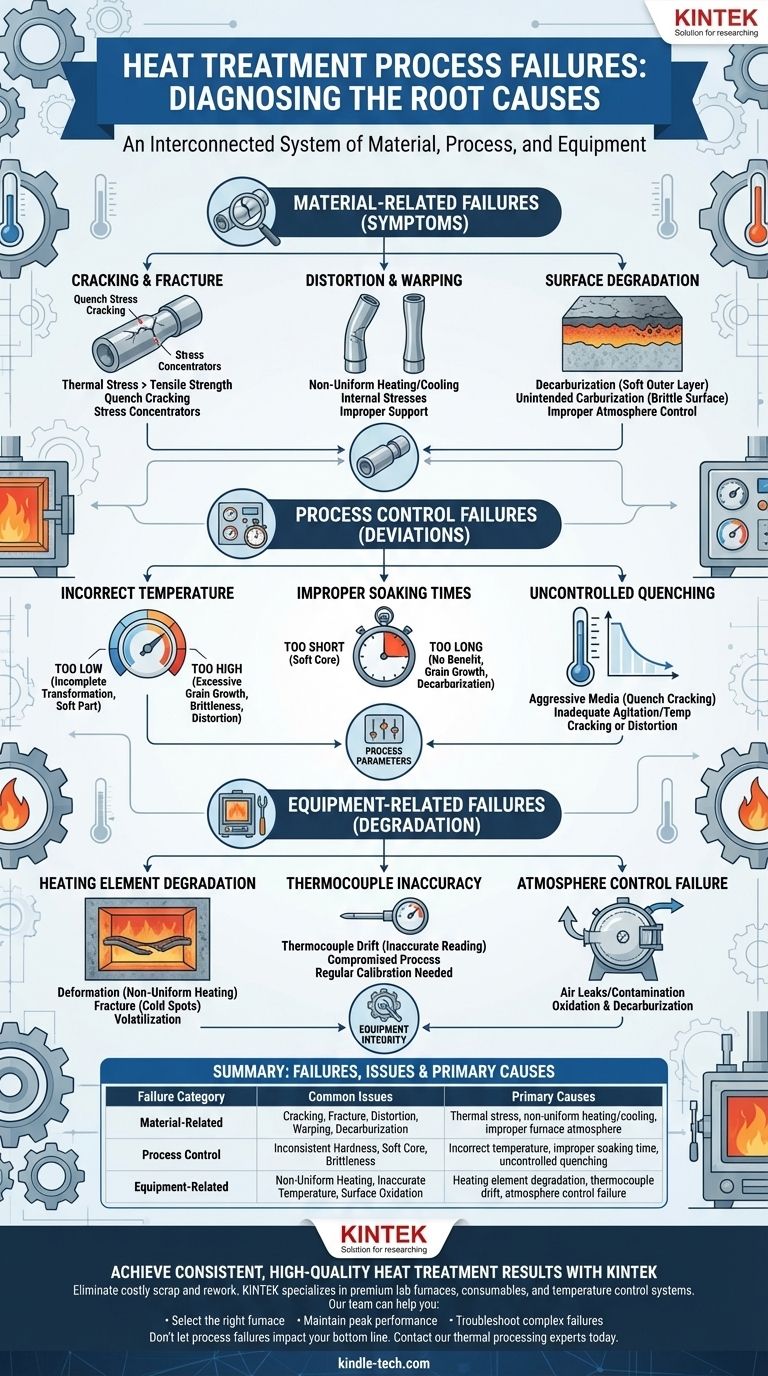
At its core, heat treatment failure manifests in three primary ways: dimensional inaccuracy (distortion and warping), surface degradation (like decarburization), and mechanical failure (cracking or fracture). These issues are rarely caused by a single error, but rather by a breakdown in the precise control of temperature, time, and cooling rates, often compounded by equipment degradation or improper material handling.
The central takeaway is that heat treatment failures are not random events. They are symptoms of an underlying deviation in the process, the material, or the equipment, and successful troubleshooting requires a systematic understanding of how these three elements interact.

Diagnosing Material-Related Failures
The most visible failures are those observed in the finished part. These are the direct result of thermal stresses and metallurgical transformations gone wrong.
Cracking and Fracture
This is the most catastrophic failure mode. Cracks typically form when thermal stresses exceed the material's tensile strength at a specific temperature.
Quench cracking is the most common type, occurring during rapid cooling when different sections of a part contract at different rates, creating immense internal stress.
Sharp internal corners, tool marks, and sudden changes in cross-section act as stress concentrators, providing an initiation point for these cracks to form.
Distortion and Warping
Distortion is a change in the size or shape of a part compared to its original dimensions. This is an extremely common and costly issue.
