Choosing the right laboratory freeze dryer is a critical decision that extends beyond budget and brand. You must primarily match the machine’s technical specifications—specifically its cold trap temperature and condenser capacity—to the chemical nature of your samples and your required daily throughput. A mismatch can lead to damaged equipment, failed experiments, and a significant waste of resources.
The core challenge in selecting a freeze dryer is not simply finding one that fits your bench space or budget. It is about deeply understanding your samples' properties and your lab's workflow to invest in a machine that ensures successful lyophilization, process repeatability, and long-term reliability.

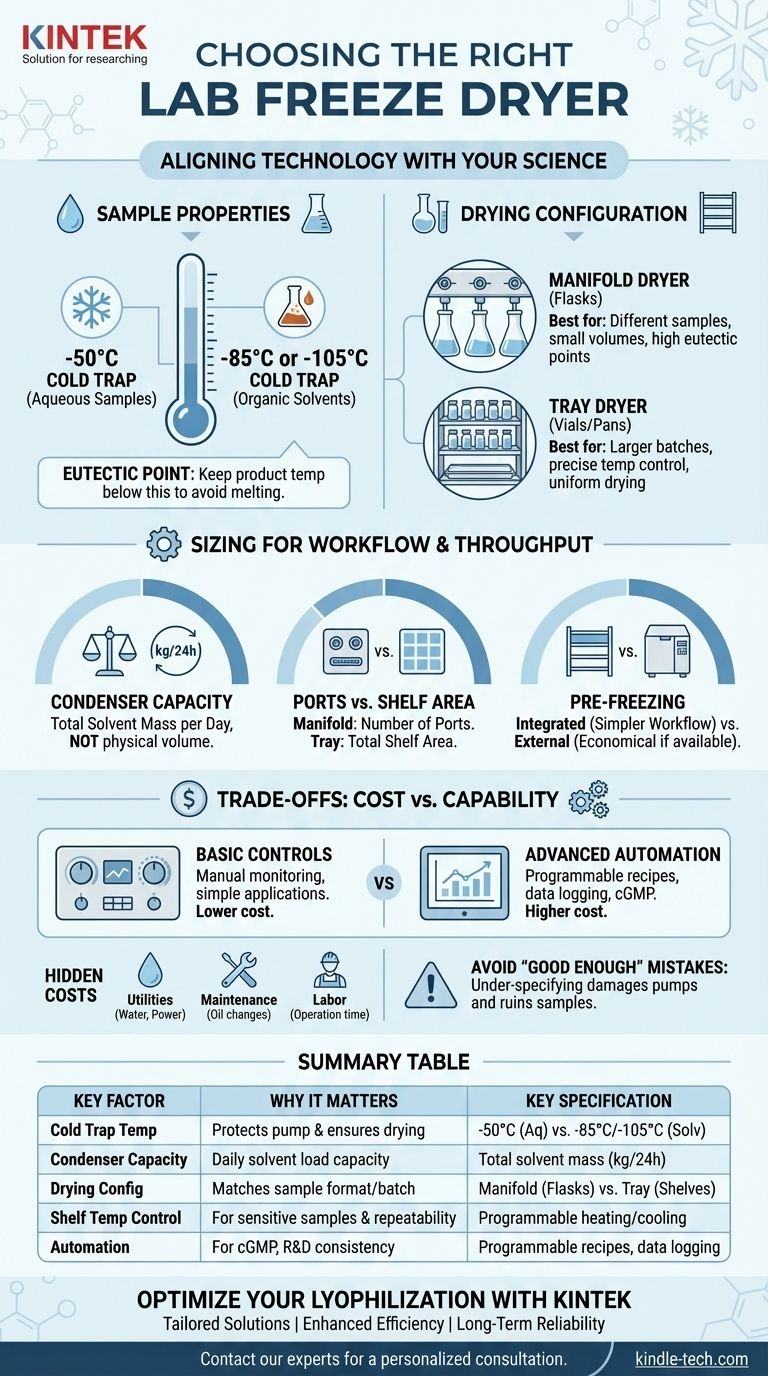
Aligning the Technology with Your Science
Your sample is the most important factor. Its physical and chemical properties dictate the fundamental requirements of the freeze dryer.
The Critical Role of Cold Trap Temperature
The cold trap is the heart of the freeze dryer, responsible for capturing sublimated moisture before it can damage the vacuum pump. The required temperature is entirely dependent on your sample's composition.
For samples dissolved in water, a standard -50°C cold trap is sufficient. Water freezes well above this temperature, ensuring it is efficiently trapped.
For samples containing organic solvents (like acetonitrile or methanol) or materials with very low freezing points, a colder trap is non-negotiable. A -85°C or -105°C cold trap is necessary to effectively freeze and capture these volatile solvents, protecting the vacuum pump from expensive damage.
Understanding Your Sample's Eutectic Point
The eutectic point is the lowest temperature at which your frozen sample will begin to melt. For successful freeze drying, the product's temperature must always be kept below this point during the primary drying phase.
