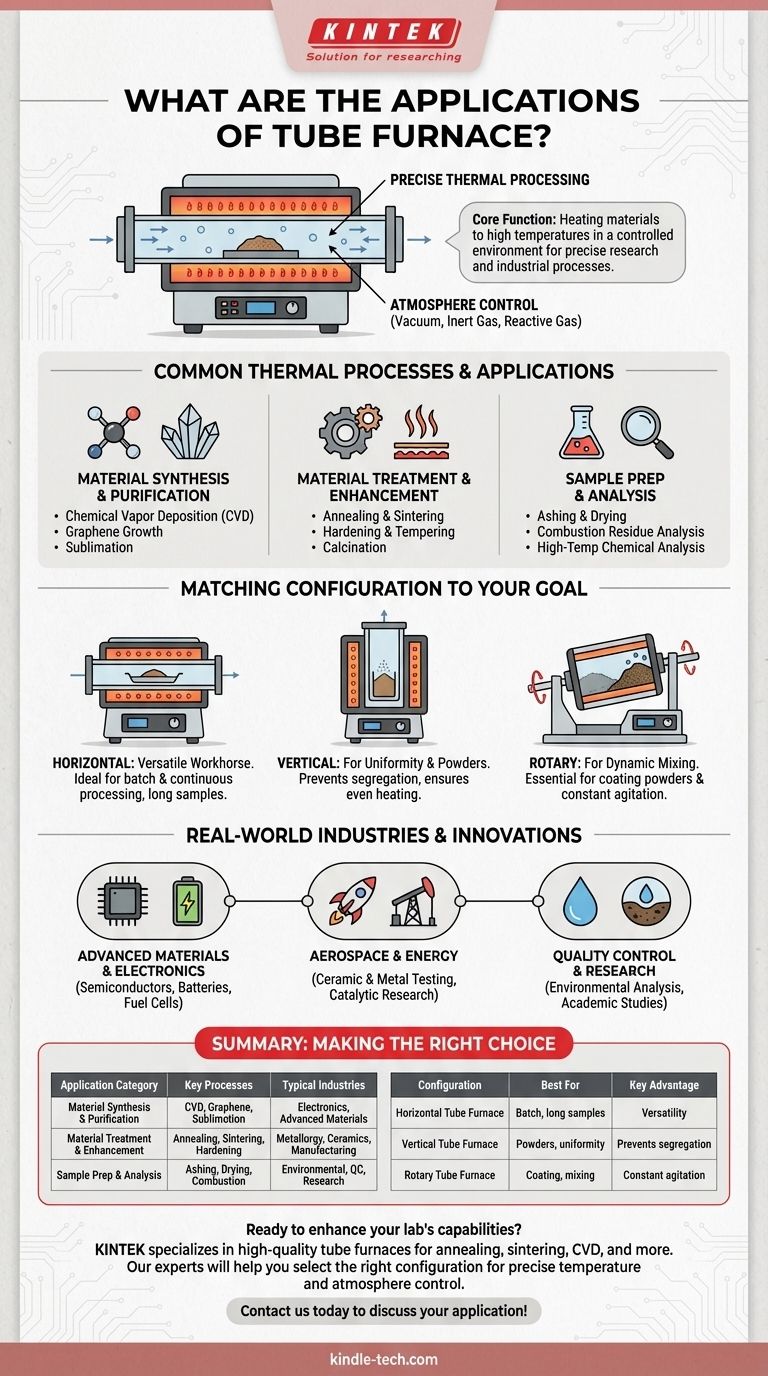
At its core, a tube furnace is a highly versatile tool for precise thermal processing used across scientific research and specialized industries. Its primary applications involve heating materials to high temperatures within a controlled atmosphere for processes like annealing, sintering, chemical synthesis, purification, and material property analysis.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to isolate a sample within a tube. This allows for precise control over the atmospheric environment (e.g., vacuum, inert gas, or reactive gas), which is critical for advanced material science and specialized industrial processes.

The Core Function: Precise Thermal Processing
A tube furnace is fundamentally a cylindrical heating chamber. Its design is simple but powerful, enabling a level of control that other furnaces cannot easily provide.
How It Works
A sample is placed inside a tube, typically made of ceramic, quartz, or metal. This tube is then inserted into the main furnace body, which contains heating elements that surround the tube and heat the sample within.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The tube isolates the sample from the outside air and the heating elements. This separation is the key to its versatility. It allows operators to create a specific environment inside the tube, such as a high-purity vacuum for degassing or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation.
