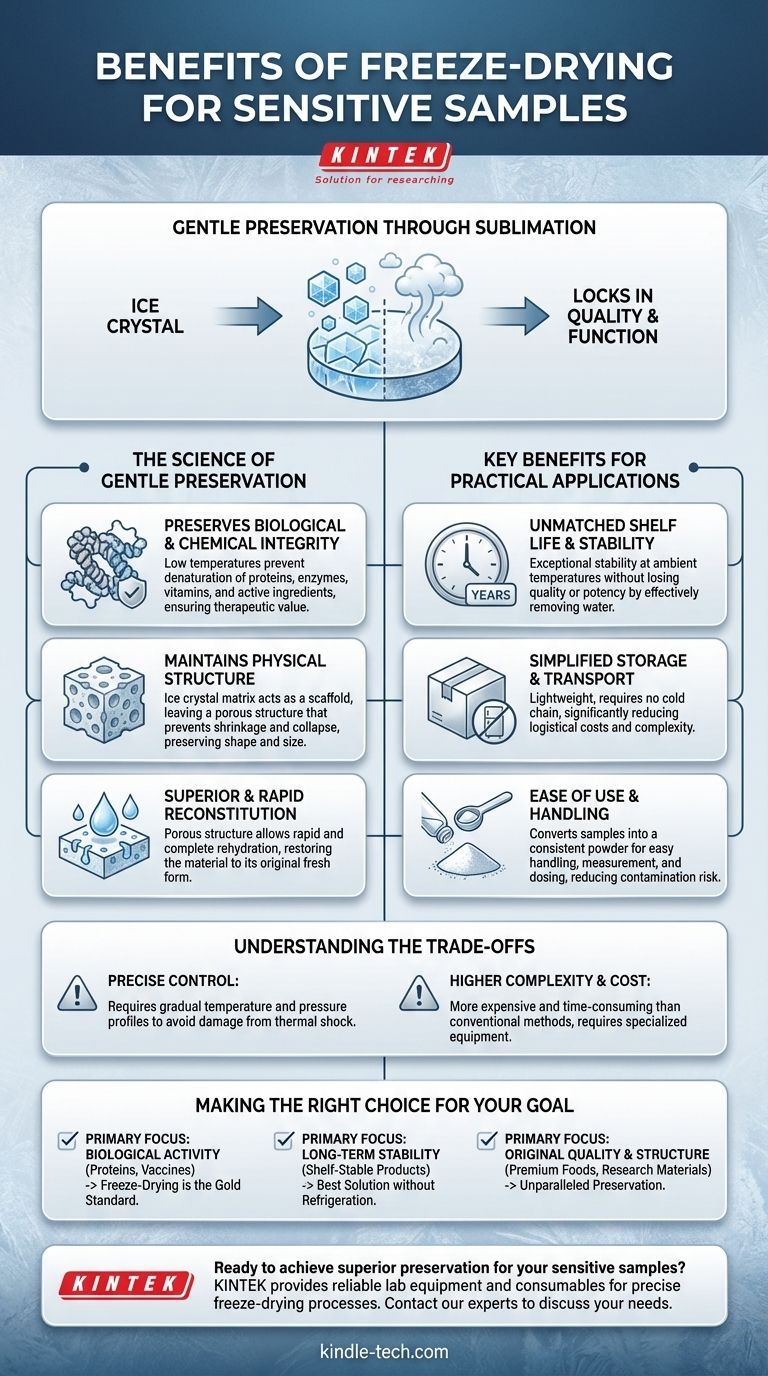
For sensitive samples, freeze-drying is the superior preservation method because it significantly extends shelf life while maintaining the material's original biological activity, chemical integrity, and physical structure. By removing water at low temperatures, it avoids the damage caused by heat and liquid-phase degradation, making it ideal for everything from pharmaceuticals and biologicals to high-value foods.
The core advantage of freeze-drying lies in sublimation—the process of turning ice directly into vapor. This gentle transition bypasses the damaging liquid water phase, effectively locking in the sample's quality and function without the destructive force of high heat.

The Science of Gentle Preservation
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is a fundamentally different process from simple dehydration. Its effectiveness comes from its ability to protect a sample's delicate composition.
