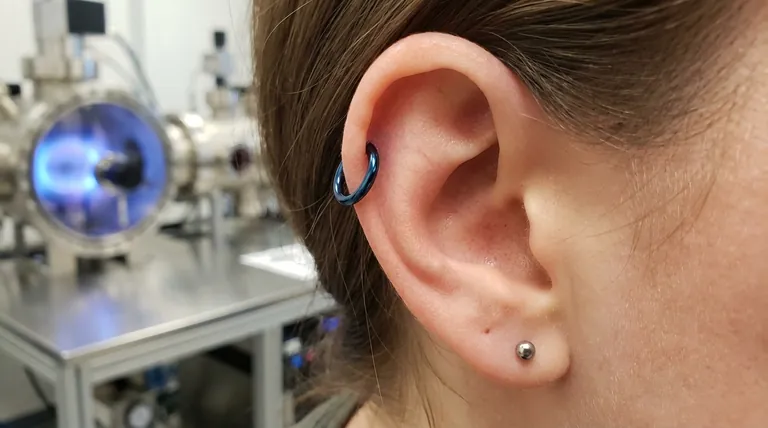
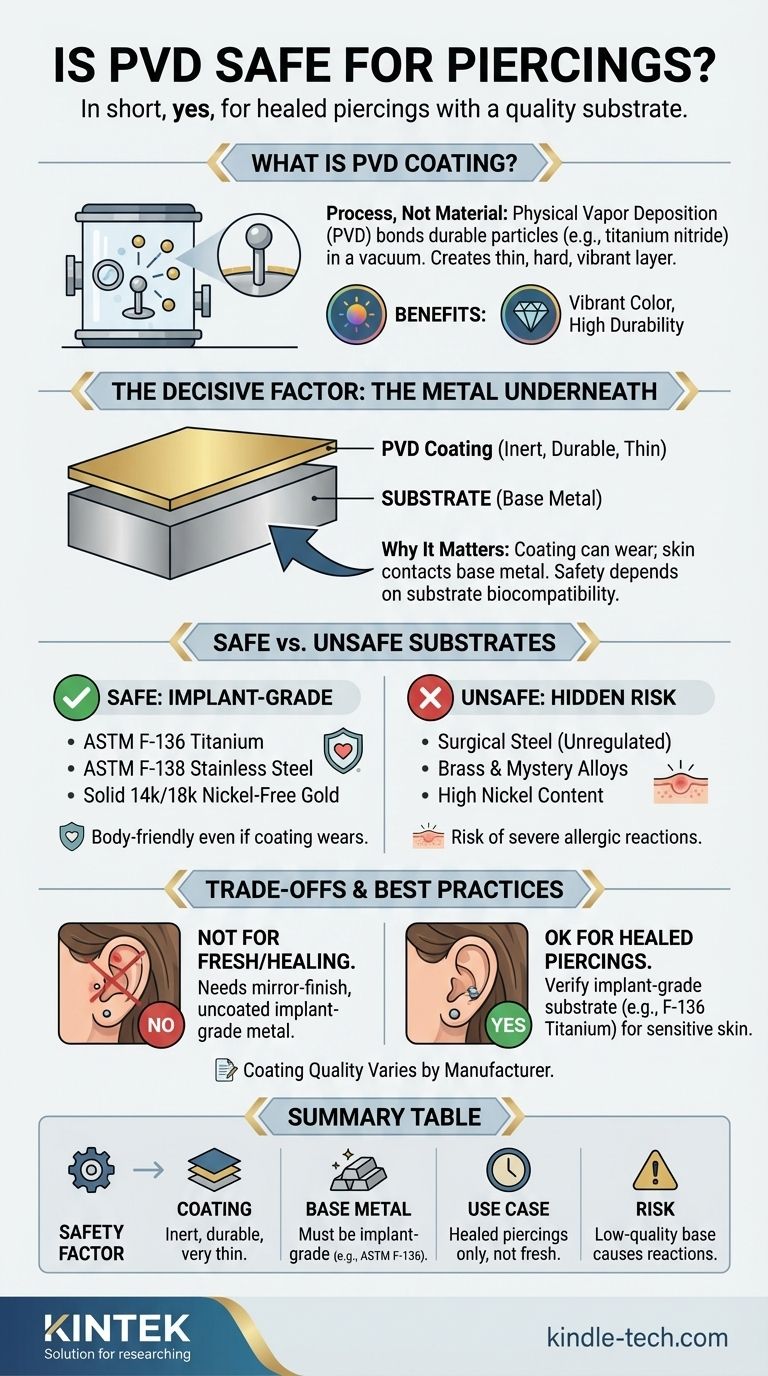
In short, yes, PVD-coated jewelry is considered safe for wear in healed piercings, provided it is from a quality manufacturer. The safety of a PVD-coated piece is not just about the coating itself, which is inert and durable, but is critically dependent on the biocompatibility of the metal underneath the coating.
