At its core, Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a compound semiconductor known for an exceptional combination of properties that far exceed those of conventional silicon. Its defining characteristics are its ability to operate at high voltages, high temperatures, and high frequencies, all while maintaining excellent thermal stability. This makes it a critical material for next-generation, high-performance applications.
The true value of Silicon Carbide isn't just its list of impressive properties, but how they combine. SiC enables the creation of electronic devices and mechanical components that are simultaneously smaller, more efficient, and far more durable than their predecessors, especially when operating under extreme conditions.
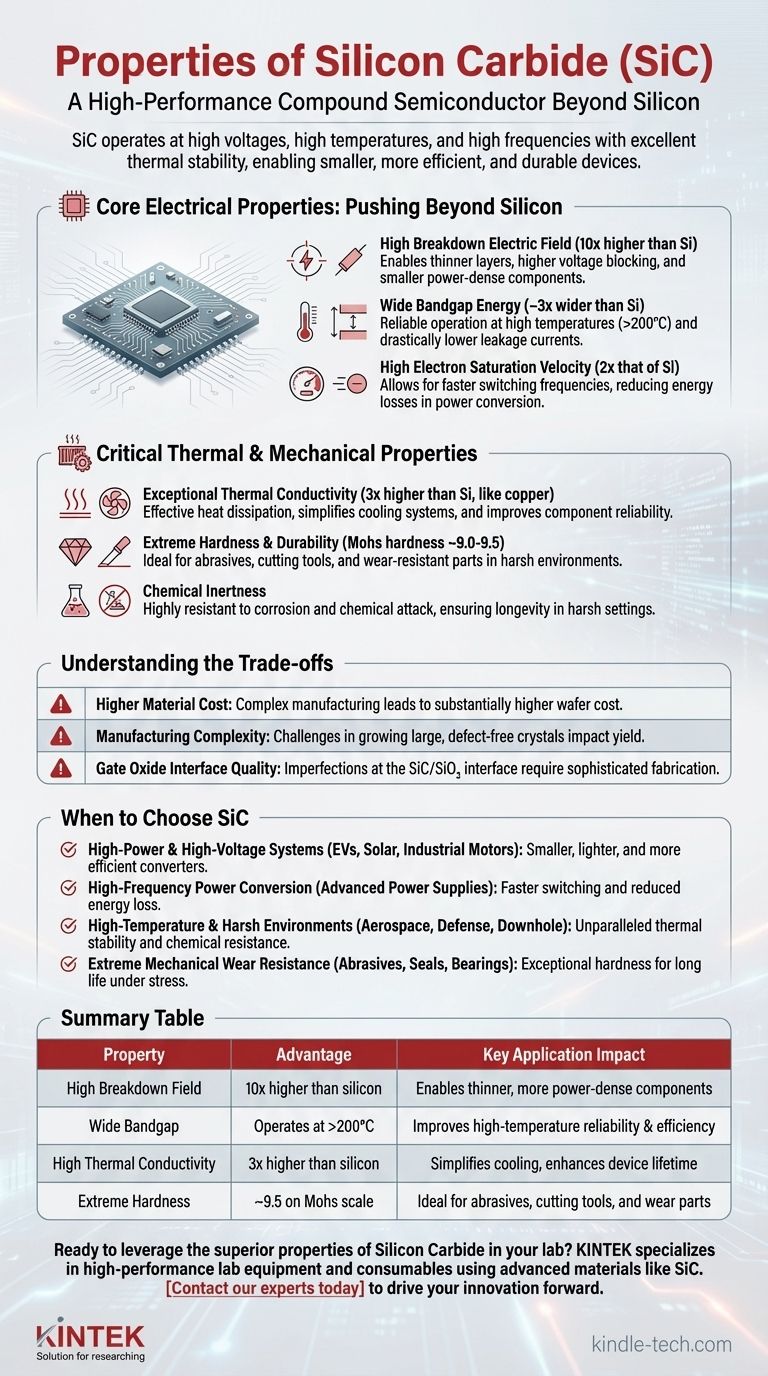
The Core Electrical Properties: Pushing Beyond Silicon
The primary driver for SiC adoption in electronics is its superior electrical characteristics compared to silicon. These properties allow for a fundamental shift in what is possible for power device design.