Preserving Biological and Chemical Integrity
The entire process operates at low temperatures. This is critical for preventing the denaturation or degradation of heat-sensitive materials like proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and other active ingredients.
By avoiding high heat, freeze-drying ensures that the biological activity and therapeutic value of the sample are preserved.
Maintaining the Physical Structure
During the freezing stage, the water in the sample forms an ice crystal matrix. This matrix acts as a structural scaffold for the material.
As the ice is removed through sublimation, it leaves behind a porous, sponge-like structure. This prevents the sample from shrinking or collapsing, preserving its original shape, size, and appearance far better than other drying methods.
Eliminating Liquid Water Damage
The key is bypassing the liquid phase. Liquid water is a primary medium for microbial growth and enzymatic reactions that lead to spoilage and degradation.
By transitioning water directly from solid to gas, freeze-drying halts these destructive processes almost completely, leading to exceptional long-term stability.
Key Benefits for Practical Applications
The principles of sublimation translate directly into significant practical advantages for storing, transporting, and using sensitive materials.
Unmatched Shelf Life and Stability
Removing water is the most effective way to stop degradation. Freeze-dried products are exceptionally stable and can often be stored for years at ambient temperatures without losing quality or potency.
Simplified Storage and Transport
Freeze-dried materials are lightweight and do not require refrigeration or a cold chain. This dramatically reduces the cost and logistical complexity of shipping and storing valuable biologicals, pharmaceuticals, or specialty foods.
Superior and Rapid Reconstitution
The porous structure left behind by the sublimated ice allows water or other solvents to penetrate the sample easily. This results in rapid and complete rehydration, restoring the material to a state that is nearly identical to its original fresh form.
Ease of Use and Handling
The process can convert samples into a consistent powder. This form is easy to handle, measure, and dose for repeat experiments, analytical testing, or final product formulation, while also reducing the risk of contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, freeze-drying is a sophisticated process that requires precision and control to yield the best results.
The Need for Precise Control
Sensitive samples can be damaged by thermal shock if temperatures are changed too quickly. Successful freeze-drying depends on carefully controlled, gradual temperature and pressure profiles to avoid cracking or degrading the material.
It Is Not a Simple Dehydration Method
Freeze-drying is a more complex, time-consuming, and expensive process than conventional heating or air-drying. It requires specialized equipment and expertise to execute properly.
This makes it most suitable for high-value materials where preserving integrity and function is the absolute priority over cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if freeze-drying is the correct method depends entirely on what attribute of your sample is most critical to preserve.
- If your primary focus is biological activity: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for preserving proteins, vaccines, and enzymes without compromising their essential function.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability without refrigeration: This method provides the best solution for creating shelf-stable products that are easy to store and transport.
- If your primary focus is maintaining original quality and structure: For premium foods or delicate research materials, freeze-drying offers unparalleled preservation of flavor, appearance, and texture.
Ultimately, freeze-drying empowers you to preserve the most delicate materials by gently removing water while leaving their essential character perfectly intact.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Impact on Sensitive Samples |
|---|---|
| Preserves Biological Activity | Maintains potency of proteins, enzymes, and vaccines by avoiding heat damage. |
| Maintains Physical Structure | Creates a porous matrix that prevents shrinkage and collapse, preserving original form. |
| Extends Shelf Life | Enables years of stable storage at ambient temperatures by removing water. |
| Simplifies Storage & Transport | Reduces or eliminates the need for refrigeration, lowering costs and complexity. |
| Ensures Rapid Reconstitution | Porous structure allows for quick and complete rehydration to near-original state. |
Ready to achieve superior preservation for your sensitive samples? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for precise freeze-drying processes. Our solutions help you maintain the integrity of your most valuable materials—from pharmaceuticals to biologicals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and enhance your preservation outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What should be considered when choosing a lab freeze dryer? Match Your Samples and Workflow for Success
- What types of products can be freeze dried? From Food to Pharmaceuticals and Beyond
- What are the three primary types of lab freeze dryers? Choose the Right Scale for Your Lab
- What role does freeze drying play in scientific research? Preserve Sample Integrity for Reliable Results
- What is the primary technique used by lab freeze dryers to process materials? Lyophilization for Superior Sample Preservation



















