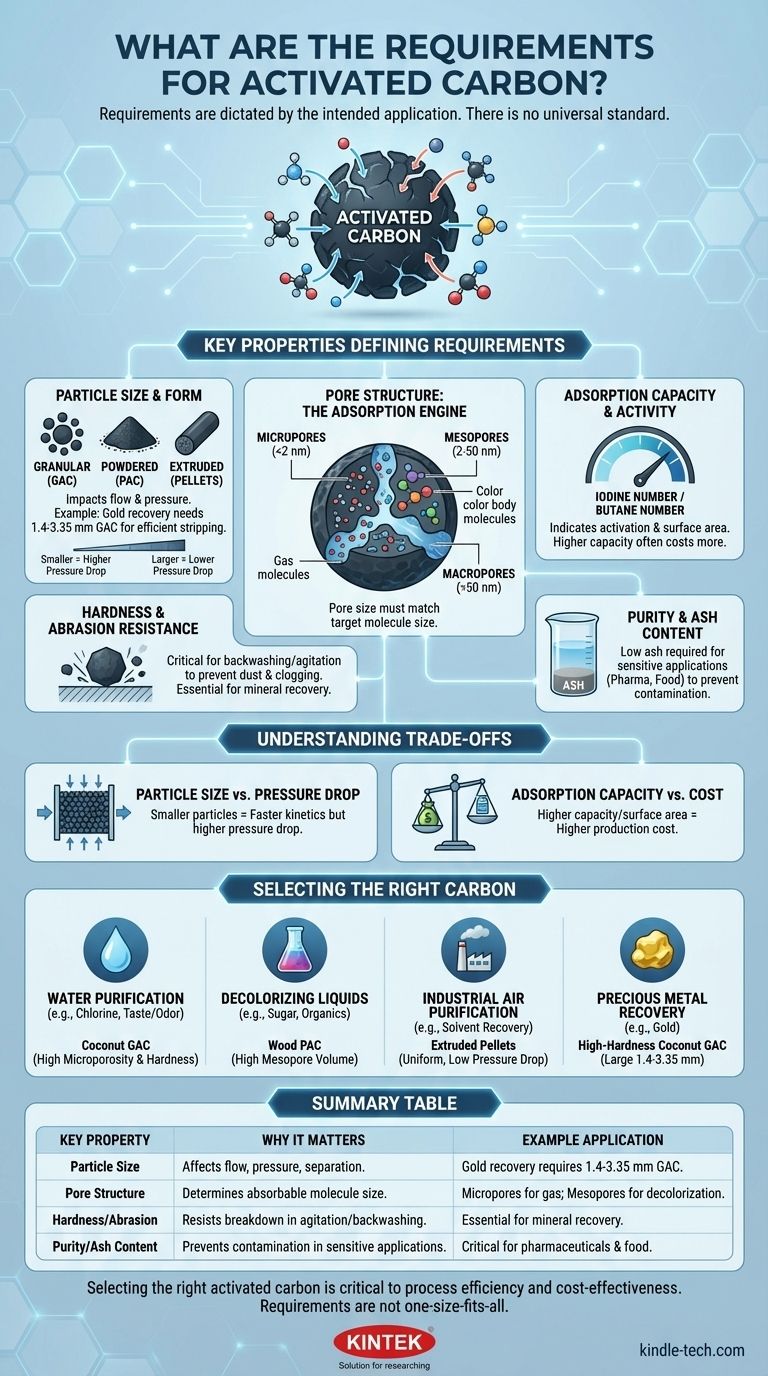
The requirements for activated carbon are dictated entirely by its intended application. There is no single universal standard; instead, key properties must be matched to a specific process. For example, in gold recovery, the particle size must be between 1.4 and 3.35 mm to ensure the mineral can be efficiently stripped from the carbon later. Using particles smaller than 1 mm would make this elution process ineffective, demonstrating how critical a single parameter can be for success.
Choosing the right activated carbon is not about finding a "good" or "bad" product. It is a technical exercise in matching the carbon's specific physical and chemical properties—like particle size and pore structure—to the exact substance you need to adsorb and the system you are using.

Key Properties That Define Activated Carbon Requirements
To select the correct activated carbon, you must evaluate it based on several fundamental properties. The ideal specification is a balance of these factors tailored to your goal.
Particle Size and Form
The physical size of the carbon particles is a primary consideration as it directly impacts how it will perform in a system.
Carbon is generally available in three main forms: Granular (GAC), Powdered (PAC), and Extruded (Pellets). The choice depends on the application's flow dynamics and pressure constraints.
