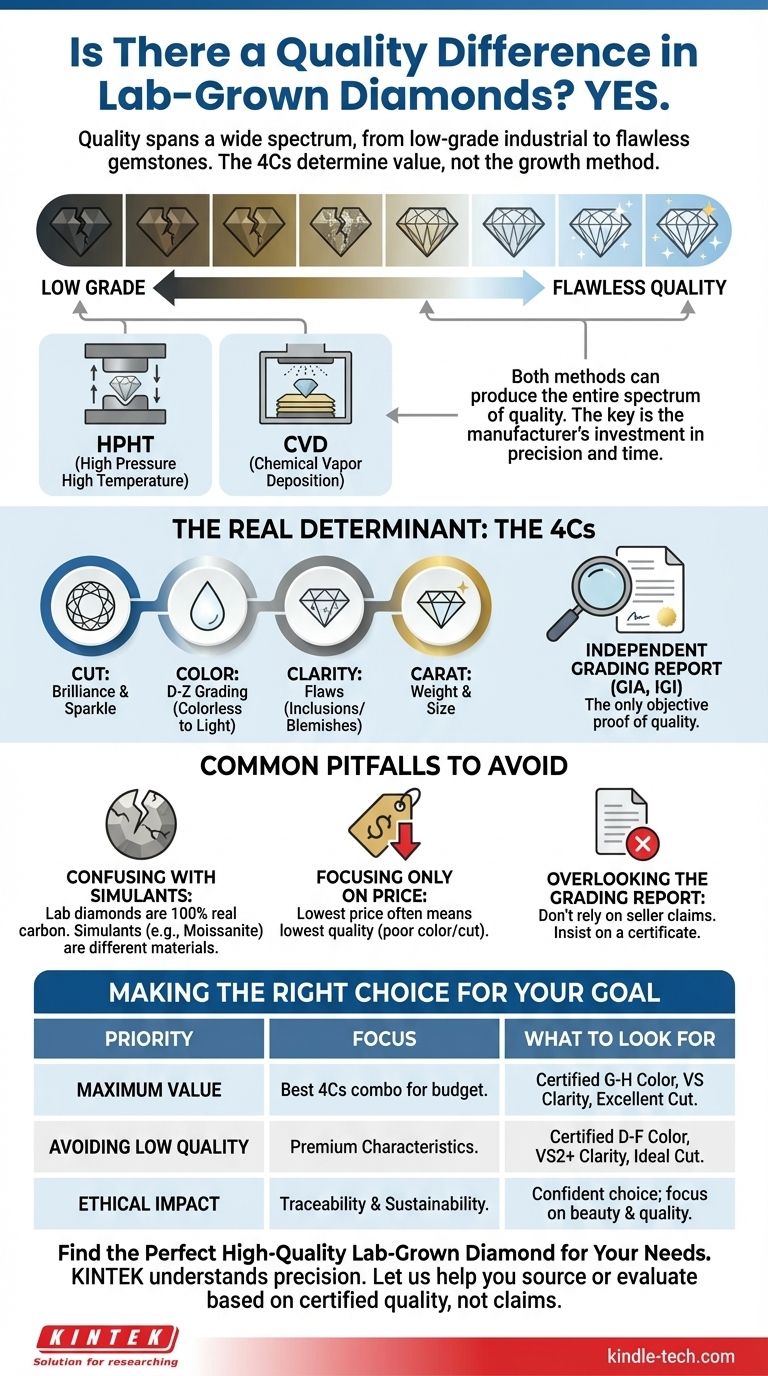
Yes, a significant quality difference exists among lab-grown diamonds. Just like mined diamonds, lab-grown diamonds are not created equal. They span a wide spectrum from low-grade, brownish industrial material to flawless, colorless gemstones suitable for fine jewelry. The cost and complexity of the growing process are the primary determinants of this final quality.
The quality of a lab-grown diamond is determined by its final graded characteristics—the 4Cs—not by its manufacturing method. A high-quality diamond can be produced via either HPHT or CVD, making the independent grading report the only reliable measure of its value.

The Core Misconception: Method vs. Outcome
Many buyers incorrectly assume that the creation method—High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)—is the primary indicator of a lab diamond's quality. This is not the case. The actual quality is a result of the precision, time, and investment in the growth process itself.