High Breakdown Electric Field
The breakdown electric field is the maximum electric field a material can withstand before it loses its insulating properties. SiC's breakdown field is about 10 times higher than that of silicon.
This single property means that a SiC device can block the same voltage as a silicon device using a layer that is 10 times thinner. This directly enables smaller, more power-dense components.
Wide Bandgap Energy
SiC is a wide-bandgap semiconductor, with an energy gap approximately three times wider than silicon's. This has two critical consequences.
First, it allows SiC devices to operate reliably at much higher temperatures (over 200°C) without significant performance degradation. Second, it results in dramatically lower leakage currents, which improves overall energy efficiency.
High Electron Saturation Velocity
Electron saturation velocity dictates how quickly charge carriers can move through the material under a high electric field. SiC possesses a velocity that is twice that of silicon.
This enables SiC devices to switch on and off much faster. Faster switching leads to higher operating frequencies and significantly lower energy losses during the switching process, a key factor in power conversion efficiency.
The Critical Thermal and Mechanical Properties
Beyond its electrical advantages, SiC's physical robustness makes it suitable for a range of demanding applications outside of pure electronics.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
SiC has a thermal conductivity that is more than three times higher than silicon and is comparable to many metals, including copper.
This means SiC devices can dissipate heat far more effectively. This property simplifies thermal management, reduces the need for bulky cooling systems, and dramatically improves the reliability and lifetime of the component.
Extreme Hardness and Durability
With a Mohs hardness of around 9.0-9.5, SiC is one of the hardest materials available, approaching the hardness of diamond.
This makes it an ideal material for abrasives, cutting tools, and wear-resistant components like mechanical seals and bearings used in high-wear industrial environments.
Chemical Inertness
Silicon Carbide is highly resistant to corrosion and chemical attack, even at elevated temperatures. This ensures longevity and stable performance in harsh chemical or industrial settings where other materials would quickly degrade.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While its properties are exceptional, SiC is not a universal replacement for silicon. Its adoption involves specific trade-offs that must be considered.
Higher Material Cost
The manufacturing process for high-purity, single-crystal SiC wafers is significantly more complex and energy-intensive than for silicon. This results in a substantially higher cost per wafer, which can be a primary barrier to adoption in cost-sensitive applications.
Manufacturing Complexity
Growing large, defect-free SiC crystals is challenging. Defects, such as micropipes and stacking faults, can negatively impact device performance, yield, and long-term reliability. This places stringent demands on the fabrication process.
Gate Oxide Interface Quality
In SiC-based MOSFETs, the interface between the SiC material and the silicon dioxide (SiO₂) gate insulator is less perfect than the revered Si/SiO₂ interface. This can lead to challenges like threshold voltage instability and reduced channel mobility, which requires sophisticated fabrication techniques to manage.
When to Choose Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Your decision to use SiC should be driven entirely by whether your application's performance requirements can justify its costs and design considerations.
- If your primary focus is high-power and high-voltage systems (EVs, solar inverters, industrial motors): Choose SiC for its high breakdown voltage and efficiency, which lead to smaller, lighter, and more efficient power converters.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency power conversion (advanced power supplies): Choose SiC for its fast switching speed, which reduces energy loss and allows for the use of smaller passive components.
- If your primary focus is operation in high-temperature or harsh environments (aerospace, defense, downhole drilling): Choose SiC for its unparalleled thermal stability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is extreme mechanical wear resistance (abrasives, seals, bearings): Choose SiC for its exceptional hardness and durability, which ensures a long operational life under intense physical stress.
Ultimately, SiC is the enabling material for applications where the performance limits of silicon have been reached and exceeded.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage | Key Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Breakdown Field | 10x higher than silicon | Enables thinner, more power-dense components |
| Wide Bandgap | Operates at >200°C | Improves high-temperature reliability & efficiency |
| High Thermal Conductivity | 3x higher than silicon | Simplifies cooling, enhances device lifetime |
| Extreme Hardness | ~9.5 on Mohs scale | Ideal for abrasives, cutting tools, and wear parts |
Ready to leverage the superior properties of Silicon Carbide in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables that harness advanced materials like SiC. Whether you are developing next-generation power electronics, need durable components for harsh environments, or require materials for high-temperature processing, our expertise can help you achieve breakthrough results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C



















