Beyond the familiar realms of food and pharmaceuticals, freeze-drying is a critical process in a surprising range of advanced fields. This technology, also known as lyophilization, is essential for preserving the integrity of materials in biotechnology, enhancing product stability in cosmetics, preventing moisture damage in sensitive electronics, and even preserving delicate chemical compounds in the cannabis industry. Its applications extend to wherever removing water without damaging the underlying structure is paramount.
The true value of freeze-drying lies not in just removing water, but in how it removes it. By converting ice directly into vapor (sublimation), the process sidesteps the destructive forces of liquid water and high heat, making it the premier method for preserving the delicate structure and chemical composition of sensitive materials.
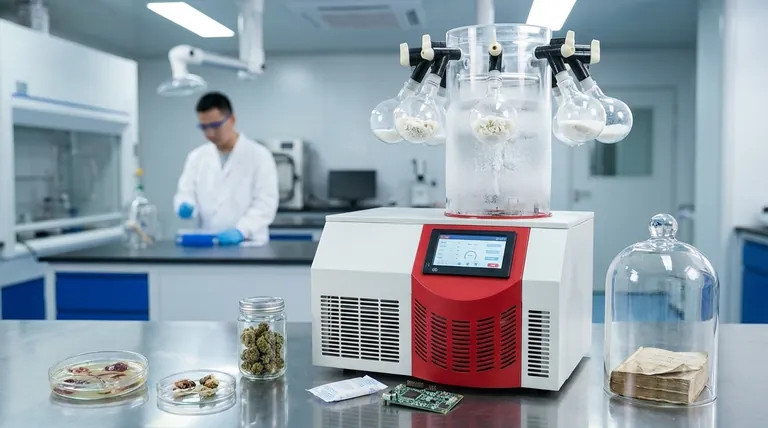

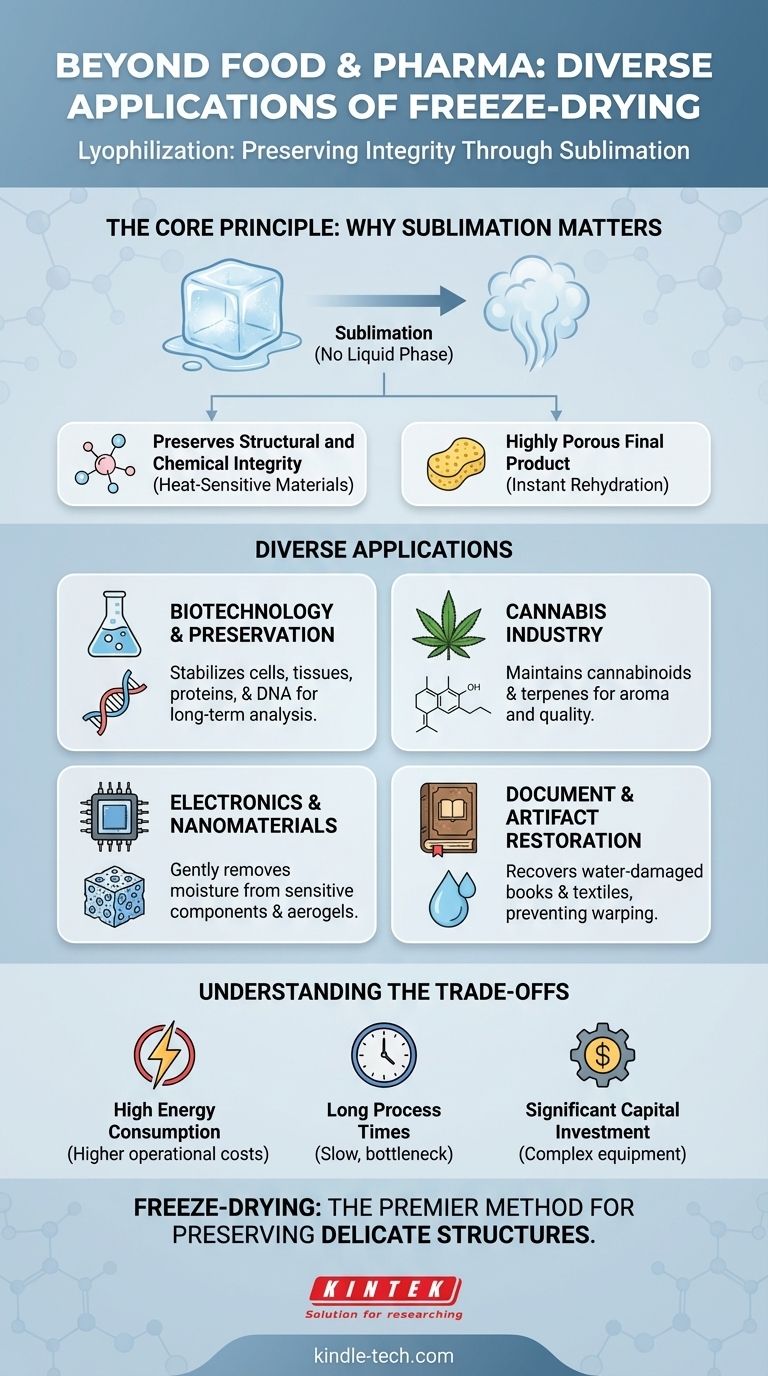
The Core Principle: Why Sublimation Matters
At its heart, freeze-drying is a sophisticated dehydration technique. Unlike conventional drying that uses heat to evaporate water, lyophilization is a three-step process: freezing the material, lowering the pressure, and then adding just enough heat to allow the frozen water to turn directly into a gas.
