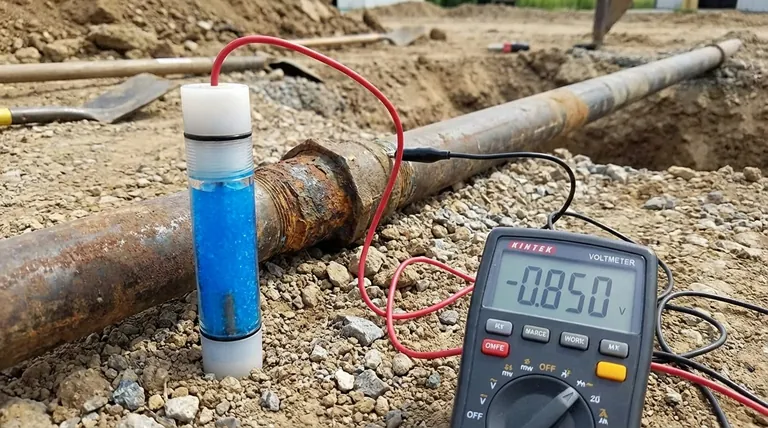
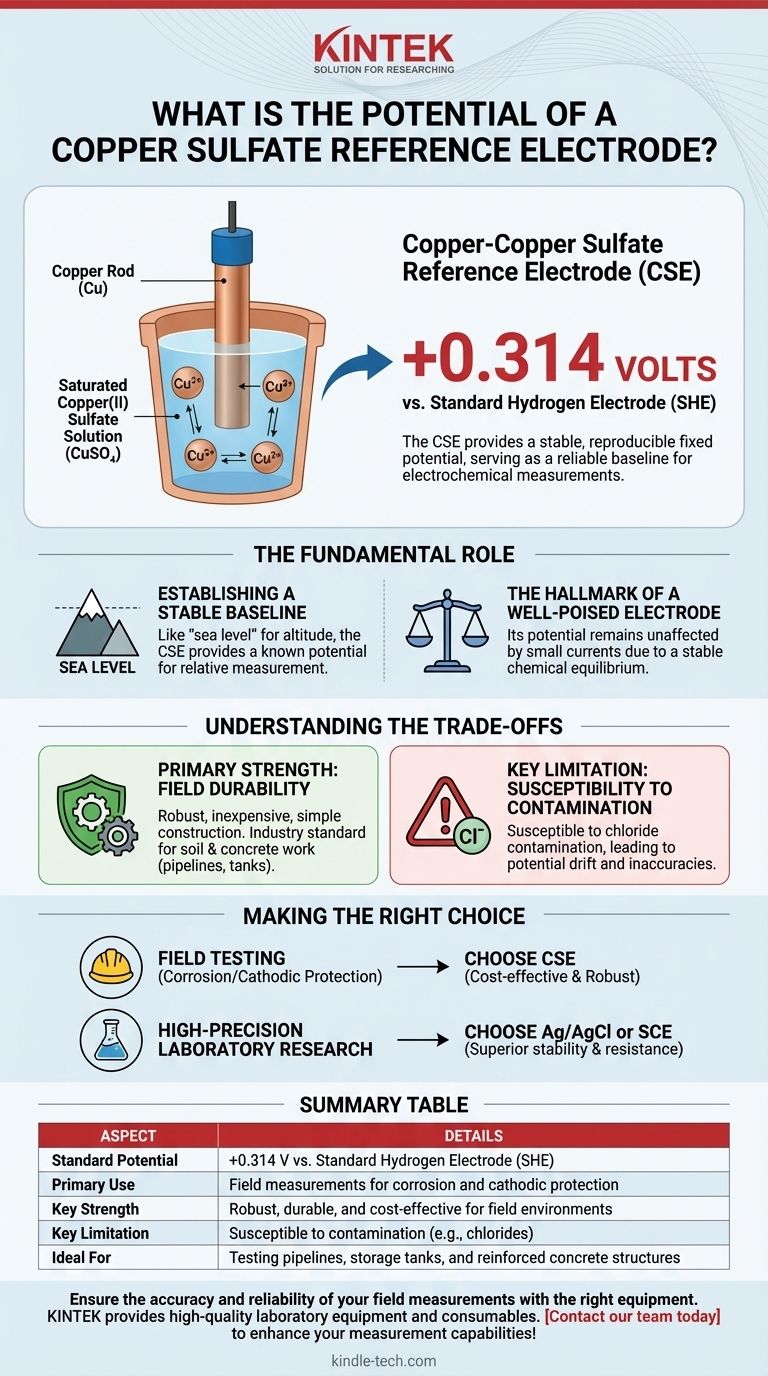
The short answer is this: The standard potential of a copper-copper sulfate reference electrode (CSE) is +0.314 volts relative to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). This fixed, reproducible potential allows it to serve as a stable baseline for measuring the electrical potential of other materials, particularly in the field of corrosion and cathodic protection.