Common Thermal Processes and Applications
Tube furnaces are defined by the processes they enable. These applications span from creating new materials to testing and refining existing ones.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Many applications focus on creating or cleaning materials. This includes sublimation to purify compounds, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to grow thin films, and the synthesis of advanced materials like graphene and polymer composites.
Material Treatment and Enhancement
These furnaces are widely used to alter the physical properties of materials. Common processes include:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
- Sintering: Fusing powders together using heat, essential for creating ceramics and solid-oxide fuel cells.
- Hardening & Tempering: Heat treatments used to increase the strength and durability of metals.
- Calcination: Heating a material to drive off volatile substances, often used in preparing catalysts or cement.
Sample Preparation and Analysis
In laboratory settings, tube furnaces are essential for preparing samples for further testing. This can involve drying a sample, performing ashed combustion residue analysis, or conducting chemical analysis at high temperatures.
Matching Furnace Configuration to Your Goal
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The physical orientation of the furnace is a critical design choice that dictates its ideal application.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Versatile Workhorse
A horizontal furnace is the most common configuration. It is ideal for batch processing of samples in crucibles, continuous processing of long materials like wires or rods, and general-purpose thermal treatments.
Vertical Furnaces: For Uniformity and Powders
Positioning the tube vertically uses gravity to its advantage. This orientation is superior for applications requiring high thermal uniformity, such as growing crystals or sintering and calcining powders, as it prevents sample segregation and ensures even heating.
Rotary Furnaces: For Dynamic Mixing
Some furnaces are designed to rotate the tube during operation. This is essential for processes that require constant mixing, such as coating powders or ensuring a chemical reaction occurs throughout the entire bulk of a material.
Real-World Industries and Innovations
The processes performed in tube furnaces are foundational to numerous high-tech industries and research fields.
Advanced Materials & Electronics
Tube furnaces are critical for producing semiconductors, batteries, and solid-oxide fuel cells. Their precise atmospheric control is essential for creating the high-purity materials and layered structures these technologies demand.
Aerospace and Energy
In the aerospace industry, these furnaces are used for testing the thermal properties of advanced ceramics and metals. In the oil and gas sector, they are used for sample analysis and research into new catalytic processes.
Quality Control and Research
From manufacturing thermocouples to testing water, waste, and soil samples, tube furnaces serve as a fundamental tool for quality control, environmental analysis, and academic research across countless disciplines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is treating powders or ensuring maximum temperature uniformity: A vertical tube furnace is the superior choice for consistent results.
- If your primary focus is processing long samples or general-purpose batch work: A standard horizontal furnace offers the greatest flexibility and is a reliable starting point.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing materials that require constant agitation: A rotary tube furnace is essential for ensuring your process is effective.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or enabling specific reactions: Your key consideration is the furnace's ability to manage a high-purity vacuum or a specific reactive gas atmosphere.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is a cornerstone tool that transforms raw substances into the advanced materials that drive modern innovation.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Purification | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Graphene growth, Sublimation | Electronics, Advanced Materials |
| Material Treatment & Enhancement | Annealing, Sintering, Hardening, Tempering, Calcination | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Manufacturing |
| Sample Prep & Analysis | Ashing, Drying, Combustion analysis | Environmental, Quality Control, Research Labs |
| Configuration | Best For | Key Advantage |
| Horizontal Tube Furnace | Batch processing, long samples | Versatility, general-purpose use |
| Vertical Tube Furnace | Powders, high uniformity | Prevents segregation, even heating |
| Rotary Tube Furnace | Coating powders, mixing reactions | Constant agitation for uniform results |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tube furnace tailored to your specific process?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including tube furnaces for annealing, sintering, CVD, and more. Our experts will help you select the right configuration—horizontal, vertical, or rotary—to achieve precise temperature and atmosphere control for your materials.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a solution that drives your research or production forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What role does a tube furnace serve in the synthesis of halogenated MXene? Optimize Your Molten Salt Etching Process
- Why are quartz reactors used inside tube furnaces? Protect Your Equipment and Ensure Accurate Biomass Corrosion Data
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- How is a tube furnace utilized in high-temperature corrosion experiments for ATF? Simulating Reactor Safety Scenarios
- What are the different types of tube furnace? A Guide to Horizontal, Vertical, Split, and Multi-Zone Designs
- What are the advantages of using U-shaped quartz reactors? Boost Accuracy in CO2 Hydrogenation & Kinetic Studies
- What is the temperature of a tube furnace? A Guide to High-Temp Heating Elements & Control



















