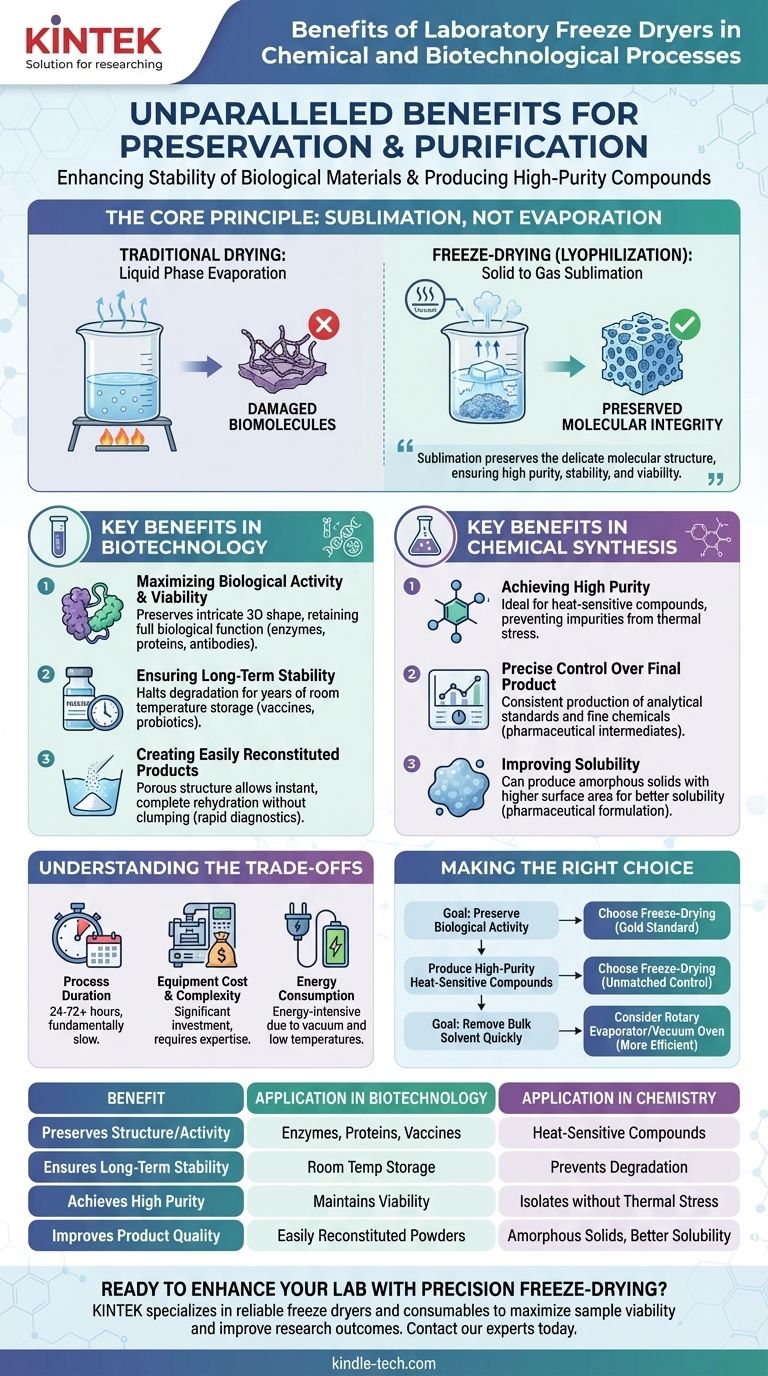
In both chemistry and biotechnology, laboratory freeze dryers offer unparalleled benefits for preservation and purification. They work by gently removing water or other solvents through sublimation—turning a solid directly into a gas—which prevents the damage caused by heat or liquid-phase evaporation. This process is critical for enhancing the long-term stability of biological materials like enzymes and cultures and for producing high-purity compounds in chemical synthesis.
The fundamental advantage of a laboratory freeze dryer is its ability to remove a solvent without passing through the destructive liquid phase. This preserves the delicate molecular structure of sensitive materials, ensuring high purity, stability, and viability where other drying methods would cause irreversible damage.
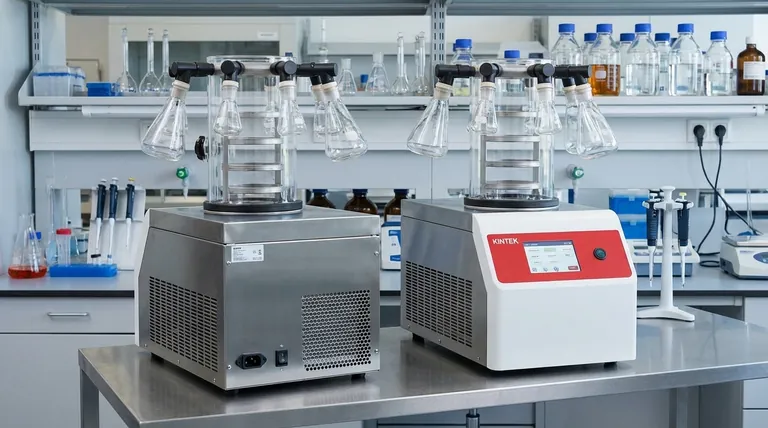

The Core Principle: Sublimation, Not Evaporation
Bypassing the Damaging Liquid Phase
Traditional drying methods rely on heat to evaporate liquid water. As water is removed, the force of surface tension can cause the delicate structures of proteins or cells to collapse and denature, destroying their function.
