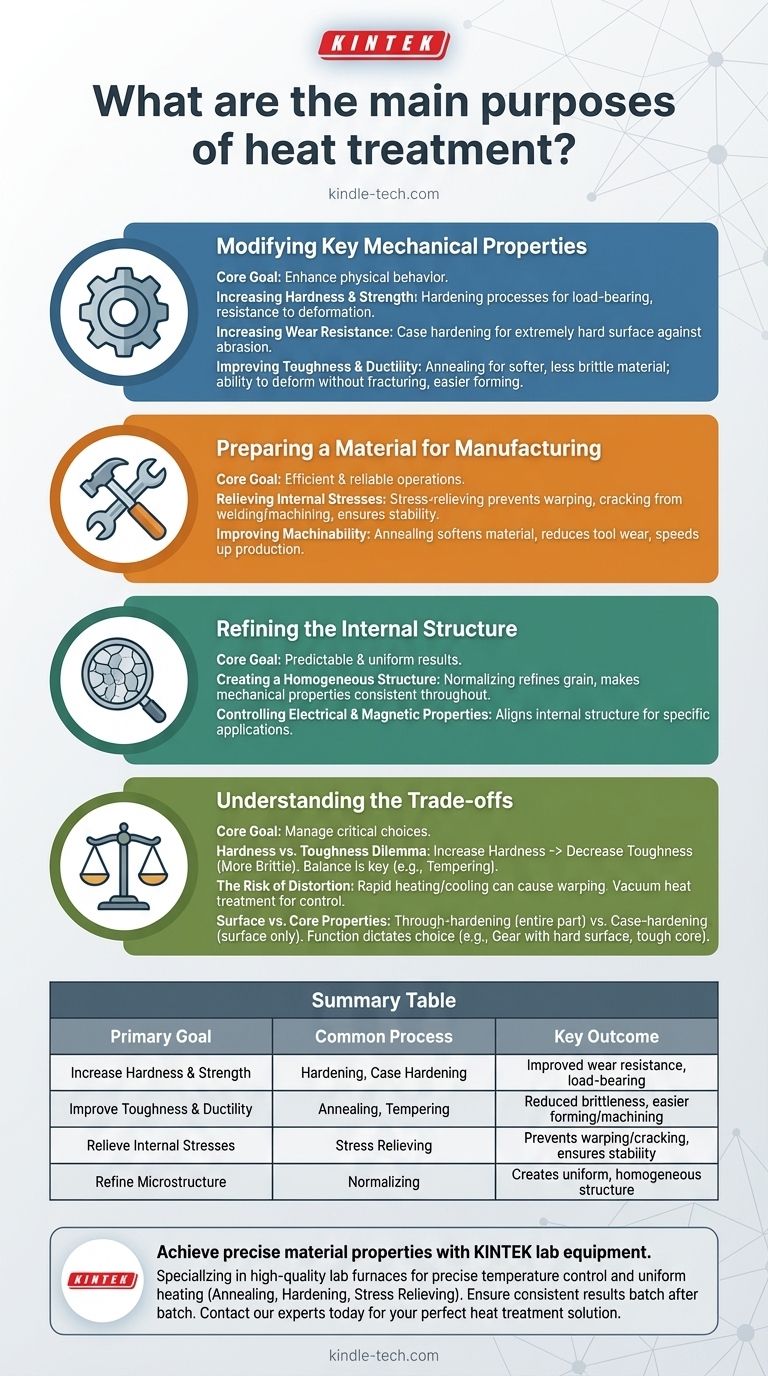
At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling a material—most often a metal like steel—to deliberately alter its internal structure. The primary purposes are to enhance specific mechanical properties, prepare the material for further manufacturing, and refine its microstructure for superior and more consistent performance. This allows a single base material to be precisely tailored for a vast range of demanding applications.
Heat treatment is not merely a finishing step; it is a fundamental engineering tool used to unlock a material's full potential, transforming its raw properties into the specific characteristics required for its intended function.

Modifying Key Mechanical Properties
The most common reason for heat treatment is to change a material's physical and mechanical behavior to meet the demands of a specific application.