A reference electrode's value isn't just its specific voltage, but its ability to hold that voltage with unwavering stability. The CSE's +0.314 V potential is a known constant, making it a reliable "zero point" for electrochemical measurements in specific environments.

The Fundamental Role of a Reference Electrode
To understand the importance of the CSE's potential, we must first understand why a reference electrode is necessary at all. Electrical potential is always a relative measurement; it is the difference in potential between two points.
Establishing a Stable Baseline
A reference electrode provides one-half of the measurement circuit with a known, constant potential. Think of it like using "sea level" as a universal reference point to measure the altitude of mountains. Without this stable baseline, any measurement you take would be meaningless because you would have no fixed point of comparison.
The Hallmark of a "Well-Poised" Electrode
An ideal reference electrode is "well-poised." This means its potential is not affected by small amounts of current that might flow through it during a measurement. This stability is achieved by using a chemical equilibrium that is difficult to disturb, ensuring your baseline remains fixed and your readings are accurate.
Deconstructing the Copper-Copper Sulfate Electrode
The CSE achieves its stability through a simple and robust chemical setup: a high-purity copper rod is immersed in a saturated solution of copper(II) sulfate.
The Standard Potential: +0.314 V
The specific value, +0.314 V, represents the potential difference between the copper-copper sulfate half-cell and the theoretical standard hydrogen electrode, which is the universally agreed-upon zero point for electrochemistry. All other electrode potentials are measured against this standard.
How It Maintains Stability
The electrode's potential is governed by the equilibrium between the solid copper metal (Cu) and the copper ions (Cu²⁺) in the solution. Because the solution is saturated, the concentration (or more accurately, the activity) of the copper ions is well-defined and constant. This stable chemical environment results in a fixed, reproducible electrode potential over time and across changing temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the copper-copper sulfate electrode is not universally perfect for every application. Its design comes with inherent strengths and weaknesses.
Primary Strength: Field Durability
The CSE is robust, inexpensive, and relatively simple to construct. This makes it the industry standard for field work, especially in soil and concrete environments for testing pipelines, storage tanks, and reinforced structures.
Key Limitation: Susceptibility to Contamination
The primary weakness of the CSE is its susceptibility to contamination, particularly from chloride ions. If chlorides enter the electrode, they can alter the chemical equilibrium and cause the reference potential to drift, leading to inaccurate measurements. For this reason, it is less common in high-precision laboratory settings where electrodes like Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) are preferred.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct reference electrode depends entirely on the requirements of your measurement environment.
- If your primary focus is field testing for corrosion or cathodic protection: The CSE is an excellent and cost-effective industry-standard choice due to its robustness.
- If your primary focus is high-precision laboratory research: A Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) or Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) will provide superior stability and resistance to contamination.
Ultimately, understanding the fixed potential of a reference electrode is the first step in choosing the right tool to ensure your measurements are both accurate and reliable.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Standard Potential | +0.314 V vs. Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) |
| Primary Use | Field measurements for corrosion and cathodic protection |
| Key Strength | Robust, durable, and cost-effective for field environments |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to contamination (e.g., chlorides) |
| Ideal For | Testing pipelines, storage tanks, and reinforced concrete structures |
Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your field measurements with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including robust reference electrodes for corrosion monitoring. Our experts can help you select the ideal tools for your specific application, ensuring precise and stable results. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and enhance your measurement capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the post-treatment procedures after using a copper sulfate reference electrode? Essential Steps for Accuracy & Longevity
- Is there a difference in performance between wood plug and ceramic core copper sulfate electrodes? Speed vs. Durability Explained
- How should a copper sulfate reference electrode be stored? A Guide to Short-Term & Long-Term Storage
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of the ceramic core type copper sulfate reference electrode?
- What is the expected lifespan of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Maximize Longevity with Proper Maintenance



















