In its pure form, metallic iron is rarely used in modern applications due to two primary disadvantages: it is highly susceptible to corrosion (rusting) and possesses relatively poor mechanical properties compared to its alloys. It is both softer and less strong than the materials we derive from it, most notably steel.
The fundamental disadvantage of iron is its reactive nature, which leads to rapid corrosion, and its inherent softness. This is precisely why we almost never use pure iron, but instead rely on its alloys—like steel and cast iron—which are engineered to overcome these exact weaknesses.

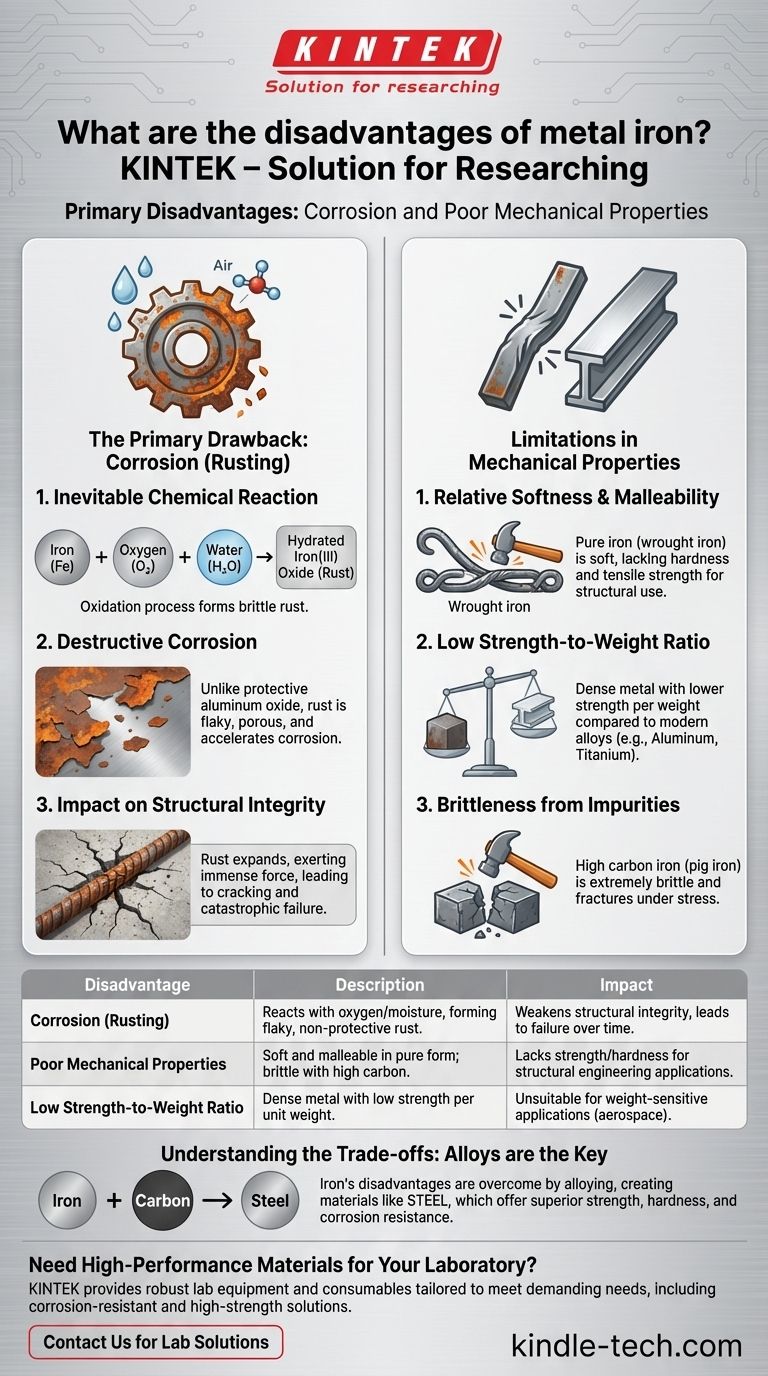
The Primary Drawback: Corrosion (Rusting)
The most well-known weakness of iron is its tendency to rust. This is not just a cosmetic issue; it's a chemical process that actively destroys the metal.
