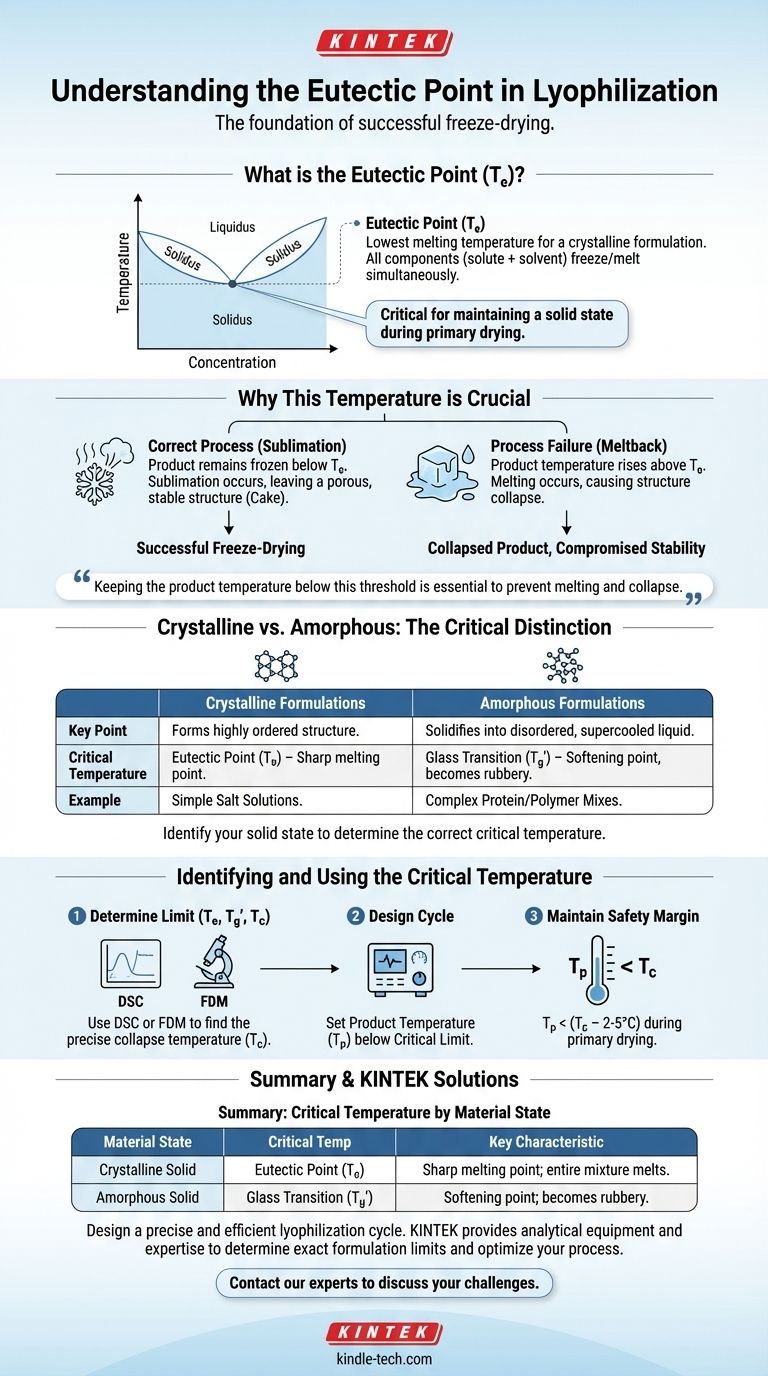
In lyophilization, the eutectic point is the lowest possible melting temperature for a formulation that freezes into a crystalline solid. It represents the specific temperature and concentration at which all components (the solute and the solvent, typically water) freeze and melt simultaneously as a single mixture. Keeping the product temperature below this critical threshold during the primary drying phase is absolutely essential to prevent the product from melting and collapsing.
The core challenge in freeze-drying is not just removing water, but preserving the product's structure. Understanding your product's critical temperature—whether it's a true eutectic point for crystalline solids or a glass transition temperature for amorphous ones—is the single most important factor in designing a successful primary drying cycle.

Why This Temperature is the Foundation of Freeze-Drying
The Role of the Solid State
Lyophilization works through a process called sublimation, where frozen water turns directly into vapor without first becoming a liquid.
