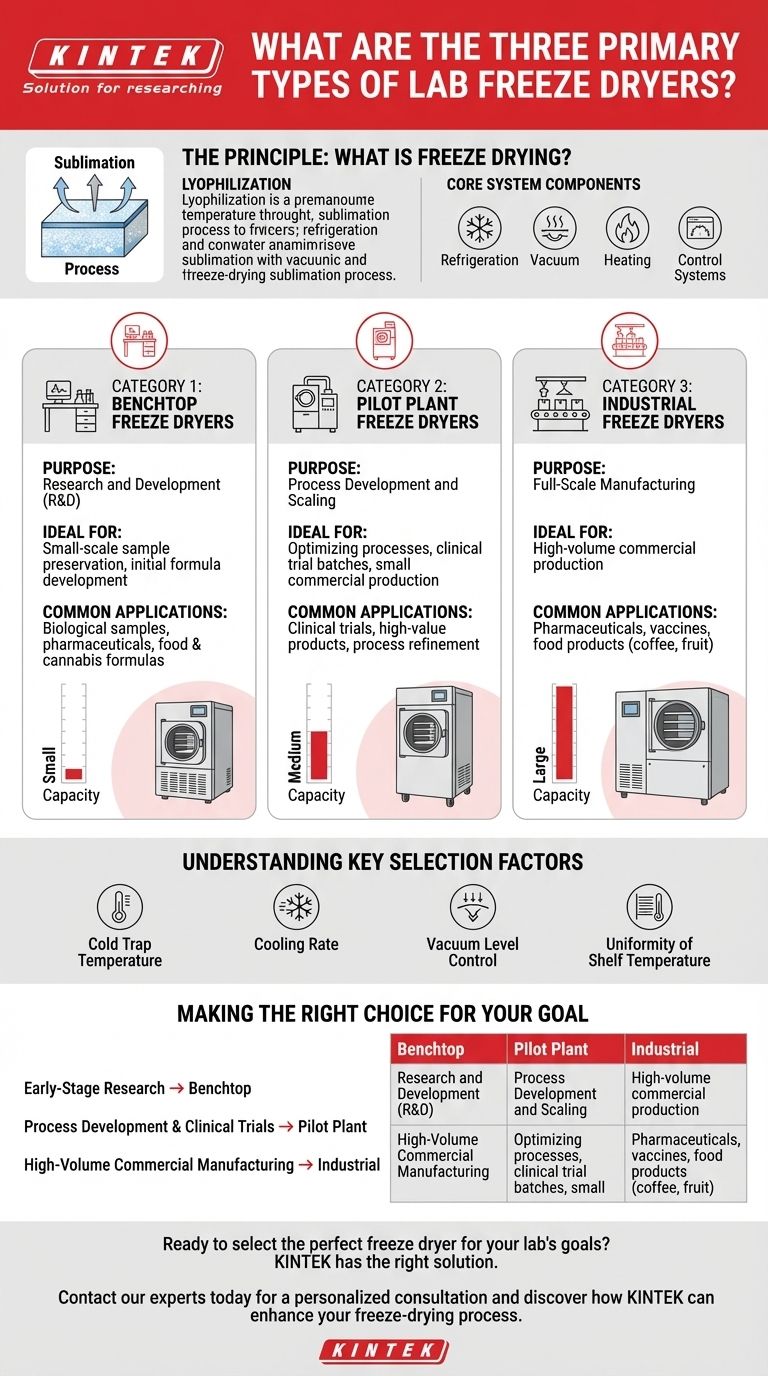
The three primary types of lab freeze dryers are categorized by their scale and application: benchtop, pilot plant, and industrial. These systems all operate on the principle of lyophilization—gently removing water from a substance—but are designed for vastly different outputs, from initial research and development to full-scale commercial manufacturing.
The choice between a benchtop, pilot, or industrial freeze dryer is not about features, but about scale. Your decision must align with your primary goal, whether that is early-stage research, process development, or commercial production.

