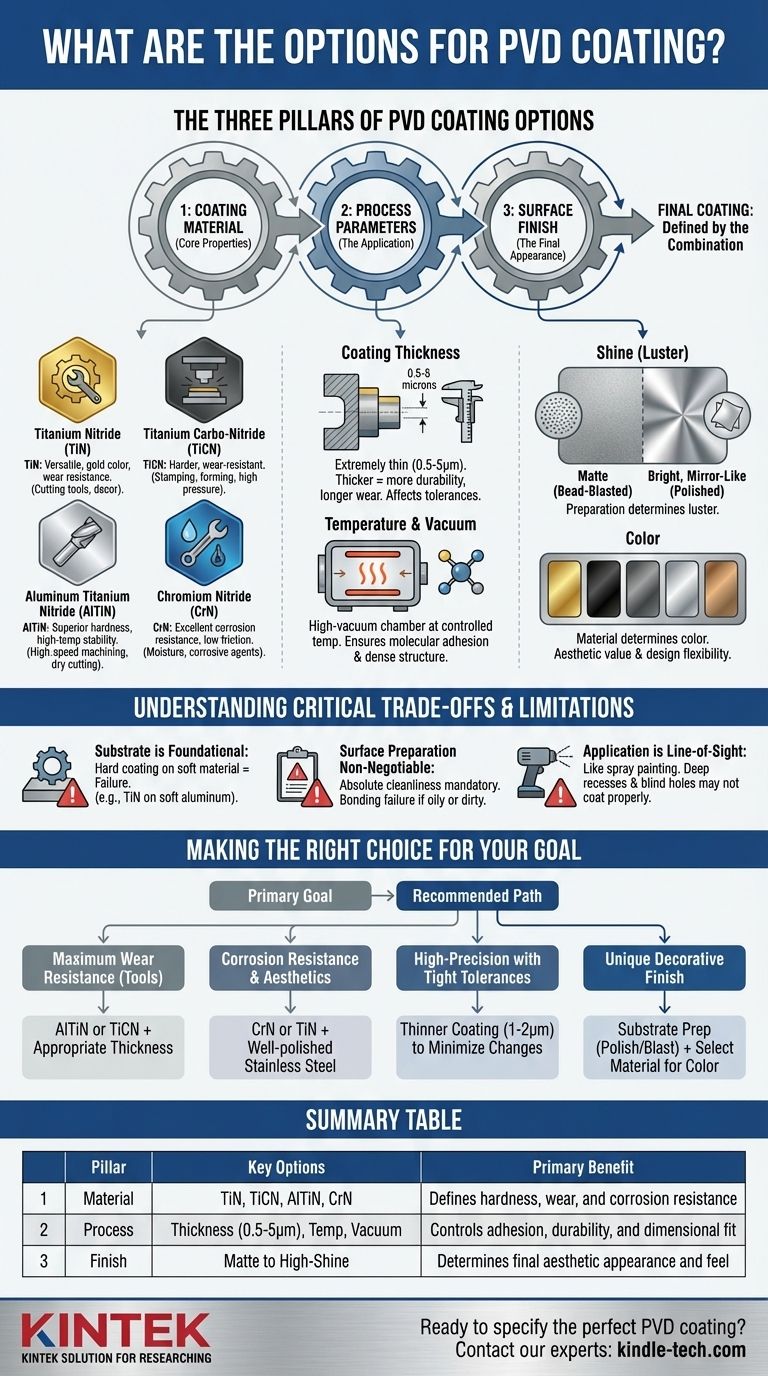
The primary options for PVD coating are best understood not as a simple list, but as a combination of three key variables: the coating material itself, the process parameters used to apply it, and the final surface finish. The material dictates the coating's core properties like hardness and corrosion resistance, while the process parameters control its thickness and adhesion. The final finish determines the aesthetic look and feel, from a matte texture to a high-shine metallic gloss.
Choosing the right PVD coating is not about selecting from a catalog. It's an engineering decision that requires you to first define your primary goal—be it durability, corrosion resistance, or aesthetics—and then specify the combination of material, process, and finish that achieves it.
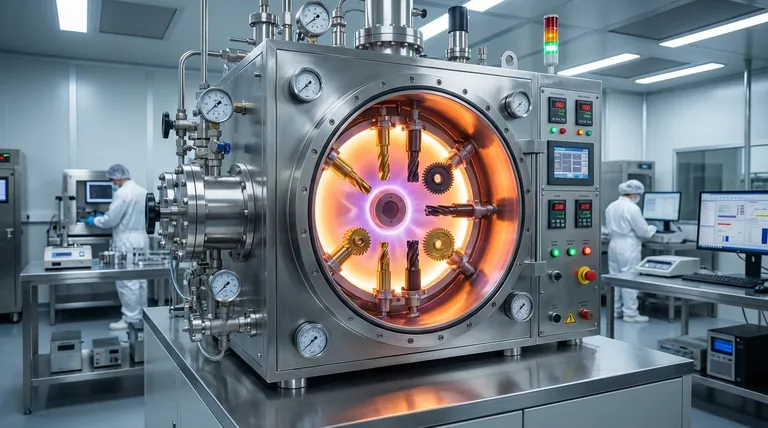

The Three Pillars of PVD Coating Options
To understand your choices, it's helpful to break them down into three fundamental pillars. The final coating on your product is a direct result of the decisions made within each of these categories.