Increasing Hardness and Strength
Hardening processes are used to make a material stronger and more resistant to deformation under load. This is critical for components that must bear significant weight or stress.
A related goal is increasing wear resistance. By creating an extremely hard surface through processes like case hardening, a component can better withstand abrasion, friction, and impact.
Improving Toughness and Ductility
Conversely, some heat treatments are designed to make a material softer and less brittle. This property, known as toughness, is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
Processes like annealing increase ductility, making the material easier to bend, stretch, or form into complex shapes without cracking.
Preparing a Material for Manufacturing
Heat treatment is a critical intermediate step that can make subsequent manufacturing operations more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses into a material. If left unaddressed, these stresses can cause a part to warp, distort, or even crack over time.
A stress-relieving heat treatment gently heats the part and allows it to cool slowly, relaxing these internal stresses and ensuring dimensional stability.
Improving Machinability
A material that is too hard can be difficult, slow, and expensive to machine. Annealing can soften the material, making it easier to cut, drill, or mill, which reduces tool wear and speeds up production.
Refining the Material's Internal Structure
At a microscopic level, heat treatment manipulates the crystal or "grain" structure of the metal to achieve highly predictable and uniform results.
Creating a Homogeneous Structure
Processes like normalizing are used to refine the grain structure of a material, making it more uniform, or homogeneous.
A homogeneous structure ensures that the mechanical properties—like strength and toughness—are consistent throughout the entire part, eliminating weak spots and improving overall reliability.
Controlling Electrical and Magnetic Properties
For specialized applications, heat treatment can also be used to enhance a material's electrical conductivity or magnetic properties by aligning its internal structure in a specific way.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful process, but it involves critical trade-offs that must be managed to achieve the desired outcome.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
One of the most fundamental trade-offs in metallurgy is that between hardness and toughness. As you increase a material's hardness, you typically decrease its toughness, making it more brittle and prone to shattering.
Successful heat treatment often involves finding the precise balance, such as in tempering, where a fully hardened part is slightly softened to regain a necessary level of toughness.
The Risk of Distortion
The rapid heating and cooling cycles inherent to heat treatment can cause complex parts to warp or distort. This risk is especially high in parts with intricate geometries or varying thicknesses.
Modern methods like vacuum heat treatment offer superior control over heating and cooling rates, which significantly minimizes distortion and ensures dimensional accuracy.
Surface vs. Core Properties
It is critical to distinguish between treatments that affect the entire part (through-hardening) and those that only modify the surface (case-hardening). The choice depends entirely on the part's function. A gear, for example, needs a very hard surface to resist wear, but a tougher, more flexible core to handle torque without fracturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process is essential for achieving your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: Use hardening and tempering or a case-hardening process to create a durable, load-bearing surface.
- If your primary focus is ease of manufacturing and forming: Use an annealing process to soften the material, increase ductility, and prepare it for stamping, bending, or machining.
- If your primary focus is component stability and reliability: Use normalizing or stress-relieving cycles to homogenize the internal structure and remove residual stresses from prior operations.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as a strategic design choice allows you to engineer materials for performance that would otherwise be impossible.
Summary Table:
| Primary Goal | Common Heat Treatment Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Strength | Hardening, Case Hardening | Improved wear resistance and load-bearing capacity |
| Improve Toughness & Ductility | Annealing, Tempering | Reduced brittleness, easier forming and machining |
| Relieve Internal Stresses | Stress Relieving | Prevents warping and cracking, ensures dimensional stability |
| Refine Microstructure | Normalizing | Creates a uniform, homogeneous structure for consistent properties |
Achieve precise material properties with the right lab equipment.
The correct heat treatment process is fundamental to your material's performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables that provide the precise temperature control and uniform heating required for reliable heat treatment cycles—from annealing and hardening to stress relieving.
Whether you are in R&D, quality control, or manufacturing, our equipment helps you eliminate weak spots, prevent distortion, and ensure consistent results batch after batch.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment solution for your laboratory's specific needs and unlock your material's full potential.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components



















