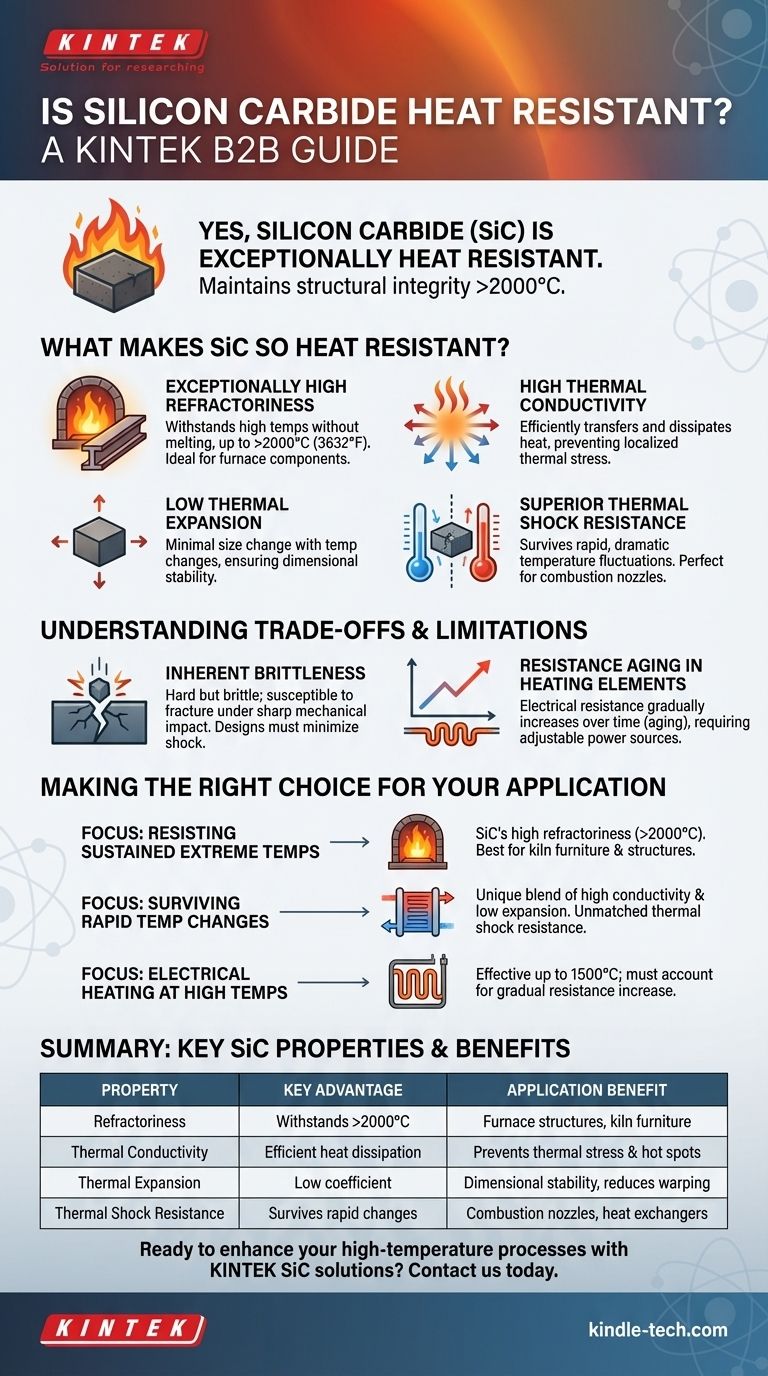
Yes, silicon carbide (SiC) is exceptionally heat resistant. Its ability to maintain structural integrity and performance at extremely high temperatures is one of its most defining characteristics. Unlike most metals that melt or deform, SiC remains stable well above 2000°C, making it a critical material for applications in extreme thermal environments.
The core reason for silicon carbide's thermal resilience is not just its high melting point, but its unique combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion. This allows it to both endure sustained heat and survive rapid, dramatic temperature changes that would shatter other materials.

What Makes Silicon Carbide So Heat Resistant?
Silicon carbide's thermal performance is not a single property but a result of several key physical characteristics working in concert. Understanding these individual factors explains why SiC is a benchmark material for high-temperature engineering.
