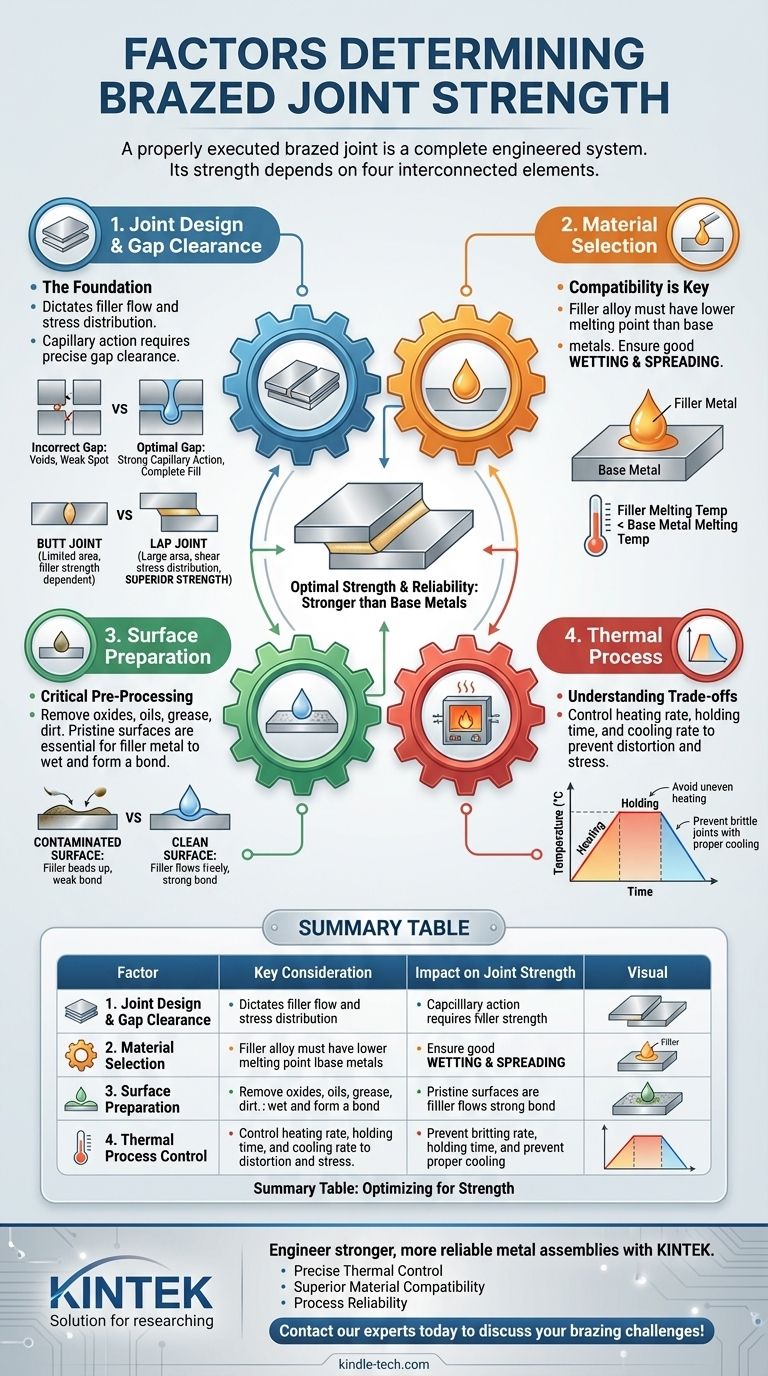
The strength of a brazed joint is not determined by a single factor, but by the precise execution of an entire system. While a correctly brazed joint can and should be stronger than the metals being joined, this strength is the outcome of carefully controlling four interconnected elements: the physical design of the joint, the selection of materials, the cleanliness of the surfaces, and the thermal process used for heating and cooling.
A properly executed brazed joint is a complete engineered system. Its strength often exceeds that of the base materials, but this outcome is only possible when joint design, material compatibility, surface preparation, and thermal processing are managed as an interconnected whole.

The Foundation: Joint Design and Gap Clearance
The physical geometry of the joint is the first and most critical factor. It dictates how the filler metal will flow and how stress will be distributed across the bond.
The Principle of Capillary Action
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the tight space between the two base materials. The strength of this action is directly controlled by the distance between the surfaces, known as the gap clearance.
An incorrect gap will prevent the filler metal from completely filling the joint, creating voids and weak spots that are destined to fail under load.
