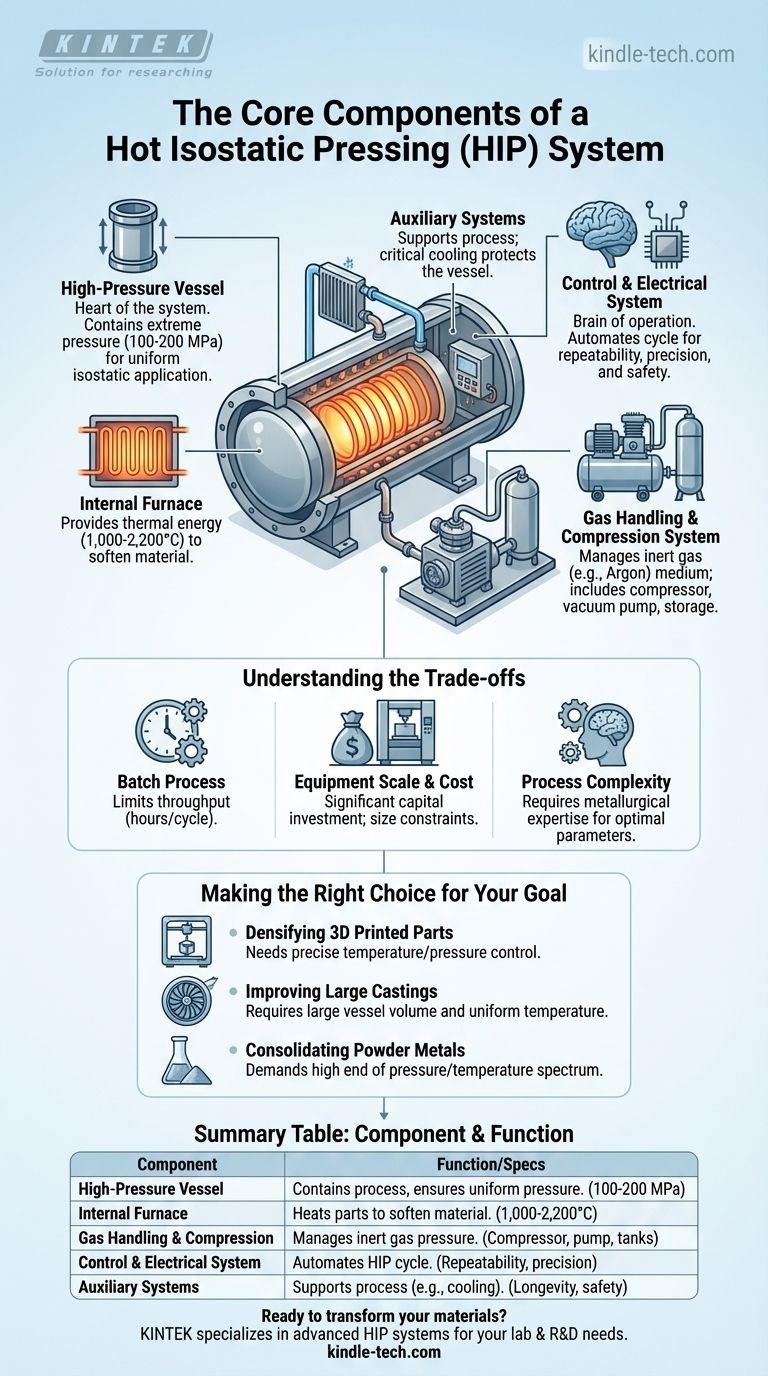
At its core, a Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) system is an integrated machine designed to apply extreme heat and uniform pressure to materials. It consists of five primary subsystems that work in concert: the high-pressure vessel, the internal furnace, the gas handling and compression system, the electrical and control system, and various auxiliary systems. Together, these components densify parts, eliminate internal defects, and dramatically improve a material's mechanical properties.
The individual components of a HIP system are not just a collection of hardware. They form a precisely controlled environment that uses inert gas as a pressure medium to simultaneously heat and squeeze a part, fundamentally transforming its internal microstructure from porous and inconsistent to fully dense and uniform.

The Core Components of a HIP System
Each component plays a critical, non-negotiable role in achieving the final material properties. Understanding their function is key to understanding the HIP process itself.