Exceptionally High Refractoriness
Refractoriness is the ability of a material to withstand high temperatures without deforming or melting. Silicon carbide has a very high refractoriness, with some products rated for service above 2000°C (3632°F).
This allows it to be used for structural components like furnace floors and guide rails, where it must bear loads at temperatures that would cause metals to fail.
High Thermal Conductivity
While many heat-resistant materials are insulators, SiC has remarkably high thermal conductivity. This means it can efficiently transfer and dissipate heat across its structure.
This property is crucial for preventing thermal stress. By moving heat away from hot spots, SiC avoids the localized temperature gradients that can lead to cracks and mechanical failure.
Low Thermal Expansion
Silicon carbide has a very small coefficient of thermal expansion. In simple terms, it does not expand or contract significantly when its temperature changes.
This dimensional stability is a key component of its overall thermal resilience. Materials that expand dramatically are prone to internal stress and warping when heated and cooled.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
The combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion gives SiC outstanding thermal shock resistance. It can withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking.
This makes it ideal for applications like combustion nozzles or heat exchangers, where it is subjected to immediate and intense temperature fluctuations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its thermal properties are elite, silicon carbide is not a perfect material for every situation. Acknowledging its trade-offs is crucial for successful implementation.
Inherent Brittleness
Like many advanced ceramics, silicon carbide is very hard but also brittle. It has excellent compressive strength and abrasion resistance but can fracture under sharp mechanical impact.
This contrasts with metals, which are ductile and will bend or deform before breaking. Designs using SiC must account for this by minimizing mechanical shock and tensile loads.
Resistance Aging in Heating Elements
When used as a resistive heating element, the electrical resistance of silicon carbide gradually increases over time. This phenomenon is known as aging.
This is not a failure but an operational characteristic. Systems using SiC heaters often require an adjustable power source, like an auto-transformer, to compensate for this change and maintain consistent power output over the component's lifespan.
Form and Purity Matter
The properties of a silicon carbide component depend heavily on its manufacturing process. "Silicon carbide" is a family of materials, not a single substance.
For example, recrystallized SiC offers high purity and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for kiln furniture. In contrast, CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) SiC is theoretically dense and exceptionally pure, making it suitable for semiconductor processing equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting silicon carbide requires matching its specific thermal strengths to your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is resisting sustained, extreme temperatures: SiC's high refractoriness (>2000°C) makes it the clear choice for structural components in furnaces and kilns.
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid temperature changes: Its unique blend of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion provides unmatched thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is electrical heating at high temperatures: SiC heating elements are highly effective up to 1500°C, provided you account for the gradual increase in resistance over their operational life.
Ultimately, silicon carbide provides a powerful solution for thermal management challenges that are simply beyond the limits of most other materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Advantage | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Refractoriness | Withstands temperatures >2000°C | Ideal for furnace structures and kiln furniture |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat dissipation | Prevents thermal stress and hot spots |
| Thermal Expansion | Low coefficient for dimensional stability | Reduces warping and internal stress |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Survives rapid temperature changes | Perfect for combustion nozzles and heat exchangers |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with silicon carbide solutions? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including silicon carbide components designed for extreme thermal environments. Whether you need durable furnace parts, reliable heating elements, or custom SiC products, our expertise ensures optimal performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how our silicon carbide solutions can meet your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential for Extreme Heat, Insulation & Purity
- What is the heat capacity of alumina? Unlock Its Full Thermal Performance for High-Temp Applications
- Why use alumina ceramic liners in SCWG reactors? Essential Protection for Biomass Gasification and Reactor Longevity
- Why is ceramic sintering used? To transform fragile powder into a strong, dense solid.
- What is the function of the sintering process in ceramic manufacturing? Achieve High Density and Structural Integrity
- How do Ceramic Honeycomb Reactors facilitate thermochemical cycles? Optimize Ferrite-Based Energy Production
- Why is high-purity alumina (Al2O3) preferred over quartz for steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity at 1773 K
- How do you prepare silicon carbide in the laboratory? Master High-Temperature Synthesis Methods



