Pillar 1: Coating Material (The Core Properties)
The material deposited onto the substrate determines the fundamental performance characteristics of the coating. While many variations exist, most fall into a few common families.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): This is a versatile, general-purpose coating known for its gold color, good hardness, and excellent wear resistance. It's often used on cutting tools and for decorative finishes.
- Titanium Carbo-Nitride (TiCN): Harder and more wear-resistant than TiN, TiCN is ideal for cutting, stamping, and forming applications where extreme pressure and friction are present.
- Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN): This family of coatings offers superior hardness and high-temperature stability, making it a top choice for high-speed machining and dry cutting applications.
- Chromium Nitride (CrN): With excellent corrosion resistance, low friction, and good adhesion, CrN is often used in environments where parts are exposed to moisture or corrosive agents. It's also less prone to sticking with certain materials.
Pillar 2: Process Parameters (The Application)
How the material is applied is just as critical as the material itself. These parameters are controlled during the coating process.
- Coating Thickness: PVD coatings are extremely thin, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns. A thicker coating generally provides more durability and a longer wear life, but it can also affect the final dimensions and tolerances of the part.
- Temperature and Vacuum: The process occurs in a high-vacuum chamber at a controlled temperature. These factors are critical for ensuring strong molecular-level adhesion and creating a dense, uniform coating structure.
Pillar 3: Surface Finish (The Final Appearance)
The final look of the part is a combination of the coating itself and the preparation of the substrate before coating.
- Shine (Luster): A part that is bead-blasted before coating will have a satin or matte finish. A part that is highly polished before coating will result in a bright, mirror-like finish.
- Color: The coating material itself determines the color palette. TiN produces gold tones, while other materials can create shades of black, gray, silver, and bronze. This provides significant aesthetic value and design flexibility.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs and Limitations
PVD is a powerful technology, but it is not a "magic bullet." Understanding its inherent limitations is crucial for successful implementation.
The Substrate is Foundational
The properties of the PVD coating are heavily influenced by the material it is applied to, known as the substrate. A hard coating on a soft substrate is like putting a layer of glass on a sponge—the coating will crack and fail under pressure because the underlying material cannot support it.
For example, a TiN coating significantly increases the endurance of a strong titanium alloy, but it would provide little functional benefit if applied to a soft aluminum.
Surface Preparation is Non-Negotiable
The PVD process relies on molecular bonding. Any oil, residue, or oxidation on the surface will prevent the coating from adhering properly, leading to flaking, poor performance, and cosmetic defects.
Absolute surface cleanliness and proper pretreatment are mandatory for a successful outcome.
Application is Line-of-Sight
Think of the PVD process like spray painting. The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the part. This means that deep recesses, internal channels, and blind holes will not be coated uniformly, if at all.
Designs must account for this line-of-sight nature. Tightly sealed tapped holes, for instance, can trap air and ruin the coating in that area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct PVD option, start by defining your most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance for tools: Choose a hard material like AlTiN or TiCN and specify a thickness appropriate for the tool's intended use.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and aesthetics: A CrN or TiN coating on a well-polished stainless steel part is an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components with tight tolerances: Opt for a thinner coating (e.g., 1-2 microns) to minimize dimensional changes and ensure all critical features remain within spec.
- If your primary focus is a unique decorative finish: Concentrate on the substrate preparation (polishing vs. blasting) to achieve the desired luster, then select a material based on your color preference.
By aligning your primary objective with the right combination of material, process, and finish, you can leverage PVD coating as a precise and powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Pillar | Key Options | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | TiN, TiCN, AlTiN, CrN | Defines hardness, wear, and corrosion resistance |
| Process | Thickness (0.5-5µm), Temperature, Vacuum | Controls adhesion, durability, and dimensional fit |
| Finish | Matte (bead-blasted) to High-Shine (polished) | Determines final aesthetic appearance and feel |
Ready to specify the perfect PVD coating for your application?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Whether you are developing cutting tools, medical devices, or high-end consumer products, our expertise ensures you select the optimal combination of material, process, and finish to achieve superior performance and aesthetics.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your product's durability, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