The Principle: What is Freeze Drying?
Understanding Lyophilization
Freeze drying, or lyophilization, is a dehydration process used to preserve perishable materials or make them more convenient for transport. It works by freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water to sublimate directly from a solid to a gas.
Core System Components
All freeze dryers, regardless of size, are built around four key systems working in concert.
These include a refrigeration system to freeze the product and condense removed vapor, a vacuum system to lower the pressure, a heating system to provide energy for sublimation, and a control system to manage the process.
Category 1: Benchtop Freeze Dryers
Purpose: Research and Development
Benchtop freeze dryers are the smallest and most common type found in academic and research laboratories. Their primary purpose is to process small quantities of material for discovery and early-stage development.
Common Applications
These units are ideal for scientists preserving biological samples, stabilizing new pharmaceutical drug candidates, or developing new formulas in the food or cannabis industries. They offer flexibility for a wide range of materials on a small scale.
Category 2: Pilot Plant Freeze Dryers
Purpose: Process Development and Scaling
Pilot plant freeze dryers are intermediate-sized systems that bridge the gap between the lab and the factory floor. They are crucial for developing and optimizing a freeze-drying process before committing to large-scale manufacturing.
Common Applications
Companies use pilot units to produce materials for clinical trials, create small batches of high-value commercial products, or refine the precise temperature and pressure settings that will be used in larger industrial machines.
Category 3: Industrial Freeze Dryers
Purpose: Full-Scale Manufacturing
Industrial freeze dryers are large, high-capacity machines built for bulk commercial production. Their design prioritizes efficiency, reliability, and repeatability for manufacturing large quantities of a single product.
Common Applications
These systems are the workhorses of the pharmaceutical industry for producing vaccines and injectable drugs. They are also used extensively in the food industry to create products like freeze-dried coffee, fruit, and emergency food supplies.
Understanding the Key Selection Factors
Beyond Just Size
While scale is the primary differentiator, several technical specifications are critical when selecting a unit. These factors determine the dryer's suitability for your specific product and process.
Critical Performance Metrics
Key factors to evaluate include the cold trap temperature, which must be colder than the product's freezing point to work effectively. You must also consider the system's cooling rate, vacuum level control, and the uniformity of the shelf temperature to ensure consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct freeze dryer requires a clear understanding of your immediate and future objectives. The right machine will align with the scale and purpose of your work.
- If your primary focus is early-stage research and sample preservation: A flexible benchtop model is the most appropriate and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is preparing for commercialization or producing clinical trial batches: A pilot plant freeze dryer is essential for developing a scalable and repeatable process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume commercial manufacturing: An industrial-scale freeze dryer is the only option that can meet your production demands.
Ultimately, matching the equipment's scale to your operational goals is the key to a successful freeze-drying process.
Summary Table:
| Type | Primary Purpose | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Benchtop | Research & Development (R&D) | Small-scale sample preservation, initial formula development |
| Pilot Plant | Process Development & Scaling | Optimizing processes for clinical trials or small-batch production |
| Industrial | Full-Scale Manufacturing | High-volume commercial production of pharmaceuticals or food |
Ready to select the perfect freeze dryer for your lab's goals?
Whether you are in the discovery phase with a benchtop unit, scaling up with a pilot plant system, or ready for full-scale manufacturing, KINTEK has the right solution. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a freeze dryer that delivers precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance for your specific application—from pharmaceuticals and biotech to food science.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your freeze-drying process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What benefits do laboratory freeze dryers provide in chemical and biotechnological processes? Preserve Purity & Stability
- What physical property enhancements does freeze drying provide for pharmaceutical products? Achieve Superior Stability & Global Distribution
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What is the eutectic point in freeze drying? The Critical Temperature for Successful Lyophilization
- What are some do's and don'ts when using a Laboratory Freeze Dryer? Master the Core Principles for Success



















