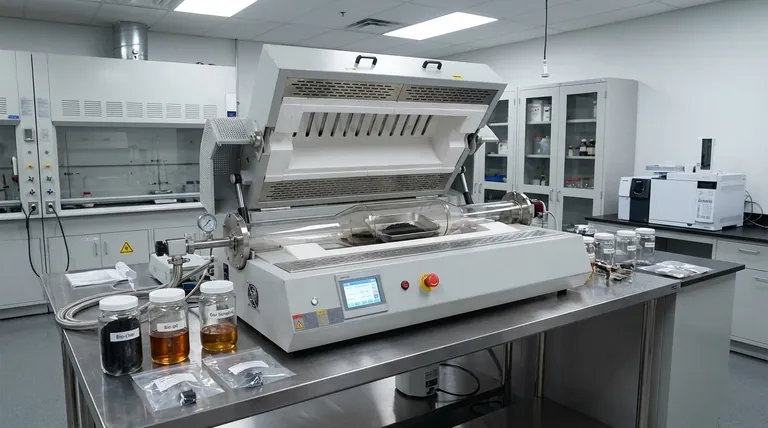
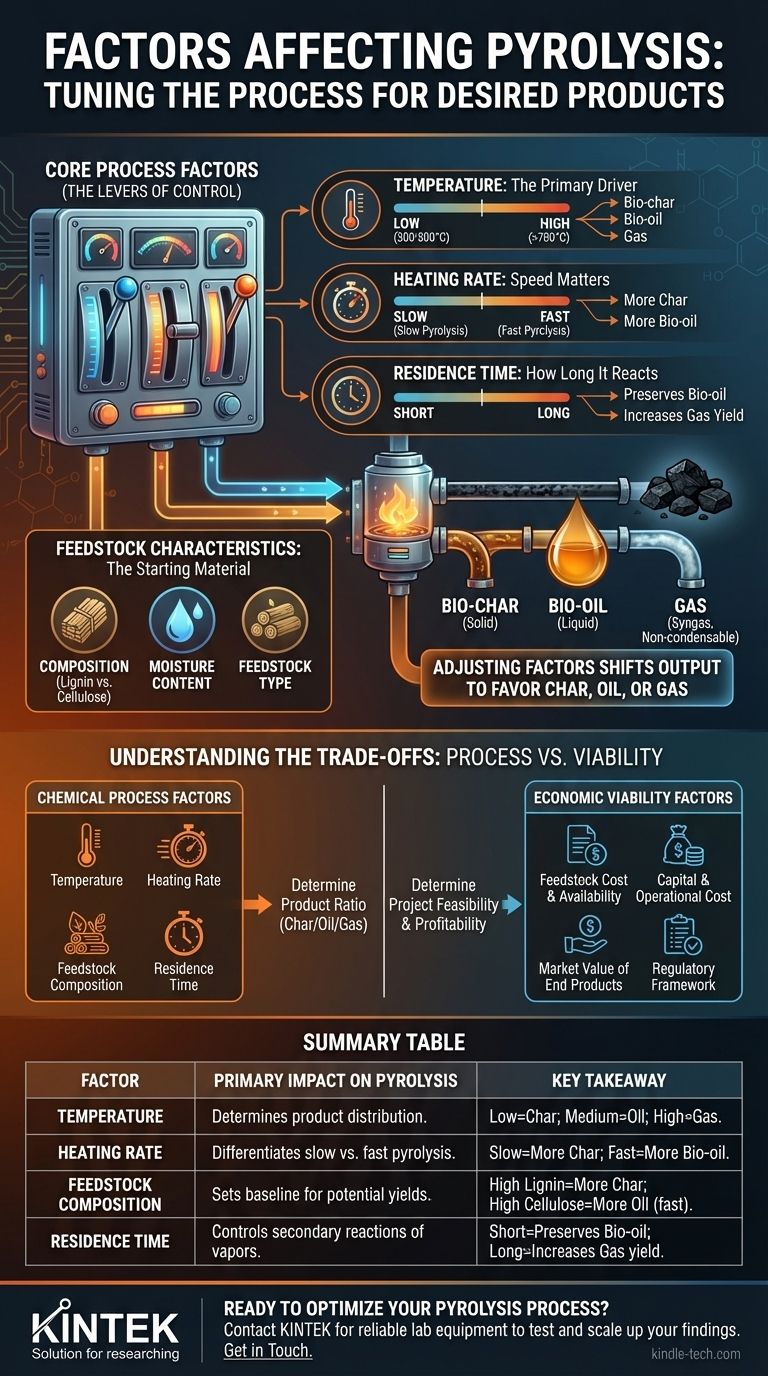
In short, the pyrolysis process is governed by two main categories of factors: the process conditions you control (like temperature and heating rate) and the inherent characteristics of the feedstock (the material being processed). These factors work together to determine the final yield and composition of the three primary products: solid bio-char, liquid bio-oil, and pyrolysis gas.
