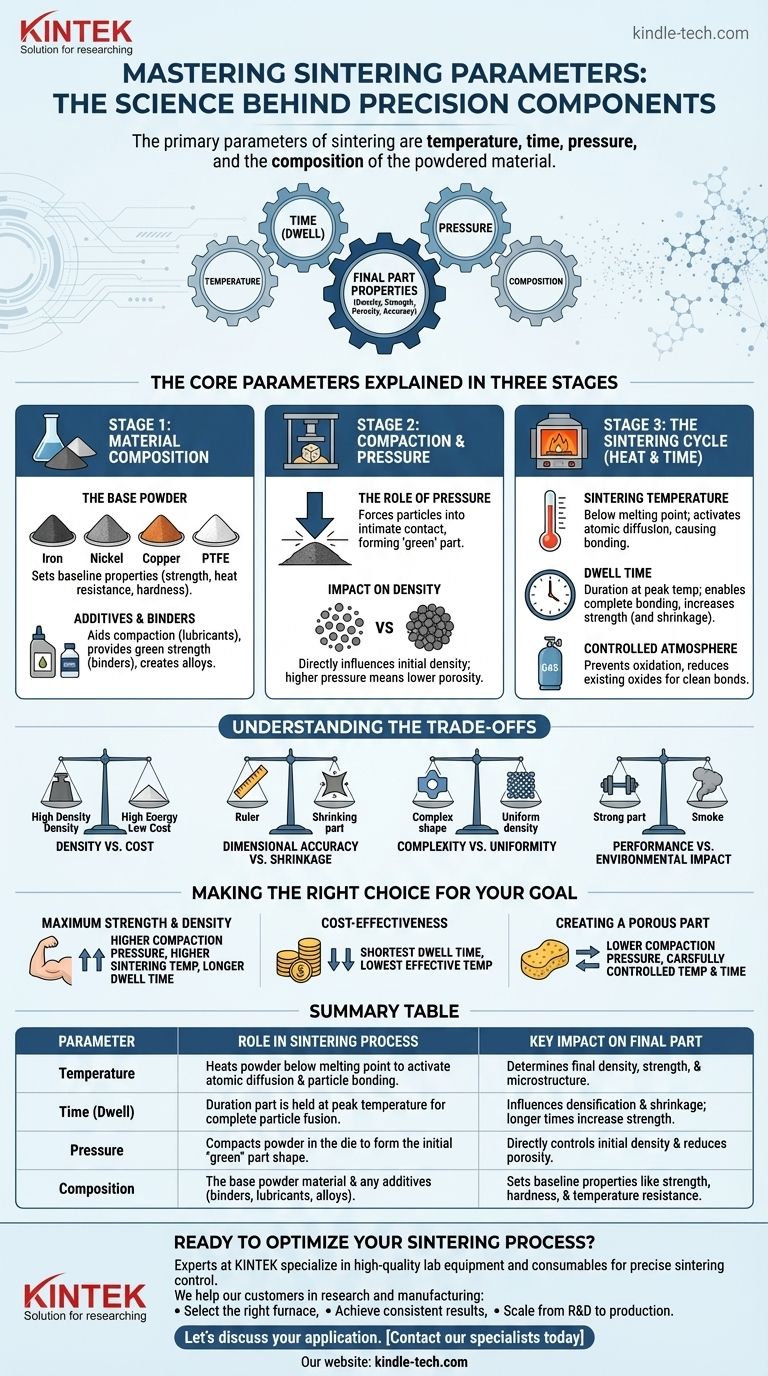
The primary parameters of sintering are temperature, time, pressure, and the composition of the powdered material. These four variables are highly interdependent and must be precisely controlled. Together, they dictate the final density, porosity, strength, and dimensional accuracy of the finished part by governing how individual powder particles bond and fuse into a solid mass.
Sintering is far more than just heating a compressed powder. It is a sophisticated engineering process where the careful manipulation of its core parameters—temperature, time, pressure, and composition—is used to deliberately design the final microstructure and performance characteristics of a component.
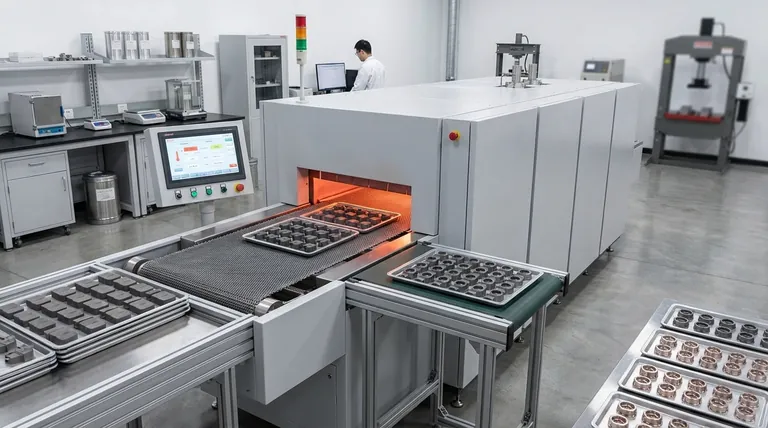

The Core Sintering Parameters Explained
To understand how each parameter functions, it's best to view them within the context of the three primary stages of the sintering process. Each stage has a dominant parameter that shapes the outcome.
