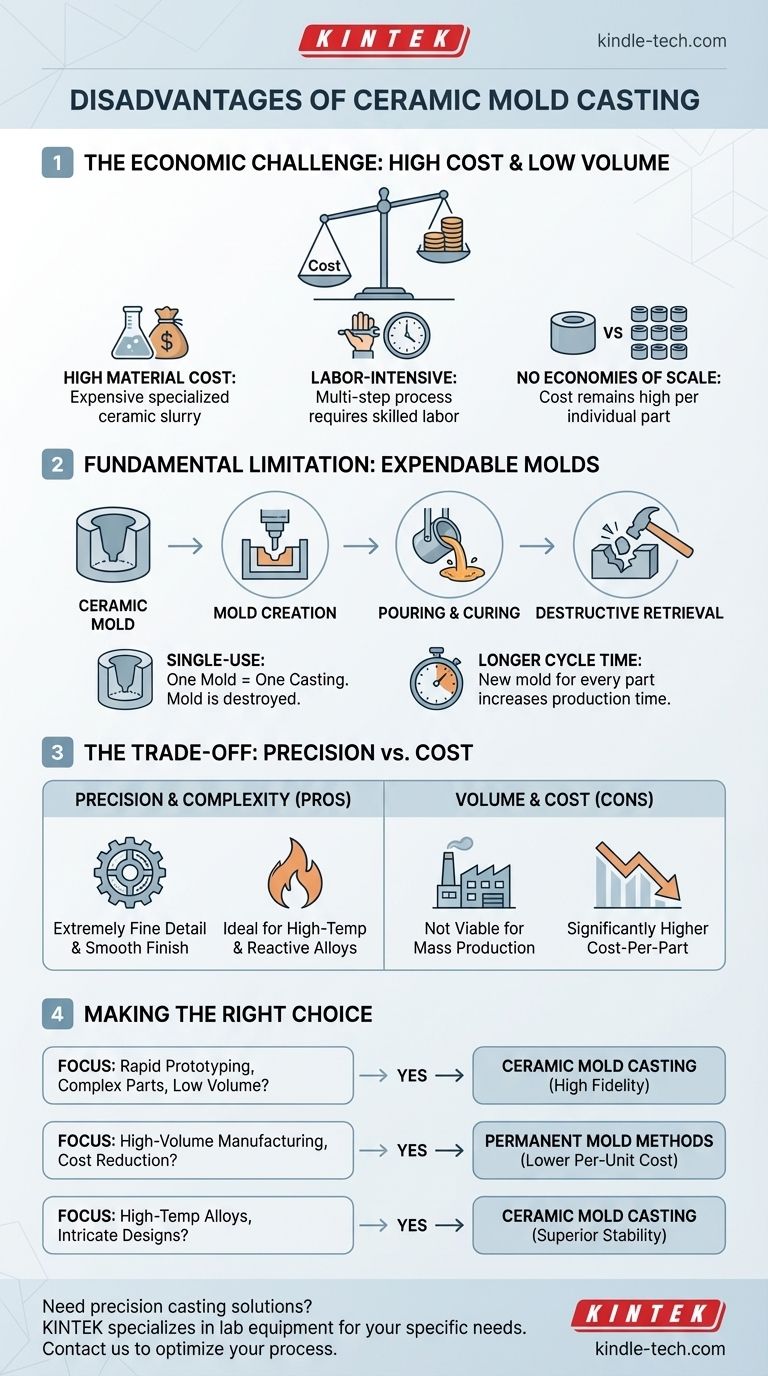
At its core, the primary disadvantages of ceramic mold casting are its high cost for large production runs and the expendable, single-use nature of its molds. This process is engineered for precision and complexity, but these benefits come with economic limitations that make it unsuitable for high-volume manufacturing.
While ceramic mold casting delivers exceptional precision and a superior surface finish, its core limitations stem from the process itself. The high cost of materials and the labor-intensive, single-use nature of the molds make it economically unviable for mass production.

The Core Economic Challenge: Production Volume
The most significant drawback is a matter of economics. The cost structure of ceramic mold casting favors quality over quantity, making it a specialized tool rather than a general-purpose manufacturing solution.
Why It's Suited for Smaller Runs
The process is most cost-effective for small- to medium-sized production runs. This is because the upfront tooling costs can be lower than permanent mold methods, but the cost per individual part remains consistently high.
