At its core, a crucible furnace is built around two primary components: the crucible, which is the high-temperature pot that holds the material, and the heating system that melts it. A complete, functional furnace integrates these parts within an insulated body and includes a temperature control system and a lid to ensure efficiency, safety, and precise operation.
While a furnace can seem complex, its design serves one purpose: to safely contain and melt a material by applying intense, controlled heat. Every component is there to support, control, or insulate this core function of heating the crucible.
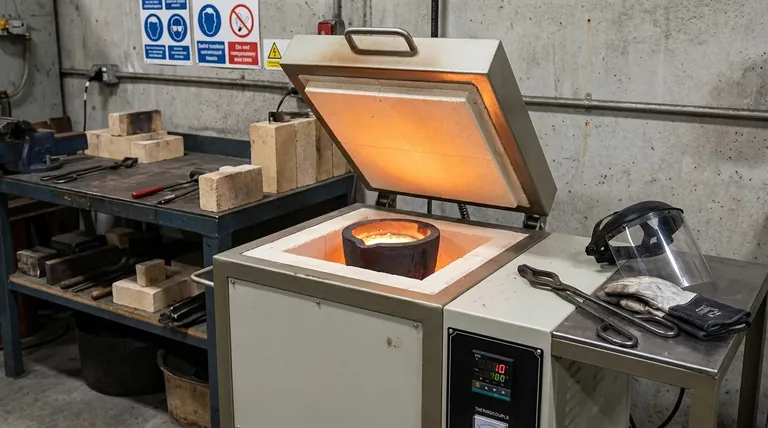

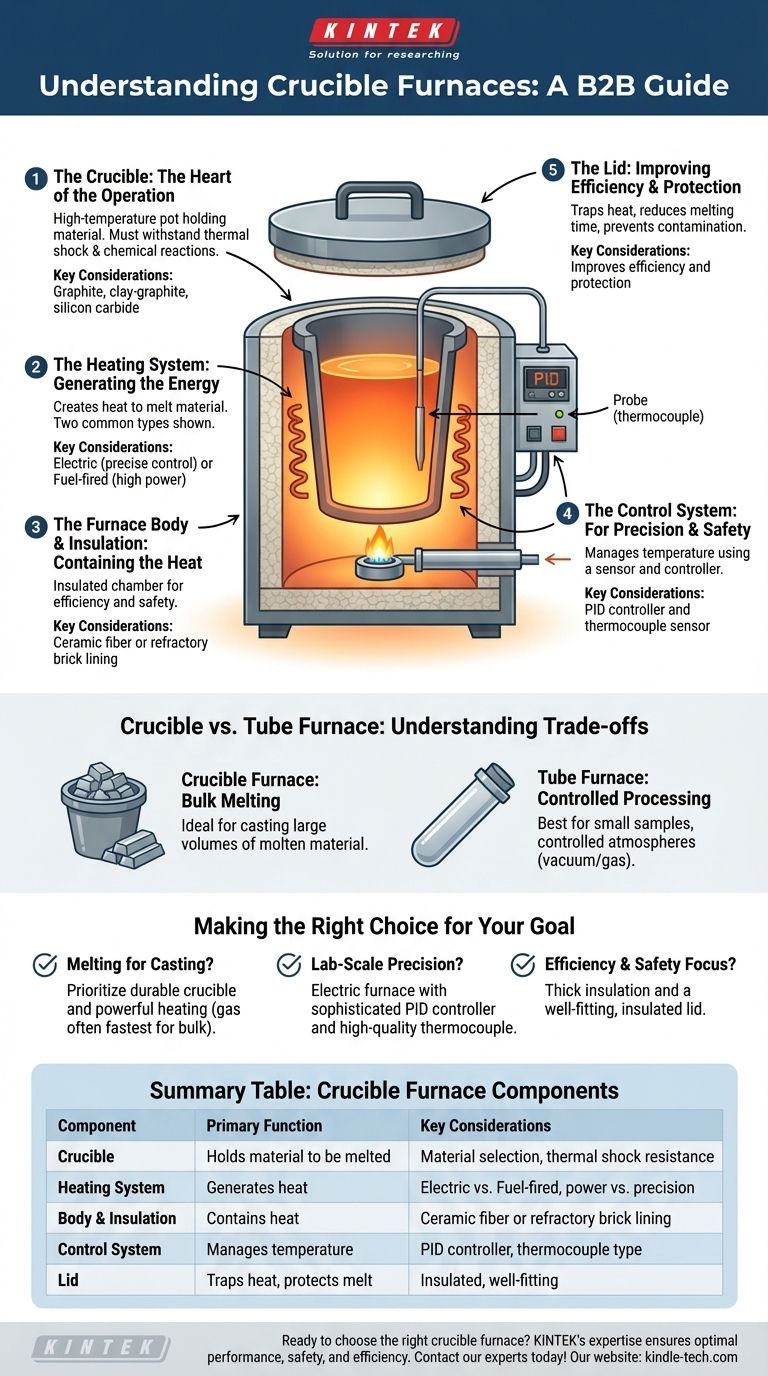
Deconstructing the Crucible Furnace: Key Components
To truly understand how a crucible furnace works, it's best to break it down by the role each part plays in the melting process.
