To properly store a Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) sheet, you must place the cleaned and dried material in a dry, cool, and clean environment. It is crucial to protect the sheet from direct sunlight and high humidity, as these conditions can compromise its structural and chemical integrity.
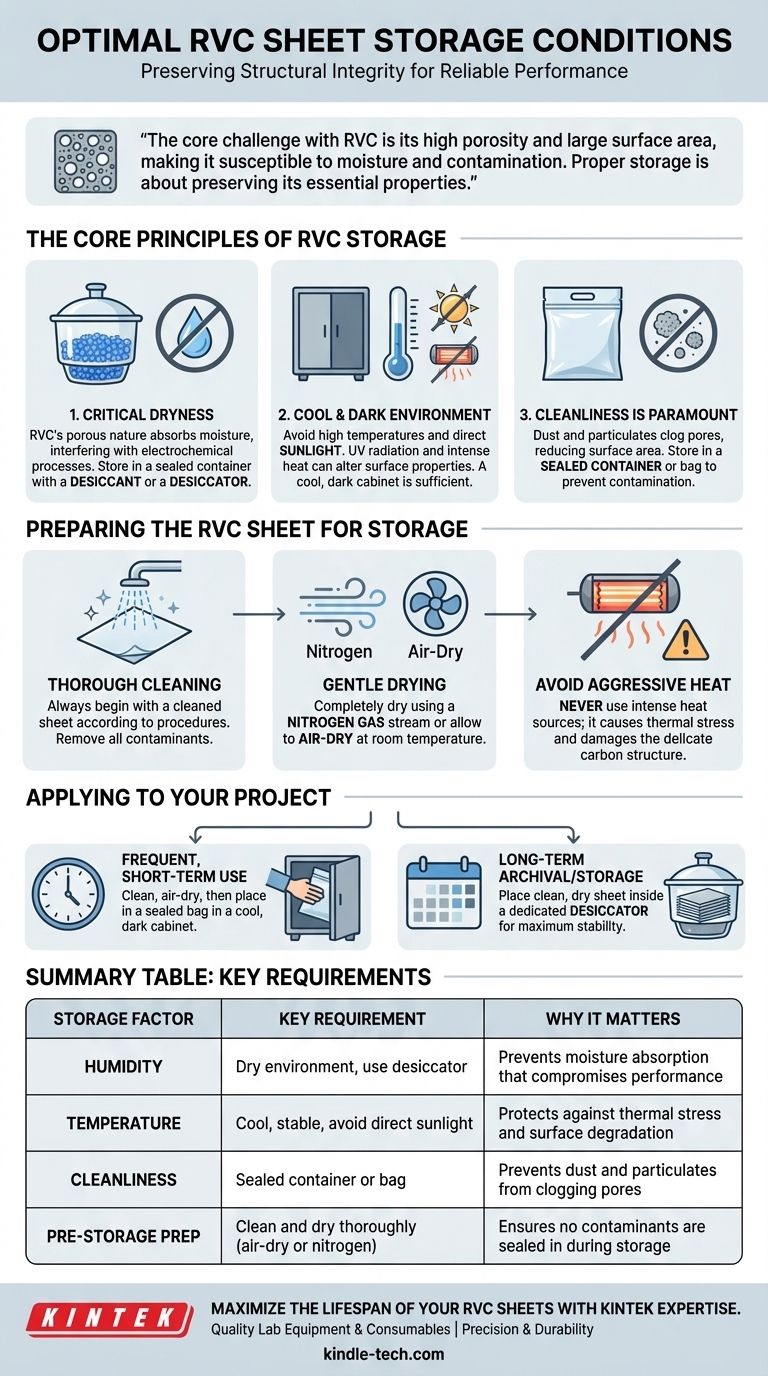
The core challenge with RVC is its high porosity and large surface area, which make it extremely susceptible to moisture and contamination. Proper storage is not simply about preventing damage; it is about preserving the material's essential properties for reliable performance.