It is primarily caused by the relief of internal stresses locked in from prior manufacturing steps or by non-uniform heating and cooling. If one side of a part cools faster than the other, it will inevitably warp.
Properly supporting long or thin parts within the furnace is critical to preventing sagging and distortion at high temperatures.
Surface Degradation
These failures affect the properties of the material's surface, which is often the most critical working area.
Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface of steel. This creates a soft outer layer, reducing wear resistance and fatigue life, even if the core is perfectly hardened.
The opposite, unintended carburization, can make the surface excessively brittle and prone to chipping. Both are caused by improper furnace atmosphere control.
Identifying Process Control Failures
Behind every material failure is a process deviation. Gaining control over the core process parameters is the key to repeatable success.
Incorrect Temperature Control
Temperature is the single most important variable. Using a temperature that is too low results in an incomplete metallurgical transformation and a part that fails to achieve the desired hardness.
Conversely, temperatures that are too high can cause excessive grain growth, leading to brittleness. It can also increase the risk of distortion and surface degradation.
Improper Soaking Times
Soaking is the period during which the part is held at the target temperature. It must be long enough for the entire cross-section to reach a uniform temperature and for the necessary phase transformations to complete.
A soak time that is too short will result in a soft core. A soak time that is excessively long provides no metallurgical benefit and can worsen grain growth and decarburization.
Uncontrolled Quenching
The rate of cooling, or quenching, is just as critical as the rate of heating. The goal is to cool the part quickly enough to achieve the desired hardness but not so quickly that it cracks or distorts.
Using a quench medium that is too aggressive (e.g., water instead of oil) for a given steel grade is a classic cause of quench cracking. Agitation and temperature of the quench bath also play a critical role.
Understanding Equipment-Related Failures
Your process control is only as good as the equipment executing it. Gradual degradation can introduce process deviations that are difficult to diagnose.
Heating Element Degradation
As noted in vacuum furnaces and other electric furnaces, heating elements are consumable components that fail over time.
These failures include high-temperature deformation (sagging), which leads to non-uniform heating, fracture, which creates cold spots in the furnace, and volatilization, where the element material slowly evaporates, reducing its effectiveness.
Such degradation directly causes the non-uniform heating that leads to distortion and inconsistent hardness across a part or batch.
Thermocouple Inaccuracy
The thermocouple is the furnace's thermometer. If it provides an inaccurate reading, your entire process is compromised.
Thermocouple drift occurs over time, where the device slowly loses accuracy. A furnace controller might "think" it is at the correct temperature when it is actually 20 degrees off, leading to failed batches. Regular calibration is essential.
Atmosphere Control Failure
For processes requiring a specific environment (e.g., vacuum, nitrogen, argon), any leak or contamination is a process failure.
Air leaks into a vacuum furnace or an inert atmosphere will cause oxidation and decarburization, ruining the surface properties of the parts being treated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Preventing heat treatment failures requires a holistic approach that balances performance requirements with process reality.
- If your primary focus is maximizing part performance: Prioritize precise control over temperature, time, and atmosphere, and always verify final properties with hardness testing and metallurgical analysis.
- If your primary focus is reducing scrap and rework: Emphasize process consistency through rigorous equipment maintenance, regular thermocouple calibration, and standardized part loading procedures.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an existing failure: Begin with a thorough review of the process data (time/temperature charts) and a visual inspection of the part for tell-tale signs like crack location or distortion patterns.
Ultimately, achieving consistent and reliable heat treatment outcomes comes from treating the process as an interconnected system.
Summary Table:
| Failure Category | Common Issues | Primary Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Material-Related | Cracking, Fracture, Distortion, Warping, Decarburization | Thermal stress, non-uniform heating/cooling, improper furnace atmosphere |
| Process Control | Inconsistent Hardness, Soft Core, Brittleness | Incorrect temperature, improper soaking time, uncontrolled quenching |
| Equipment-Related | Non-Uniform Heating, Inaccurate Temperature, Surface Oxidation | Heating element degradation, thermocouple drift, atmosphere control failure |
Achieve consistent, high-quality heat treatment results with KINTEK.
Eliminate costly scrap and rework by ensuring your process is built on a foundation of reliable equipment and expert support. KINTEK specializes in premium lab furnaces, consumables, and temperature control systems designed for precision and durability.
Our team can help you:
- Select the right furnace for your specific material and process requirements.
- Maintain peak equipment performance with genuine parts and expert service.
- Troubleshoot complex failures and optimize your process parameters.
Don't let process failures impact your bottom line. Contact our thermal processing experts today for a consultation and see how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space



