The most critical concept to grasp is that pyrolysis is not a single, fixed process. It is a tunable platform where adjusting specific factors—primarily temperature and heating rate—allows you to deliberately shift the output to favor the production of either solid char, liquid oil, or gas.

Core Process Factors: The Levers of Control
To understand pyrolysis is to understand the variables you can manipulate. Each of these factors acts as a lever, allowing you to fine-tune the reaction to achieve a specific outcome.
Temperature: The Primary Driver
Temperature is the single most influential factor in pyrolysis. It directly dictates the extent and speed of thermal decomposition.
Different temperature ranges favor different products. As a general rule, lower temperatures (around 300-500°C) favor the production of solid bio-char. As temperatures increase (500-700°C), the process favors the production of liquid bio-oil. At very high temperatures (>700°C), thermal cracking becomes dominant, breaking down larger molecules into non-condensable gases (syngas).
Heating Rate: Speed Matters
The heating rate is how quickly the feedstock reaches the target pyrolysis temperature. This factor is the key differentiator between "slow" and "fast" pyrolysis.
A slow heating rate (slow pyrolysis) allows more time for char-forming reactions, maximizing the solid product yield. Conversely, a very fast heating rate (fast pyrolysis) rapidly breaks down the material, minimizing char formation and maximizing the yield of vapors that are then condensed into liquid bio-oil.
Feedstock Composition: The Starting Material
The chemical makeup and physical properties of the input material, or feedstock, establish the foundation for the entire process. Key characteristics include moisture content and the composition of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Materials with high moisture content require more energy to heat, affecting process efficiency. Materials rich in lignin (like wood) tend to produce more bio-char, while those rich in cellulose often yield more bio-oil under the right conditions.
Residence Time: How Long It Reacts
Residence time refers to the duration the material (or its vapor) is held at the reaction temperature.
A shorter residence time for vapors is crucial for fast pyrolysis to prevent secondary reactions, where the valuable components of bio-oil might "crack" into lower-value gases. Longer residence times, especially at high temperatures, will consistently increase the gas yield.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process vs. Viability
It is critical to distinguish between the factors that affect the chemical process itself and those that affect the economic viability of a pyrolysis project. While intertwined, they are not the same.
Chemical Process Factors
These are the variables discussed above: temperature, heating rate, feedstock composition, and residence time. They directly impact the chemistry and determine the ratio of char, oil, and gas you produce. Mismanaging these will result in an inefficient process and undesirable product yields.
Economic Viability Factors
These factors determine whether a pyrolysis operation makes financial sense. A chemically perfect process can still fail if the economics are unfavorable.
Key economic factors include the cost and availability of feedstock, the capital and operational cost of the pyrolysis technology, and the market value of the end products (bio-char, bio-oil, syngas). Furthermore, the local regulatory framework and the availability of government incentives or funding can make or break a project's feasibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy must be dictated by your desired end product. By adjusting the core process factors, you can steer the outcome to meet a specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-char: Employ slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures (e.g., 400°C) and slow heating rates to give the solid carbon structure time to form.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil: Use fast pyrolysis with moderate temperatures (e.g., 500°C), extremely high heating rates, and a short vapor residence time to capture the liquids before they break down.
- If your primary focus is maximizing gas production: Utilize very high temperatures (>700°C) to ensure comprehensive thermal cracking of all components into non-condensable gases.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis means understanding that you are not just applying heat; you are conducting a controlled transformation where every factor is a choice.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Primary Impact on Pyrolysis | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Determines product distribution. | Low (300-500°C) = Char; Medium (500-700°C) = Oil; High (>700°C) = Gas. |
| Heating Rate | Differentiates slow vs. fast pyrolysis. | Slow = More Char; Fast = More Bio-oil. |
| Feedstock Composition | Sets the baseline for potential yields. | High Lignin = More Char; High Cellulose = More Oil (with fast pyrolysis). |
| Residence Time | Controls secondary reactions of vapors. | Short time = Preserves Bio-oil; Long time = Increases Gas yield. |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
The right laboratory equipment is essential for researching and perfecting the factors that control pyrolysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and analytical systems designed for precise control over temperature, heating rate, and residence time.
We provide the reliable tools you need to:
- Accurately test different feedstocks and process conditions.
- Scale up your findings from lab to pilot plant.
- Achieve consistent, high-quality yields of bio-char, bio-oil, or syngas.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can help you master your pyrolysis research and development.
Get in Touch for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