Defining the Optimal Gap
Achieving the correct gap requires precise mechanical processing. The ideal dimension is not a single number but depends on the filler metal, base materials, and the length of the overlap.
This gap must be small enough to promote strong capillary action but large enough to allow the filler metal and flux (if used) to flow freely throughout the entire joint area.
Lap Joints vs. Butt Joints
For maximum strength, a lap joint is far superior to a butt joint. A butt joint's strength is limited by the strength of the filler metal itself and the small bonding area.
A lap joint, however, creates a much larger surface area for the bond. By overlapping the parts, the load is transferred as shear stress across this larger area, resulting in a joint that is significantly stronger and more durable.
Material Selection: Base Metals and Filler
The chemical and metallurgical compatibility between the base metals and the filler metal is fundamental to forming a strong bond.
Compatibility is Key
The brazing filler alloy must have a melting temperature significantly lower than that of the base metals being joined. This ensures that the base materials retain their structural integrity and are not melted or distorted during the heating process.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The primary job of the filler metal is to melt at its specified temperature, then wet and spread evenly across the joint surfaces. Good "wetting" indicates a strong molecular attraction between the molten filler and the solid base metal, which is essential for a continuous, void-free bond.
Critical Pre-Processing: Surface Preparation
No amount of process control can compensate for a contaminated surface. The cleanliness of the joint surfaces directly impacts the filler metal's ability to wet the material and form a strong metallurgical bond.
Removing Oxides and Contaminants
All surfaces must be completely clean and free of oils, greases, dirt, and oxide films. Metal oxides, which form naturally on surfaces like aluminum, are a primary barrier to wetting and must be removed chemically (e.g., with an alkali solution) or mechanically.
The Goal: A Pristine Surface
The objective is to create a surface that is chemically receptive to the molten filler metal. Without this pristine condition, the filler will bead up rather than flow, resulting in an incomplete and catastrophically weak joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Control
Even with perfect design and preparation, the final strength is determined by the control of the thermal cycle.
The Gap Dilemma: Too Wide vs. Too Narrow
A gap that is too wide will disrupt capillary action, leading to large voids and insufficient filler distribution. A gap that is too narrow can prevent the filler from penetrating the joint at all, starving the bond. This is a critical parameter that must be optimized.
Thermal Control Issues: Heating and Cooling
The heating rate, holding time, and cooling rate are crucial variables. Heating too quickly or unevenly can cause thermal stress and part distortion. Holding at temperature for too long can damage the base metals. Cooling too rapidly can introduce residual stresses, making the joint brittle.
Process Optimization
Factors like the specific aluminum alloy, vacuum level (in vacuum brazing), and filler brand all influence the ideal thermal profile. There is no universal setting; these parameters must be optimized through experimentation to find the best combination for your specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final approach should be guided by your primary goal. The principles of brazing are constant, but your focus may shift depending on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and reliability: Prioritize a lap joint design with a large overlap and invest heavily in processes that guarantee a perfectly clean surface and a precisely controlled gap.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Concentrate on creating a highly repeatable process for surface preparation and automate the thermal cycle to ensure consistency from part to part.
- If you are troubleshooting joint failures: Begin your investigation with the two most common culprits—improper joint gap and inadequate surface cleanliness—before moving on to thermal process parameters.
By systematically controlling these factors, you move from simply joining metals to engineering a bond that is stronger than the parts themselves.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Impact on Joint Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Design & Gap | Optimal gap clearance for capillary action; use of lap joints over butt joints. | Determines filler metal flow and stress distribution. Incorrect gap creates weak spots. |
| Material Selection | Filler metal must have a lower melting point and be compatible with the base metals. | Ensures proper wetting and a continuous, void-free metallurgical bond. |
| Surface Preparation | Complete removal of oils, grease, dirt, and oxide films. | Critical for filler metal to wet and spread evenly. Contamination causes beading and failure. |
| Thermal Process Control | Precise control of heating rate, hold time, and cooling rate. | Prevents part distortion, base metal damage, and brittle joints from residual stress. |
Engineer stronger, more reliable metal assemblies with KINTEK.
Whether your priority is maximum joint strength, high-volume production consistency, or troubleshooting existing failures, the right equipment and consumables are critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing and material joining applications.
Our expertise can help you optimize the four key factors for a perfect braze:
- Precise Thermal Control: Achieve the exact heating and cooling profiles your specific materials require.
- Superior Material Compatibility: Access the right filler metals and fluxes for your base materials.
- Process Reliability: Ensure repeatable results batch after batch.
Let's strengthen your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your brazing challenges and goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease



