For instance, the reference to gold recovery demands a specific GAC size (1.4-3.35 mm). This larger size prevents the carbon from being washed away and allows for easy separation, while also being robust enough to withstand the mechanical stress of the process.
Pore Structure: The Adsorption Engine
The effectiveness of activated carbon comes from its vast network of internal pores. The size of these pores determines what molecules it can capture.
- Micropores (less than 2 nm) are ideal for adsorbing small molecules, making them perfect for gas purification and removing trace organic contaminants from water.
- Mesopores (2 to 50 nm) are suited for larger molecules like color bodies in liquids. They are essential in applications like sugar decolorization or removing complex organic compounds.
- Macropores (greater than 50 nm) act as highways, allowing molecules to travel deeper into the carbon's structure to reach the smaller, adsorptive pores.
A carbon's pore distribution must match the size of the target contaminant molecules for adsorption to be efficient.
Adsorption Capacity and Activity
This measures how much contaminant the carbon can hold. It is often indicated by an Iodine Number or Butane Number.
A higher number generally signifies more activation, a larger internal surface area, and a greater capacity for adsorption. While a high number is often desirable, it may not be necessary for applications where the contaminant load is low.
Hardness and Abrasion Resistance
This property measures the carbon's ability to resist breaking down under physical stress. It is a critical requirement in applications involving water backwashing, mechanical agitation, or regeneration.
Low-hardness carbons will create fine dust that can clog systems, increase pressure drop, and lead to product loss. For demanding processes like mineral recovery, a very high hardness number is essential.
Purity and Ash Content
Ash is the non-carbon, inorganic material left over from the raw material source (like coal or coconut shells).
High ash content reduces the overall activity of the carbon and can be a source of contamination, potentially leaching inorganics like heavy metals into the treated liquid or gas. For high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals or food processing, a very low ash content is a strict requirement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Balancing Act
Selecting an activated carbon is rarely about maximizing every property. More often, it involves making calculated compromises to achieve the most effective and economical outcome.
Particle Size vs. Pressure Drop
Smaller particles provide a greater external surface area and allow for faster adsorption kinetics. However, they create a tightly packed bed that significantly increases the pressure drop, requiring more energy to pump fluid or gas through the system.
Adsorption Capacity vs. Cost
Carbons with extremely high surface areas and activity levels are more complex and expensive to produce. The goal is to select a carbon with sufficient capacity for the job without over-engineering the solution. A moderately active carbon is often the most cost-effective choice for many industrial processes.
Pore Specificity vs. Contaminant Mix
A carbon that is highly microporous will be excellent for removing small solvent molecules from the air but will be ineffective at removing large color bodies from a liquid. If you are dealing with a mixture of contaminant sizes, you may need a carbon with a broader range of pore sizes, even if it's less specialized.
Selecting the Right Carbon for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by your primary objective. Evaluate the target contaminant, the process conditions, and your economic constraints to determine the best fit.
- If your primary focus is general water purification (e.g., removing chlorine and taste/odor): A coconut shell-based Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) is often ideal due to its high microporosity and hardness.
- If your primary focus is decolorizing liquids or removing large organics: A wood-based Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) with a high mesopore volume is the standard choice for its effectiveness with large molecules in batch treatments.
- If your primary focus is industrial air purification or solvent recovery: An extruded pelletized carbon is preferred for its uniform shape, low dust, and minimal pressure drop in vapor-phase systems.
- If your primary focus is precious metal recovery: A high-hardness GAC from coconut shell with a specific, large particle size (e.g., 1.4-3.35 mm) is required to withstand mechanical stress and allow for efficient elution.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the precise activated carbon required to solve your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Affects flow, pressure drop, and separation efficiency. | Gold recovery requires 1.4-3.35 mm GAC for elution. |
| Pore Structure | Determines the size of molecules that can be adsorbed. | Micropores for gas purification; Mesopores for decolorization. |
| Hardness/Abrasion | Resists breakdown in systems with agitation or backwashing. | Essential for mineral recovery to prevent dust and product loss. |
| Purity/Ash Content | Prevents contamination in sensitive applications. | Critical for pharmaceuticals and food processing. |
Selecting the right activated carbon is critical to your process efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The requirements are not one-size-fits-all.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including a range of activated carbons tailored for specific applications like water purification, air treatment, and precious metal recovery. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between particle size, pore structure, and hardness to find the optimal solution for your lab's needs.
Ensure your project's success with the perfect carbon match. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance



