Stage 1: Material Composition
The process begins before any heat or pressure is applied. The choice of materials is the foundational parameter that determines the potential properties of the final product.
The Base Powder
The selection of the primary metal or ceramic powder (such as iron, nickel, copper, or PTFE) sets the baseline for characteristics like strength, temperature resistance, and hardness.
Additives and Binders
Lubricants are often mixed in to aid in the compaction stage, while binders provide initial "green strength" to the un-sintered part. Reinforcing agents or other elements can be added to create specific alloys or enhance properties.
Stage 2: Compaction and Pressure
Once the powder is blended, it is formed into its desired shape, typically by being pressed into a die. This is where pressure becomes the critical variable.
The Role of Pressure
High pressure is used to compact the powder, forcing the particles into intimate contact. This action forms the initial shape, known as a "green" part.
Impact on Density
The amount of pressure applied directly influences the initial density of the green part. Higher pressure reduces the space (porosity) between particles, which leads to a denser and stronger final product after heating.
Stage 3: The Sintering Cycle (Heat and Time)
The green part is placed in a furnace for the final, transformative stage. Here, temperature and time work in concert to fuse the particles into a unified whole.
Sintering Temperature
The part is heated in a controlled atmosphere to a temperature just below the melting point of the primary material. This thermal energy activates atomic diffusion, causing the boundaries between individual particles to blur and bond together.
Dwell Time
This is the duration the part is held at the peak sintering temperature. A longer dwell time allows for more complete particle bonding and densification, which typically increases strength but can also increase shrinkage.
Controlled Atmosphere
The atmosphere within the furnace is a subtle but critical parameter. It is carefully controlled (e.g., using inert gases) to prevent oxidation of the metal powder and to help reduce any existing oxides, ensuring clean, strong bonds between particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing sintering parameters is always a balancing act. Achieving a desired property often involves a compromise with another.
Density vs. Cost
Higher temperatures and longer dwell times produce stronger, denser parts. However, they also consume more energy and reduce furnace throughput, increasing the cost per part.
Dimensional Accuracy vs. Shrinkage
As particles fuse and pores are eliminated, the part naturally shrinks. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial die design. Aggressive sintering cycles that maximize density can make controlling this shrinkage more challenging.
Complexity vs. Uniformity
Complex part geometries can lead to non-uniform density during the compaction stage. Areas with lower initial density may not sinter as effectively, creating potential weak points in the final component.
Performance vs. Environmental Impact
The high temperatures involved in sintering can release emissions. As a result, manufacturers must adhere to strict environmental regulations, which can influence process choices and production rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal parameters are entirely dependent on the application of the final part. You must adjust your approach based on the most critical performance requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Utilize higher compaction pressures, higher sintering temperatures, and longer dwell times to minimize porosity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for high-volume parts: Optimize for the shortest possible dwell time and the lowest effective temperature that still meets the minimum performance specifications.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous part (e.g., for filters or self-lubricating bearings): Use lower compaction pressures and carefully control the temperature and time to create strong bonds between particles while preserving the desired level of porosity.
Mastering these parameters transforms a simple powder into a precisely engineered component designed for its specific task.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Sintering Process | Key Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Heats powder below melting point to activate atomic diffusion and particle bonding. | Determines final density, strength, and microstructure. |
| Time (Dwell) | Duration part is held at peak temperature for complete particle fusion. | Influences densification and shrinkage; longer times increase strength. |
| Pressure | Compacts powder in the die to form the initial "green" part shape. | Directly controls initial density and reduces porosity. |
| Composition | The base powder material and any additives (binders, lubricants, alloys). | Sets baseline properties like strength, hardness, and temperature resistance. |
Ready to Optimize Your Sintering Process?
Choosing the right parameters is critical for achieving the desired density, strength, and dimensional accuracy in your sintered components. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise sintering control.
We help our customers in research and manufacturing:
- Select the right furnace for controlled temperature and atmosphere sintering.
- Achieve consistent results with reliable equipment and expert support.
- Scale from R&D to production with solutions tailored to your specific material and performance goals.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our sintering specialists today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in Li2MnSiO4 synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Battery Materials
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes
- Why is precise temperature control in a sintering furnace critical for NASICON electrolytes? Ensure Material Purity



