The High Cost of Materials
The specialized ceramic slurry used to create the molds is inherently more expensive than materials like sand used in other casting methods. This material cost is incurred for every single part produced.
Labor-Intensive Preparation
Creating a ceramic mold is a multi-step, technical process that requires skilled labor. This consistent labor cost does not diminish with volume, preventing the economies of scale seen in other manufacturing techniques.
The Fundamental Limitation: Expendable Molds
Unlike methods that use durable, reusable molds, ceramic casting is an expendable-mold process. This reality is the root cause of its economic and speed limitations.
One Mold, One Casting
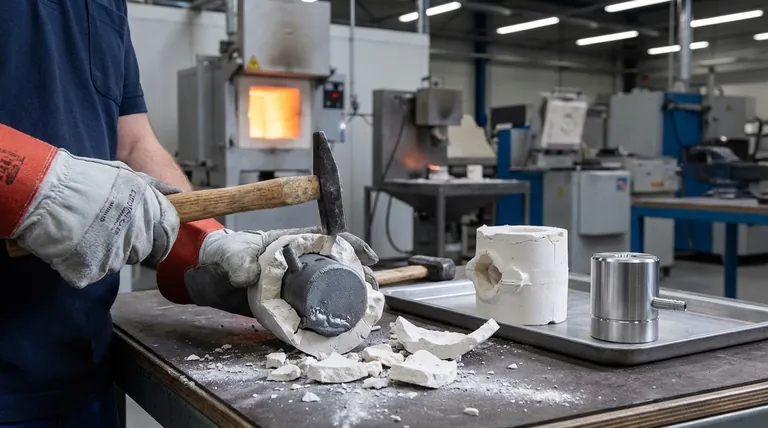
To retrieve the finished part, the ceramic mold must be broken apart and destroyed. It cannot be reused for a subsequent casting under any circumstances.
No Economies of Scale
Permanent mold processes, like die casting, have a high initial tooling cost that is amortized over thousands of units, driving the per-unit price down. Ceramic casting never achieves this benefit because a new, costly mold must be created for every single item.
Impact on Cycle Time
Because a new mold must be prepared, poured, cured, and destroyed for each casting, the overall production cycle time per part is significantly longer than automated, high-volume methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Cost
Choosing a casting method is always a balancing act. The disadvantages of ceramic casting must be weighed against its unique strengths, particularly when working with challenging materials or complex designs.
When to Accept the Cost
The higher cost is justified when the part requires extremely fine detail, tight dimensional tolerances, and a smooth surface finish that would otherwise require expensive and time-consuming secondary machining. It is also a preferred method for casting high-temperature alloys, including ferrous metals, titanium, and stainless steels, due to the mold's chemical stability.
When to Choose Another Method
If the primary driver is low cost-per-part and the production volume is in the thousands or millions, other methods are far more suitable. For high-volume work, die casting or permanent mold casting offer superior economic efficiency, assuming the part geometry and material are compatible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if ceramic mold casting fits your project, evaluate your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or low-volume production of complex parts: Ceramic mold casting is an excellent choice, as it delivers high fidelity and minimizes the need for post-machining.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing and cost reduction: You should explore permanent mold methods, as the per-unit cost will be significantly lower once you reach mass production scale.
- If your primary focus is casting high-temperature or reactive alloys with intricate designs: The chemical inertness and thermal stability of the ceramic mold make it a superior technical option, often justifying the higher cost.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations allows you to leverage ceramic mold casting for its intended purpose: achieving unparalleled detail where precision, not volume, is the ultimate measure of success.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Cost per Part | Not economical for large production runs due to expensive ceramic slurry and labor. |
| Expendable Molds | Each mold is single-use, preventing economies of scale and increasing cycle time. |
| Labor-Intensive Process | Requires skilled labor for mold creation, driving up costs without volume discounts. |
| Limited to Small Runs | Best suited for prototypes or low-volume production of complex, high-precision parts. |
Need precision casting solutions for your lab? While ceramic mold casting has its place, choosing the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working with high-temperature alloys or require intricate designs, our expertise ensures you get the best tools for the job. Contact us today to optimize your casting processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why are high-strength graphite molds essential for vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Your Diamond/Copper Composites
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- What role do customized metal molds play in solid-state battery densification? Achieving Precision at 500 MPa
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What functions do high-purity graphite molds serve for IZO targets? Ensure Density and Prevent Sintering Cracks



