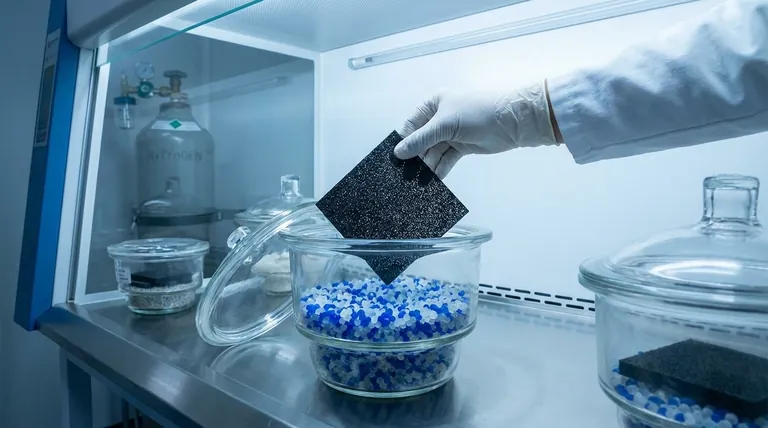

The Core Principles of RVC Storage
Reticulated Vitreous Carbon is a specialized material whose performance depends entirely on its unique physical structure. The goal of proper storage is to maintain this structure in a pristine state.
Why Dryness is Critical
The interconnected, porous nature of an RVC sheet means it can easily absorb moisture from the atmosphere. This absorbed water can introduce impurities or interfere with subsequent electrochemical processes.
For long-term preservation, the environment must be actively kept dry. Storing the sheet in a desiccator or in a sealed container with a desiccant is the recommended best practice.
The Impact of Temperature and Sunlight
High temperatures or direct exposure to sunlight should be avoided. While RVC is thermally stable, intense heat (like from an infrared lamp) or UV radiation can potentially alter its surface properties over time.
A cool, dark location like a cabinet or drawer is sufficient to mitigate these risks.
The Necessity of a Clean Environment
Dust and other airborne particulates can physically clog the pores of the RVC sheet. This contamination reduces the material's effective surface area and can introduce unwanted variables into your work.
Storing the sheet in a sealed container or bag ensures it remains free from environmental debris.
Preparing the RVC Sheet for Storage
The condition of the sheet before it goes into storage is as important as the storage environment itself.
Ensuring Proper Cleaning
Always begin with a thoroughly cleaned RVC sheet according to your established procedures. Any contaminants left on the surface can become more difficult to remove later.
Choosing the Right Drying Method
After cleaning, the sheet must be completely dry. You can use a gentle stream of nitrogen gas or simply allow it to air-dry at room temperature.
What to Avoid During Drying
Never use intense heat sources, such as baking the sheet under an infrared lamp. This aggressive heating can cause thermal stress and damage the delicate carbon structure.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your storage strategy depends on how frequently you use the material.
- If your primary focus is frequent, short-term use: Ensure the sheet is clean and fully air-dried, then place it in a sealed bag or container in a cool, dark cabinet.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival or storage: Place the clean, dry sheet inside a dedicated desiccator to provide the most stable, moisture-free environment possible.
Ultimately, disciplined storage practices are fundamental to ensuring the consistency and longevity of your RVC materials.
Summary Table:
| Storage Factor | Key Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Humidity | Dry environment, use desiccator | Prevents moisture absorption that compromises performance |
| Temperature | Cool, stable, avoid direct sunlight | Protects against thermal stress and surface degradation |
| Cleanliness | Sealed container or bag | Prevents dust and particulates from clogging pores |
| Pre-Storage Prep | Clean and dry thoroughly (air-dry or nitrogen) | Ensures no contaminants are sealed in during storage |
Maximize the lifespan and performance of your RVC sheets with KINTEK's expertise. Proper storage is just one part of ensuring reliable results in your lab. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including RVC materials, designed for precision and durability. Whether you're managing frequent use or long-term archival storage, our products and support help you maintain material integrity. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and consistency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Copper Nickel Foam Metal Sheet
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
People Also Ask
- What is the proper procedure for cleaning a glassy carbon sheet after use? A Definitive Guide to Ensure Reliable Results
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- What actions and conditions are strictly prohibited when working with a glassy carbon sheet? Protect Your Investment and Data Integrity
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