This process is only possible if the product is maintained in a completely solid, frozen state.
Preserving the Product Structure
As ice crystals sublimate from the frozen matrix, they leave behind a porous, solid scaffold of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients.
This porous "cake" is what allows for rapid reconstitution and ensures the stability of the final product.
The Consequence of Melting
If the product temperature rises above the eutectic point during primary drying, the frozen material will begin to melt.
This liquid phase causes the delicate solid scaffold to soften and collapse, a catastrophic failure known as meltback. A collapsed product will not dry properly, will be difficult to reconstitute, and will have compromised stability.
Crystalline vs. Amorphous: A Critical Distinction
While the term "eutectic point" is often used broadly, it technically applies only to materials that form a crystalline structure upon freezing. Many complex biological and pharmaceutical formulations do not.
Crystalline Formulations and the Eutectic Point (Te)
A crystalline material has a highly ordered, repeating molecular structure. For these products, the eutectic temperature (Te) is a sharp, distinct thermodynamic point.
When a simple solution like salt water freezes, pure ice forms first, concentrating the salt in the remaining liquid water until it reaches the eutectic concentration, at which point the entire mixture solidifies at the eutectic temperature.
Amorphous Formulations and the Glass Transition (Tg')
Many complex formulations, especially those containing proteins or polymers, do not crystallize. Instead, they solidify into a disordered, supercooled liquid state known as an amorphous glass.
These materials do not have a true eutectic point. Instead, they have a glass transition temperature (Tg'). Below this temperature, the material is a rigid, brittle solid. Above it, it softens and becomes a viscous, rubbery fluid, which also leads to collapse.
Why the Distinction Matters
For process development, you must know which type of solid your product forms. The goal is the same—keep the product colder than its critical temperature—but the specific property you measure (Te vs. Tg') is different.
Identifying and Using the Critical Temperature
Determining the Limit
The critical temperature of a formulation is typically measured using analytical techniques like Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), which detects the heat flow associated with melting or glass transitions.
Another powerful tool is Freeze-Dry Microscopy (FDM), which allows for direct visual observation of the product structure as it is heated under vacuum, identifying the precise temperature at which collapse begins (Tc). The collapse temperature is often the most practical limit for process design.
The Process Control Imperative
Once the critical temperature is known, the lyophilization cycle is designed to ensure the product temperature (Tp) always remains below it during primary drying.
Typically, a safety margin of 2-5°C is used, meaning Tp < (Tc - 2°C). This is achieved by carefully balancing the shelf temperature and the chamber pressure to control the rate of sublimation and the heat input to the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The primary goal is always to design a cycle that is both safe (no collapse) and efficient (as short as possible). Understanding the critical temperature is the key to balancing these two objectives.
- If your primary focus is developing a new formulation: Your first step must be to determine its critical temperature (Te, Tg', or Tc) to establish the absolute processing limit.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing cycle: Carefully measure your product temperature and compare it to the known critical temperature to see if you can safely increase shelf temperature to shorten the primary drying phase.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a failed batch: A collapsed or melted product is almost always a sign that the product temperature exceeded its critical limit at some point during primary drying.
Mastering your product's critical temperature transforms lyophilization from a guessing game into a precise, controllable science.
Summary Table:
| Critical Temperature Type | Material State | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Eutectic Point (Te) | Crystalline Solid | Sharp melting point; entire mixture melts at once. |
| Glass Transition (Tg') | Amorphous Solid | Softening point; material becomes rubbery, not liquid. |
Design a precise and efficient lyophilization cycle for your product.
Understanding your product's critical temperature is the foundation of successful freeze-drying. KINTEK specializes in providing the analytical equipment and expertise you need to determine your formulation's exact limits and optimize your process.
We supply reliable lab equipment for thermal analysis and process development, helping you prevent costly batch failures and ensure product stability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lyophilization challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of freeze dryers in biotechnology? Preserving Life-Saving Samples for Research
- What happens during the freezing phase of lyophilization? Master the Critical First Step for Product Integrity
- What is the primary function of a freeze dryer in a laboratory setting? Preserve Delicate Materials with Sublimation
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory freeze dryer? Achieve Unmatched Sample Preservation
- How does freeze drying compare to conventional freezing for biological material preservation? Achieve Long-Term, Shelf-Stable Preservation



