Preserving Structural and Chemical Integrity
The key benefit is the avoidance of the liquid phase. When water evaporates, it creates surface tension that can shrink, warp, or crack delicate structures like cell walls or complex molecular chains. Sublimation leaves the original structure almost perfectly intact.
This is why freeze-drying is the gold standard for preserving heat-sensitive materials. It protects the activity of proteins, enzymes, and other volatile compounds that would be destroyed by the high temperatures of conventional dehydration.
Creating a Highly Porous Final Product
As ice crystals sublimate, they leave behind microscopic pores. This creates a sponge-like structure in the final product, which has a significant advantage: it allows for almost instantaneous rehydration. This is crucial for products ranging from instant coffee to injectable vaccines that need to be reconstituted quickly and completely.
Diverse Applications in Technology and Research
The unique benefits of lyophilization have made it an indispensable tool in fields where precision and preservation are non-negotiable.
Biotechnology and Sample Preservation
Researchers rely on freeze-dryers to stabilize and store biological samples for long periods. This includes preserving cells, tissues, proteins, and DNA for later analysis. The process effectively pauses biological activity without causing the cellular damage associated with simple freezing and thawing.
The Cannabis Industry
To preserve the quality of cannabis, producers are increasingly turning to freeze-drying. This method perfectly maintains the cannabinoids and delicate terpenes, which are volatile compounds responsible for the plant's aroma, flavor, and therapeutic effects. Traditional curing methods can degrade these compounds, but lyophilization locks them in place.
Electronics and Nanomaterials
In specialized manufacturing, freeze-drying is used to gently remove moisture from sensitive electronic components or advanced materials. For porous nanomaterials or aerogels, it's a way to dry the structure without causing it to collapse from the surface tension of evaporating water.
Document and Artifact Restoration
One of the most remarkable applications is in the recovery of water-damaged books, documents, and even textiles. By freeze-drying these priceless artifacts, archivists can remove water without causing the ink to run or the paper fibers to warp and stick together, preserving history.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its powerful advantages, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. It involves clear and significant trade-offs that limit its use.
High Energy Consumption
The combination of deep freezing and pulling a hard vacuum is an extremely energy-intensive process. The operational costs are substantially higher than for heat-based drying methods, making it unfeasible for low-value bulk materials.
Long Process Times
Sublimation is a very slow physical process. A single freeze-drying cycle can take anywhere from several hours to multiple days to complete, depending on the material and the amount of water to be removed. This creates a bottleneck in high-throughput production.
Significant Capital Investment
Industrial and even laboratory-grade freeze-dryers are complex, precision-engineered machines. The initial capital cost for the equipment is significant, representing a major investment for any organization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use freeze-drying requires a clear understanding of your primary objective and constraints.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological or chemical integrity: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for maintaining the original structure and activity of sensitive molecules, cells, or tissues.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-potency, stable final product: The process creates an extremely low-moisture product that is uniquely resistant to microbial growth and chemical degradation over long periods.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost and maximizing speed: You should explore alternative dehydration methods, as freeze-drying is inherently slow, expensive, and energy-intensive.
Ultimately, understanding freeze-drying as a tool for structural preservation, not just water removal, reveals its true potential across nearly any scientific or industrial discipline.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of Freeze-Drying |
|---|---|
| Biotechnology | Preserves cells, tissues, proteins, and DNA for long-term storage. |
| Cannabis Industry | Maintains delicate cannabinoids and terpenes for high-quality products. |
| Electronics & Nanomaterials | Dries sensitive components without structural collapse. |
| Document Restoration | Saves water-damaged artifacts by removing moisture without warping. |
Need to preserve the integrity of your sensitive materials?
Freeze-drying is the premier method for protecting delicate structures in biotech, cannabis, electronics, and more. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including freeze dryers, to meet the precise needs of research and production laboratories.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment to enhance your product stability and preservation efforts. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- How much can proper freeze drying reduce drying times? Cut Drying Time by Up to 30%
- How does cooling rate affect freeze dryer performance? Unlock Faster, More Reliable Lyophilization
- What is collapse in freeze drying? A Critical Failure Event Explained
- Why is freeze drying important for certain chemical products? Preserve Integrity & Extend Shelf Life



