The Freeze-Drying Process
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, avoids this entirely through a controlled three-step process. First, the material is frozen, locking its molecular structure in a solid state. Next, under a deep vacuum, the temperature is raised slightly, causing the frozen solvent to sublimate directly into vapor. Finally, a secondary drying phase gently removes any remaining unfrozen solvent molecules.
Preserving Molecular Integrity
By locking the product's structure in place while frozen and then removing the solvent as a gas, the original shape, size, and characteristics of the material are perfectly maintained. This results in a porous, structurally intact product.
Key Benefits in Biotechnology
Maximizing Biological Activity and Viability
For enzymes, proteins, antibodies, and microbial cultures, function is directly tied to their three-dimensional shape. Freeze-drying preserves this intricate structure, ensuring that the material retains its full biological activity upon rehydration.
Ensuring Long-Term Stability
The removal of water halts most biological and chemical degradation pathways. This allows sensitive materials like vaccines, probiotics, and diagnostic reagents to be stored for years at room temperature without significant loss of potency.
Creating Easily Reconstituted Products
The output of freeze-drying is a porous, lightweight cake or powder. This structure allows water to penetrate instantly, leading to rapid and complete rehydration without clumping, which is critical for consistent results in research and diagnostics.
Key Benefits in Chemical Synthesis
Achieving High Purity
Freeze-drying is ideal for isolating heat-sensitive compounds that would degrade or decompose if dried in a conventional oven. It gently removes solvents without thermal stress, preventing the formation of impurities.
Precise Control Over the Final Product
The precise control over temperature and pressure allows for the consistent production of high-quality compounds. This is essential for creating analytical standards, pharmaceutical intermediates, and other fine chemicals where purity is paramount.
Improving Solubility
For some compounds, freeze-drying can produce an amorphous (non-crystalline) solid. This form often has a higher surface area and better solubility than its crystalline counterpart, which can be a significant advantage in pharmaceutical formulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Duration
Lyophilization is a fundamentally slow process. A typical laboratory-scale run can take anywhere from 24 to 72 hours or longer, depending on the sample type and volume.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Freeze dryers are a significant capital investment compared to simple ovens or desiccators. They require a vacuum pump, refrigeration system, and precise controls, demanding more operational expertise and maintenance.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining very low temperatures while simultaneously running a high-power vacuum pump makes freeze-drying an energy-intensive process. This is a key consideration for scaling up production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a freeze dryer should be based on the specific requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for stabilizing enzymes, proteins, vaccines, and microbial cultures for long-term storage.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, heat-sensitive compounds: This method offers unmatched control, preventing thermal degradation and ensuring a clean final product.
- If your primary focus is simply removing bulk solvent quickly: A less complex method like a rotary evaporator or vacuum oven may be more efficient and cost-effective.
Ultimately, freeze-drying provides a level of precision and preservation that is simply unattainable with conventional drying techniques.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Application in Biotechnology | Application in Chemistry |
|---|---|---|
| Preserves Structure/Activity | Enzymes, proteins, vaccines, cultures | Heat-sensitive compounds, pharmaceuticals |
| Ensures Long-Term Stability | Room temperature storage for years | Prevents degradation of fine chemicals |
| Achieves High Purity | Maintains viability of diagnostics | Isolates compounds without thermal stress |
| Improves Product Quality | Creates easily reconstituted powders | Can produce amorphous solids for better solubility |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision freeze-drying?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory freeze dryers and consumables, providing the reliable equipment you need to preserve sensitive biologicals and achieve high-purity chemical synthesis. Our solutions help you maximize sample viability, ensure long-term stability, and improve your research outcomes.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze-drying solution for your biotechnology or chemistry laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What problems should be avoided when using a lyophilizer? Prevent Product Collapse and Equipment Overload
- What is the critical temperature in freeze drying? The Key to Successful Lyophilization
- What is a lyophilizer and how does it work? Unlock Superior Preservation for High-Value Materials
- What is a Laboratory Freeze Dryer and what is its primary function? Achieve Perfect Preservation of Sensitive Materials
- What is the eutectic point in lyophilization? Master the Critical Temperature for Success



