The Crucible: The Heart of the Operation
The crucible is the removable container that directly holds the metal or material you intend to melt. Its composition is critical.
It must withstand extreme thermal shock and resist chemical reactions with the molten material. Common materials include graphite, clay-graphite, and silicon carbide.
The Heating System: Generating the Energy
This system creates the heat needed to achieve melting temperatures. There are two common types.
Electric furnaces use resistance coils that glow hot when electricity passes through them, providing clean and highly controllable heat. Fuel-fired furnaces burn propane, natural gas, or oil to generate a powerful flame that heats the chamber.
The Furnace Body and Insulation: Containing the Heat
The body provides the structure for the furnace and, most importantly, houses the insulation. This is typically a chamber lined with lightweight ceramic fiber blankets or dense refractory bricks.
Proper insulation is crucial for two reasons: it directs the maximum amount of heat toward the crucible for energy efficiency, and it keeps the outer shell of thefurnace at a safer temperature.
The Control System: For Precision and Safety
Modern furnaces rely on a control system to manage the temperature. This consists of two main parts.
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor that extends into the heating chamber. It sends data to a PID controller, which acts as the furnace's brain, turning the heating element on and off to precisely maintain your desired temperature.
The Lid: Improving Efficiency and Protection
A simple but vital component, the lid covers the top of the furnace. It traps heat that would otherwise escape, significantly reducing melting times and fuel or electricity consumption.
The lid also prevents oxygen from excessively reacting with the melt and stops debris or contaminants from falling into your material.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Crucible vs. Other Furnace Types
The components of a crucible furnace are specifically chosen for melting bulk materials. Understanding how it differs from other designs, like a tube furnace, clarifies its purpose.
The Crucible Furnace Advantage: Bulk Melting
Crucible furnaces are designed to melt a quantity of material in an open-top pot. This makes them the standard choice for applications like metal casting, where a volume of molten metal needs to be prepared and then poured into a mold.
The Tube Furnace Advantage: Controlled Processing
A tube furnace, by contrast, heats materials inside a long, sealed horizontal or vertical tube (often made of quartz or alumina).
Their design is not for bulk melting and pouring. Instead, they excel at processing small samples in a tightly controlled atmosphere, often under a vacuum or surrounded by a specific gas. This is common in laboratory research, material synthesis, and annealing processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace configuration depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for casting: Prioritize a durable crucible (silicon carbide is excellent for longevity) and a powerful heating system, with gas often providing the fastest melts for larger volumes.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale precision or working with precious metals: An electric furnace with a sophisticated PID controller and a high-quality thermocouple is essential for its precise temperature management and clean operation.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and safety: Look for a furnace with thick, high-density ceramic fiber insulation and a well-fitting, insulated lid to minimize heat loss and reduce external temperatures.
Understanding these components transforms the furnace from a simple heat source into a precise and controllable tool for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible | Holds the material to be melted | Material (graphite, clay-graphite, silicon carbide); must withstand thermal shock |
| Heating System | Generates heat to melt the material | Electric (precise control) or Fuel-fired (high power) |
| Body & Insulation | Contains heat for efficiency and safety | Ceramic fiber or refractory brick lining |
| Control System | Manages temperature precisely | PID controller and thermocouple sensor |
| Lid | Traps heat and protects the melt | Improves efficiency and prevents contamination |
Ready to choose the right crucible furnace for your application? Whether you're in metal casting, precious metal work, or R&D, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a furnace configured for optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific melting needs and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