1. The High-Pressure Vessel
The pressure vessel is the heart of the HIP system. It is a robust, typically cylindrical chamber designed to safely contain the immense pressures required for the process.
This cylindrical geometry is essential for ensuring that the pressure exerted on the parts inside is perfectly uniform, or isostatic. The pressure is applied equally from all directions, which allows the part to densify without changing its net shape.
These vessels are built to withstand pressures ranging from 100 to 200 MPa (14,500 to 29,000 psi), making them the most critical safety and performance component of the equipment.
2. The Internal Furnace
Located inside the pressure vessel, the furnace provides the thermal energy for the process. It is responsible for heating the components to temperatures between 1,000 and 2,200°C (1832 to 3992°F).
This high temperature softens the material, allowing the high pressure to effectively collapse internal voids and pores. The furnace's ability to maintain a stable and uniform temperature is crucial for consistent and repeatable results.
3. The Gas Handling & Compression System
This system manages the inert gas (typically Argon) that acts as the pressure-transmitting medium. It includes several key parts.
A compressor raises the gas to the target pressure, a vacuum pump first removes atmospheric air from the vessel to prevent contamination, and storage tanks hold the gas before and after a cycle. This system is responsible for pressurizing, holding, and depressurizing the vessel in a controlled manner.
4. The Control & Electrical System
This is the brain of the entire operation. The control system links the vessel, furnace, and gas handling systems into a single, functional tool.
It executes the pre-programmed HIP cycle, precisely managing the rates of heating, pressurization, hold times, and cooling. This automation ensures the repeatability and consistency required for producing high-quality, certified parts for critical applications.
5. Auxiliary Systems
This category includes all the supporting hardware necessary for a safe and efficient cycle.
The most important auxiliary is the cooling system. It circulates fluid through the walls of the pressure vessel to protect it from the extreme internal temperatures of the furnace, ensuring the structural integrity of the vessel over many cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, the HIP process and its systems come with inherent operational considerations.
Process Time and Throughput
Hot Isostatic Pressing is a batch process, not a continuous one. A full cycle, including heating, soaking at temperature and pressure, and cooling, can take many hours. This limits the overall throughput compared to continuous manufacturing methods.
Equipment Scale and Cost
HIP systems are a significant capital investment. The physical size of the pressure vessel, which can range from a few inches to over 80 inches in diameter, directly dictates the size and quantity of parts that can be processed in a single batch.
Process Complexity
Achieving optimal results requires a deep understanding of metallurgy. The specific parameters of temperature, pressure, and time must be carefully developed for each material and application to improve its properties without causing unwanted effects like grain growth or distortion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The configuration of a HIP system is directly tied to its intended application.
- If your primary focus is densifying 3D printed metal parts: You need a system that offers precise temperature and pressure control to effectively close internal porosity without compromising the part's fine features.
- If your primary focus is improving large aerospace or industrial castings: Your key factor is the vessel's internal working volume and its ability to handle large, heavy components while maintaining temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is consolidating powder metals into solid parts: You require a system capable of reaching the high end of the pressure and temperature spectrum to achieve full theoretical density from a powder starting material.
Understanding these components empowers you to see a HIP system not just as machinery, but as a strategic tool for achieving fundamental material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| High-Pressure Vessel | Contains the process; ensures uniform isostatic pressure. | Withstands 100-200 MPa pressure. |
| Internal Furnace | Heats the parts to soften the material. | Reaches 1,000-2,200°C (1832-3992°F). |
| Gas Handling & Compression | Manages the inert gas (e.g., Argon) pressure medium. | Includes compressor, vacuum pump, and storage tanks. |
| Control & Electrical System | The "brain" that automates the entire HIP cycle. | Ensures repeatability, precision, and safety. |
| Auxiliary Systems | Supports the main process (e.g., cooling the vessel). | Critical for equipment longevity and safety. |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Understanding the components of a Hot Isostatic Pressing system is the first step. The next is partnering with an expert who can provide the right equipment for your specific application—whether you are densifying 3D-printed metals, improving aerospace castings, or consolidating advanced powders.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including HIP systems, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. We help you achieve superior material density, eliminate defects, and enhance mechanical properties. Let our expertise guide you to the optimal solution.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can empower your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components



