The true safety of PVD jewelry lies not in the coating, but in the substrate. A thin, colored coating cannot make a low-quality base metal safe. For long-term wear, the underlying material must be implant-grade in case the coating ever wears or gets scratched.
What Exactly is PVD Coating?
It's a Process, Not a Material
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a modern finishing process performed in a vacuum. It physically bonds microscopic particles of a durable material, often a ceramic like titanium nitride, onto a base metal.
This process creates a thin, dense, and very hard layer that is far more durable than traditional plating. The result is a piece of jewelry with a vibrant and long-lasting color, such as black, gold, or iridescent "oil slick."
Why PVD is Used in Body Jewelry
The primary benefits of PVD are color and durability. It allows manufacturers to produce jewelry in a variety of colors on a biocompatible base like titanium without using paints or dyes.
This coating is highly resistant to scratches, tarnishing, and the corrosive effects of sweat and daily wear, making it superior to older methods like electroplating.
The Decisive Factor: The Metal Underneath
Why the Substrate is Everything
The safety of PVD jewelry is ultimately determined by the quality of the base metal, or substrate. The PVD layer itself is extremely thin, often only a few microns thick.
While durable, no coating is indestructible. Over years of wear, it can eventually sustain scratches or wear away in high-friction areas. If this happens, your skin will come into direct contact with the metal underneath.
Safe Substrates: Implant-Grade Materials
For a PVD-coated piece to be truly safe for long-term wear, it must be applied over a proven, biocompatible material. Look for jewelry specified as:
- ASTM F-136 Implant-Grade Titanium
- ASTM F-138 Implant-Grade Stainless Steel
- Solid 14k or 18k Nickel-Free Gold
When PVD is applied to these materials, the jewelry remains safe even if the coating were to fail, as the exposed metal is already body-friendly.
Unsafe Substrates: The Hidden Risk
The primary danger comes from cheap, uncertified jewelry where PVD is used to cover a low-quality base metal. These often include "surgical steel" (an unregulated marketing term), brass, or other mystery alloys.
These metals frequently contain high levels of nickel, a common and potent allergen. If the PVD coating on such a piece is compromised, the exposed nickel can cause severe skin irritation, allergic reactions, and discoloration.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PVD Jewelry
Not for Fresh or Healing Piercings
Coated jewelry of any kind, including PVD, should never be used for initial piercing or in a piercing that is still healing.
The healing process requires the most inert and flawlessly smooth surface possible. Only implant-grade, mirror-polished, uncoated materials like titanium, niobium, or platinum should be used to ensure the best possible outcome and avoid complications.
Coating Quality is Not Universal
The quality of the PVD application process varies significantly between manufacturers. A high-quality application from a reputable body jewelry brand results in a smooth, durable finish.
Conversely, a poor-quality application on a cheap piece can result in a coating that is more likely to chip, flake, or wear unevenly, prematurely exposing the questionable base metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Piercing
Your approach to PVD jewelry should depend entirely on the status of your piercing and your personal sensitivity.
- If you have a fresh or healing piercing: Avoid all coated jewelry, including PVD. Stick exclusively to implant-grade, mirror-finish titanium, niobium, or solid nickel-free gold from a professional piercer.
- If you have a fully healed piercing and sensitive skin: Choose PVD jewelry only when the base metal is explicitly verified as implant-grade titanium (ASTM F-136) from a trusted manufacturer.
- If you have a well-healed, non-sensitive piercing: You have more flexibility, but you should still prioritize PVD pieces with a specified, quality substrate over cheap fashion jewelry to ensure longevity and avoid potential issues.
Ultimately, investing in jewelry with a verified, high-quality base material is the only way to guarantee long-term safety and peace of mind.
Summary Table:
| Safety Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Coating | PVD is inert and durable, but very thin |
| Base Metal | Must be implant-grade (e.g., ASTM F-136 Titanium) |
| Use Case | Safe for healed piercings only, not fresh ones |
| Risk | Low-quality base metals can cause allergic reactions |
Ensure your lab's piercing safety standards are met with KINTEK's precision equipment.
Just as a quality substrate is critical for safe PVD jewelry, reliable lab equipment is the foundation of accurate research and testing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that demand precision and biocompatibility in their work.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's safety and efficiency. Let's build a foundation of quality together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















