At its core, the copper sulfate reference electrode is characterized by its exceptional stability, ruggedness, and portability. It is engineered to provide a constant and reproducible potential, making it a reliable benchmark for electrochemical measurements, particularly in demanding field environments. Its design prioritizes long service life and ease of use over high-precision laboratory applications.
The true value of a copper sulfate electrode isn't just its stable potential, but its ability to maintain that stability under the harsh conditions of on-site fieldwork. It is the industry-standard tool for assessing corrosion on pipelines and structures buried in soil or embedded in concrete.

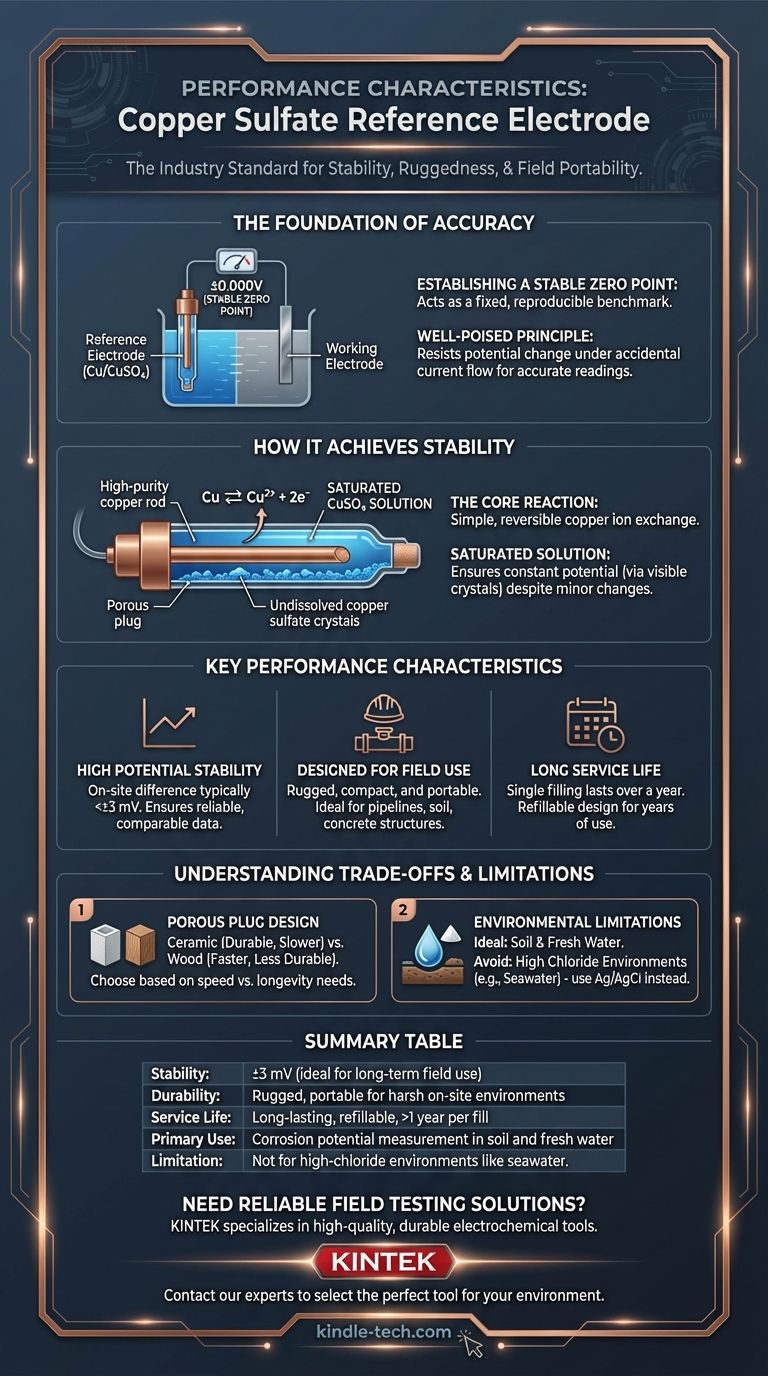
The Foundational Role of a Reference Electrode
Establishing a Stable Zero Point
A reference electrode acts as a stable "zero point" in an electrochemical circuit. Its potential is designed to be fixed and reproducible, allowing you to accurately measure the unknown potential of another material (like a steel pipeline).