Knowing this temperature is crucial for setting shelf temperatures on a tray dryer. A machine with precise shelf temperature control is vital for sensitive biologicals, pharmaceuticals, or any application where product structure is critical.
Flask vs. Tray Drying
Your choice between a manifold (flask) dryer and a tray dryer depends on your sample format and batch consistency.
A manifold dryer uses ports to connect individual flasks. It is ideal for drying different samples simultaneously, small volumes, or materials with high eutectic points that don't require precise temperature control.
A tray dryer holds samples in vials or bulk pans on shelves. It is essential for larger batches, pilot-scale production, and any sample requiring precise temperature control and a uniform drying process.
Sizing for Workflow and Throughput
Beyond the science, you must consider the scale and efficiency of your daily operations. A system that is too small creates a bottleneck, while one that is too large is an inefficient use of capital and energy.
Condenser Capacity: More Than Just Ice
Condenser capacity is one of the most misunderstood specifications. It does not refer to the total physical volume of your samples but to the total mass of solvent (usually water) the condenser can trap over a 24-hour period.
To calculate your need, estimate the total liquid volume you intend to dry per day. Choose a condenser with a capacity that comfortably exceeds this amount to ensure efficient drying cycles.
Manifold Ports vs. Tray Shelf Area
For a manifold dryer, the key metric is the number of ports. Ensure you have enough ports to handle your typical batch size, with a few extra for flexibility.
For a tray dryer, the critical factor is the total shelf area. Calculate the footprint of your vials or pans to determine the required square footage to process a full batch in a single run.
Pre-Freezing: Integrated or External?
Your samples must be completely frozen before the vacuum is applied. You can achieve this with an external freezer (e.g., a -80°C lab freezer) or with the freeze dryer itself if it has shelf-freezing capabilities.
Integrated freezing simplifies the workflow but adds to the machine's initial cost and complexity. Using an external freezer is more economical if you already have one available and your workflow can accommodate the extra step.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Capability
A higher price often corresponds to greater automation, control, and durability. You must weigh these features against your budget and regulatory requirements.
Basic Controls vs. Advanced Automation
A basic system requires manual monitoring and control of the vacuum and temperature. This is often sufficient for simple, non-critical applications.
Advanced systems offer programmable recipes, which automate the drying cycle for consistency and repeatability. Features like data logging and endpoint detection are essential for process development, cGMP environments, and optimizing run times.
The Hidden Costs of Operation
The initial purchase price is only part of the total cost of ownership. You must also account for supporting utilities, maintenance, and labor.
Consider the water and electricity consumption of the unit. Also, factor in routine maintenance, such as changing the vacuum pump oil, and the labor time required to operate the machine.
When "Good Enough" Is the Wrong Choice
Attempting to save money by under-specifying a freeze dryer is a costly mistake. Using a -50°C trap for low-freezing-point solvents will lead to inefficient drying and eventual vacuum pump failure. Likewise, forgoing necessary temperature control can ruin entire batches of valuable product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a system by aligning its core capabilities with your primary application and workflow needs.
- If your primary focus is routine academic research with aqueous samples: A basic manifold dryer with a -50°C cold trap offers the best balance of cost and functionality.
- If your primary focus is product development or pilot-scale batches: A tray dryer with programmable shelf temperature control and data logging is essential for process optimization and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is working with organic solvents or low-eutectic-point samples: A system with a -85°C or colder cascade refrigeration cold trap is a non-negotiable requirement to protect your investment.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and operational efficiency: Prioritize a larger condenser capacity and consider advanced automation features to minimize manual intervention and ensure consistent results.
Making an informed choice on a freeze dryer is an investment in the long-term success and reliability of your work.
Summary Table:
| Key Selection Factor | Why It Matters | Key Specification to Check |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Trap Temperature | Protects pump & ensures drying; critical for solvents. | -50°C (aqueous) vs. -85°C/-105°C (solvents) |
| Condenser Capacity | Determines daily solvent load capacity. | Total solvent mass (kg/24h) your samples require |
| Drying Configuration | Matches sample format & batch size. | Manifold (flasks) vs. Tray (shelves) |
| Shelf Temperature Control | Essential for sensitive samples & repeatability. | Programmable heating/cooling shelves |
| Automation & Data Logging | Critical for cGMP, R&D, and process consistency. | Programmable recipes, endpoint detection |
Optimize Your Lyophilization Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right freeze dryer is crucial for your lab's productivity and the integrity of your samples. Whether you're processing aqueous solutions in academic research or handling volatile solvents in pharmaceutical development, KINTEK's range of laboratory freeze dryers is engineered to meet your precise needs.
We provide:
- Tailored Solutions: From basic manifold dryers to advanced tray dryers with cascade refrigeration (-85°C to -105°C).
- Enhanced Efficiency: Systems designed for high throughput, with large condenser capacities and automated controls.
- Long-Term Reliability: Durable equipment backed by expert support to protect your investment.
Let our experts help you select the ideal freeze dryer for your specific applications. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure successful, repeatable lyophilization results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for drying nickel nanoparticle precursors? Prevent Hard Agglomeration Now
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures



















