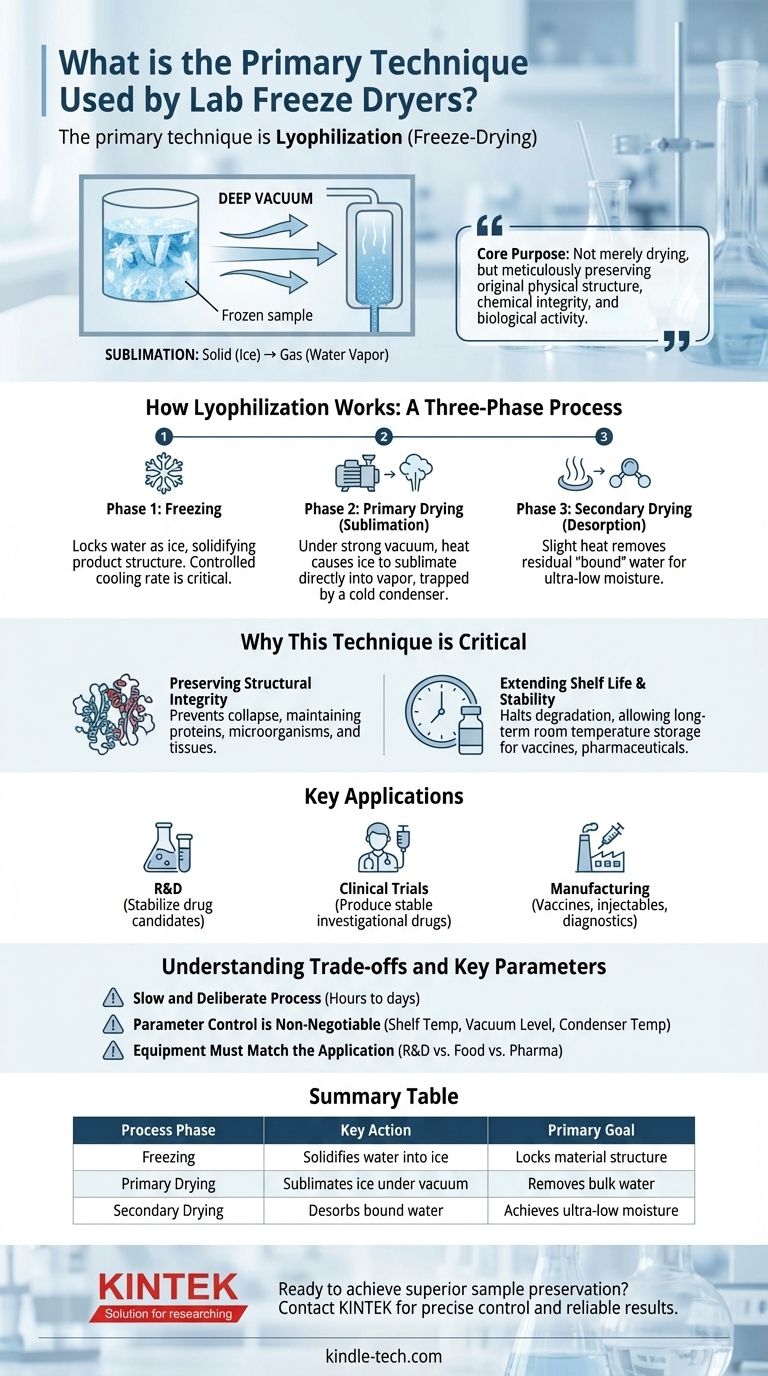
The primary technique used by lab freeze dryers is lyophilization, a process that removes water from a material while it is frozen. This is achieved through sublimation, where the frozen water transitions directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (water vapor) under a deep vacuum, completely bypassing the damaging liquid phase.
The core purpose of lyophilization is not merely to dry a substance, but to do so while meticulously preserving its original physical structure, chemical integrity, and biological activity. It transforms sensitive materials into stable, lightweight solids that can be stored for long periods and easily reconstituted.

How Lyophilization Works: A Three-Phase Process
Lyophilization is a carefully controlled, multi-stage process. Each phase is managed by the freeze dryer's integrated refrigeration, vacuum, and heating systems to ensure the sample's integrity is maintained.