Without this stable reference, any measured voltage would be meaningless, as you wouldn't know if the change was in your structure or your measurement device.
The Principle of Being "Well-Poised"
An ideal reference electrode is well-poised. This means its potential does not change even if a small amount of electrical current accidentally flows through it during measurement.
This resistance to change, also known as polarization resistance, is critical for obtaining accurate and repeatable readings in the field.
How the Copper Sulfate Electrode Achieves Stability
The Core Electrochemical Reaction
The electrode's stability comes from a simple, reversible electrochemical reaction. A high-purity copper rod is immersed in a saturated solution of copper sulfate (CuSO₄).
This creates an equilibrium where copper ions (Cu²⁺) are constantly dissolving from the rod and re-depositing onto it. This balanced exchange generates a predictable and highly stable voltage.
The Importance of a Saturated Solution
Using a saturated solution is key to maintaining a constant potential. As long as there are undissolved copper sulfate crystals present, the concentration of copper ions in the solution remains constant, even with minor water loss or temperature changes.
Many designs feature a transparent body, allowing technicians to visually confirm that the solution remains saturated.
Key Performance Characteristics
High Potential Stability
The copper sulfate electrode provides a very steady potential. The on-site potential difference between two separate electrodes is typically less than ±3 millivolts (mV).
This level of consistency ensures that measurements taken by different technicians or at different times can be reliably compared.
Designed for Field Use
The electrode is engineered for portability and durability. Its compact size and robust construction make it suitable for on-site applications.
It is the go-to instrument for measuring the potential of underground pipelines, cable sheaths, and steel reinforcement in concrete.
Long Service Life and Maintainability
These electrodes are built to last. A single filling of the copper sulfate solution can last for over a year.
Most models feature a screw-threaded cap, allowing for easy refilling. This design ensures the electrode can be used for many years, provided its chamber remains intact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Porous Plug Design: Speed vs. Durability
The connection to the soil or water is made through a porous plug. The material of this plug presents a trade-off.
A ceramic core is highly durable and minimizes the loss of the internal solution, but it can have a slightly slower reaction speed. Other materials, like wood, may react faster but be less durable.
Environmental Limitations
The copper sulfate electrode is ideal for use in soil and fresh water.
However, it is generally not recommended for use in environments with high chloride concentrations, such as seawater. In these cases, a Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is the preferred choice to avoid contamination and inaccurate readings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is field testing of buried or submerged structures: The copper sulfate electrode is the industry standard, offering an unmatched combination of stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is laboratory work or testing in high-chloride environments: An Ag/AgCl or Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) will provide more accurate and reliable data for those specific conditions.
- If your primary focus is obtaining readings very quickly: Be aware of the porous plug material, as some designs may require a longer time for the potential to stabilize.
Ultimately, selecting the correct reference electrode is about matching the tool to the specific electrochemical environment you need to measure.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Stability | Potential stable to within ±3 mV; ideal for long-term field use. |
| Durability | Rugged, portable design built for harsh on-site environments. |
| Service Life | Long-lasting; a single filling can last over a year. |
| Primary Use | Industry standard for measuring corrosion potential in soil and fresh water. |
| Limitation | Not recommended for high-chloride environments like seawater. |
Need a reliable reference electrode for your field testing?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable electrochemical tools. Our copper sulfate reference electrodes are designed for the stability and ruggedness your on-site corrosion assessments demand.
Let our experts help you select the perfect tool for your specific environment.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and ensure accurate, long-lasting performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How should a copper sulfate reference electrode be maintained? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the operating principle of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Reliable Potential Measurement Explained
- What is the expected lifespan of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Maximize Longevity with Proper Maintenance
- How should a copper sulfate reference electrode be stored? A Guide to Short-Term & Long-Term Storage
- What precautions should be taken when handling and using a copper sulfate reference electrode? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements



