The Inevitable Chemical Reaction
Iron reacts readily with oxygen in the presence of water or air moisture. This electrochemical process, known as oxidation, forms hydrated iron(III) oxide, which we call rust.
A Destructive Form of Corrosion
Unlike the protective oxide layer that forms on aluminum, rust is flaky, brittle, and porous. It flakes away, exposing fresh iron underneath to continue the corrosion process, effectively eating away at the material from the outside in.
The Impact on Structural Integrity
The rust that forms is also less dense than the original iron. This expansion can exert immense force, causing surrounding materials like concrete to crack and leading to catastrophic structural failure over time.
Limitations in Mechanical Properties
While we think of iron as strong, its pure form is mechanically unimpressive for most engineering needs. Its properties are highly sensitive to impurities, especially carbon.
Relative Softness and Malleability
Pure iron, sometimes found as wrought iron, is quite soft and malleable. While this makes it easy to work with for decorative purposes, it lacks the hardness and tensile strength required for structural beams, tools, or engine components.
Lower Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Iron is a dense metal. Compared to modern materials like aluminum alloys or titanium, its strength for a given weight is significantly lower. This makes it unsuitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or performance vehicles.
Brittleness from Impurities
Conversely, iron with a high carbon content (like pig iron straight from a blast furnace) is extremely brittle. It will fracture under stress or impact rather than bending. The entire science of steelmaking is a precise balancing act of controlling this carbon content.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Iron's disadvantages are significant, but they must be weighed against its single greatest advantage, which explains why it remains the most widely used metal on Earth.
Unbeatable Cost and Abundance
Iron is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. This incredible abundance makes it, and the steel derived from it, extraordinarily inexpensive compared to virtually any other metal. For most applications, its cost-effectiveness outweighs its flaws.
The Power of Alloying
The limitations of pure iron are the very reason we developed steel. By adding a small, controlled amount of carbon and other elements (like chromium for stainless steel), we dramatically enhance its strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Steel is not a different metal; it's iron, perfected.
Essential Magnetic Properties
Iron is one of the few naturally ferromagnetic materials. This unique property is essential for creating electric motors, generators, transformers, and data storage devices, applications where no other common element can substitute for it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "disadvantages" of iron are better understood as baseline properties that we modify through alloying to fit a specific purpose.
- If your primary focus is structural strength and durability: Use steel, as it is specifically an iron alloy engineered to overcome iron's inherent softness and improve its resilience.
- If your primary focus is fighting corrosion in a harsh environment: Use stainless steel or galvanized (zinc-coated) steel, which directly addresses iron's tendency to rust.
- If your primary focus is low-cost casting for complex shapes: Cast iron is the ideal choice, but you must design around its inherent brittleness.
- If your primary focus is decorative metalwork: Wrought iron is a viable option, but it will require a protective coating to prevent rust.
Understanding the limitations of pure iron is the key to appreciating why its alloys built, and continue to support, the modern world.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion (Rusting) | Reacts with oxygen and moisture, forming flaky, non-protective rust. | Weakens structural integrity, leading to material failure over time. |
| Poor Mechanical Properties | Soft and malleable in pure form; becomes brittle with high carbon content. | Lacks the strength and hardness needed for most structural or engineering applications. |
| Low Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Dense metal with lower strength per unit weight compared to modern alloys. | Unsuitable for weight-sensitive applications like aerospace or high-performance vehicles. |
Need High-Performance Materials for Your Laboratory?
Understanding material limitations is the first step to finding the right solution. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories. Whether you require corrosion-resistant components or high-strength materials for your applications, our expertise ensures you get reliable, efficient, and durable products.
Let us help you overcome material challenges and enhance your lab's performance. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research and operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Grinding Bowl
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the density of graphite? A Key Indicator for Performance and Quality
- At what temperature does graphite melt? Understanding Its Extreme Phase Change
- How does an induction graphitization furnace facilitate the transformation of unburned carbon into synthetic graphite?
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure



