Phase 1: Freezing
The first and most critical step is freezing the material. This is done to lock the water molecules in place as ice crystals, solidifying the product's structure before the drying process begins. The cooling rate must be carefully controlled to influence the size of the ice crystals, which affects the subsequent drying steps.
Phase 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
Once frozen, the material is placed under a strong vacuum. A vacuum pump lowers the pressure inside the drying chamber well below the triple point of water. At this low pressure, gently applying heat gives the ice molecules enough energy to sublimate—turning directly into vapor without melting. This vapor is then drawn away and trapped on a very cold condenser coil.
Phase 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
After all the ice has been sublimated, a small amount of "bound" water may still be attached to the material's surface. A slight increase in temperature and continued vacuum pressure during this phase removes these residual water molecules, resulting in a final product with extremely low moisture content.
Why This Technique is Critical
Lyophilization is the gold standard for preserving sensitive materials precisely because it avoids the destructive forces present in conventional heat-drying.
Preserving Structural Integrity
By keeping the material frozen solid while water is removed, lyophilization prevents the collapse of delicate structures. This is essential for maintaining the form of proteins, the viability of microorganisms, and the cellular structure of tissues.
Extending Shelf Life and Stability
Water is the medium for most chemical and biological reactions that cause degradation. By removing water, freeze-drying effectively halts these processes, allowing products like vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and probiotics to be stored for years at room temperature without losing efficacy.
Key Applications: From Lab to Market
The benefits of lyophilization make it indispensable across many fields. It is used in research to stabilize new drug candidates, in clinical trials to produce stable investigational drugs, and in manufacturing to create commercial products like vaccines, injectable drugs, and diagnostic reagents.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
While powerful, lyophilization is a resource-intensive process with specific requirements that must be understood to achieve success.
It is a Slow and Deliberate Process
Freeze-drying is not fast. A typical cycle can take anywhere from several hours to several days, depending on the sample type, volume, and equipment. This makes it more time-consuming and energy-intensive than other drying methods.
Parameter Control is Non-Negotiable
Success hinges on precise control over several variables. Key parameters like shelf temperature, vacuum level, and condenser temperature must be optimized for each specific product. An improperly designed cycle can easily ruin a valuable batch.
Equipment Must Match the Application
There is no one-size-fits-all freeze dryer. A unit for basic food preservation has very different requirements than one used for manufacturing sterile pharmaceuticals. Factors like temperature accuracy, condenser capacity, and vacuum control must be matched to the specific application to avoid compromising the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal approach to lyophilization depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize a freeze dryer with precise control over shelf temperature and vacuum to develop robust and repeatable cycles for high-value, sensitive samples.
- If your primary focus is food preservation: Focus on capacity and efficiency to extend the shelf life of products while maintaining their nutritional value, flavor, and texture.
- If your primary focus is pharmaceutical manufacturing: Emphasize process control, data logging, sterility, and system validation to ensure product quality, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Ultimately, mastering lyophilization is about controlling a physical process to achieve a specific biological or chemical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Freezing | Solidifies water into ice | Locks material structure |
| Primary Drying | Sublimates ice under vacuum | Removes bulk water |
| Secondary Drying | Desorbs bound water | Achieves ultra-low moisture |
Ready to achieve superior sample preservation with a freeze dryer tailored to your needs? Whether your focus is R&D, food preservation, or pharmaceutical manufacturing, KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables are designed to deliver precise control and reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect lyophilization solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- What factors should guide the final decision when choosing a lab freeze dryer? Match Your Science to the Right Specs
- How is freeze-drying applied in the pharmaceutical industry? Stabilize Delicate Drugs for Long-Term Efficacy
- How should sample volume influence the choice of a lab freeze dryer? A Guide to Capacity, Specs & Cost
- What are the benefits of freeze-drying for sensitive samples? Preserve Delicate Materials with Unmatched Quality
- What are the main pharmaceutical applications of lab freeze dryers? Stabilize Drugs from R&D to Manufacturing



