The Two Creation Methods
Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds, possessing the same chemical and physical properties as their mined counterparts. They are primarily made in one of two ways.
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) mimics the natural diamond-growing process of the Earth's mantle. A diamond seed is exposed to immense pressure and heat, causing carbon to melt and crystallize around it.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) builds a diamond in layers. A diamond seed is placed in a chamber filled with carbon-rich gas, which is then ionized into plasma, causing carbon atoms to attach to the seed and grow a crystal.
Why the Method Doesn't Define Quality
Both HPHT and CVD are capable of producing flawless, colorless diamonds as well as lower-quality, flawed stones. The final outcome depends entirely on the manufacturer's control over the environment and the resources they invest.
Growing a perfectly colorless and clear diamond is difficult, time-consuming, and expensive with either method. Conversely, producing lower-quality diamonds with brownish tints or inclusions is faster and cheaper.
The Real Determinant of Quality: The 4Cs
Because lab-grown diamonds are physically identical to natural diamonds, they are graded using the exact same standard: the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat). This is the universal language for diamond quality.
An independent grading report from a reputable gemological lab is your objective proof of quality, rendering the growth method largely irrelevant to the final evaluation.
Common Pitfalls and What to Avoid
Understanding the potential for quality variation allows you to make a more informed decision and avoid common mistakes. The key is to differentiate between the diamond and its story.
Confusing Lab Diamonds with Simulants
A critical error is confusing lab-grown diamonds with diamond simulants. Simulants like moissanite or cubic zirconia look similar but are chemically different materials.
Lab-grown diamonds are 100% real carbon diamonds. Simulants do not have the same hardness, brilliance, or chemical structure and are easily identified by a jeweler.
Focusing Only on Price
While lab-grown diamonds are significantly more affordable than mined diamonds, the lowest price often corresponds to the lowest quality.
Extremely cheap lab diamonds may have noticeable color tints (often brownish or grayish), poor clarity, or an inferior cut that reduces their brilliance. As with any diamond, an unusually low price should be scrutinized.
Overlooking the Grading Report
The single most important tool for assessing quality is the grading certificate from an independent lab like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the International Gemological Institute (IGI).
This report provides an unbiased, expert analysis of the diamond's 4Cs. Without it, you are relying solely on the seller's claim of quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by your priorities. The objective grading report is your best tool for finding a stone that aligns with your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum value and size: Concentrate on finding the best combination of Cut, Color, and Clarity grades for your budget, paying no attention to whether the stone is HPHT or CVD.
- If your primary focus is avoiding low-quality stones: Insist on a reputable third-party grading certificate and prioritize diamonds in the colorless (D-F) or near-colorless (G-H) range with high clarity grades (VS2 or better).
- If your primary focus is ethical and environmental impact: You can be confident that any lab-grown diamond is a more traceable and less environmentally disruptive choice than a mined diamond, allowing you to focus purely on the stone's beauty and quality.
Ultimately, evaluating a lab-grown diamond requires the same discipline as assessing a natural one: trust the certificate, not the story.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Quality | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Method (HPHT/CVD) | Not a direct indicator of quality. | Focus on the final graded characteristics, not the method used. |
| The 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) | The definitive measure of a diamond's quality and value. | An independent grading report from GIA or IGI. |
| Manufacturing Investment | Higher investment yields better color and clarity. | Avoid stones with brown/gray tints; prioritize near-colorless grades (G-H or better). |
| Price | Extremely low prices often indicate lower quality. | Scrutinize the grading certificate for any stone with an unusually low price. |
Find the Perfect High-Quality Lab-Grown Diamond for Your Needs
Navigating the nuances of lab-grown diamond quality can be complex. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment and consumables, understands the precision required to create and evaluate these exceptional materials.
Whether you are a jeweler, researcher, or a discerning consumer, we provide the expertise and resources to help you make an informed decision based on certified quality, not just marketing claims.
Let us help you source or evaluate a diamond that meets your exact standards for brilliance and value.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
- What is the process of lab created diamonds? A Clear Guide to HPHT & CVD Methods
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality



















