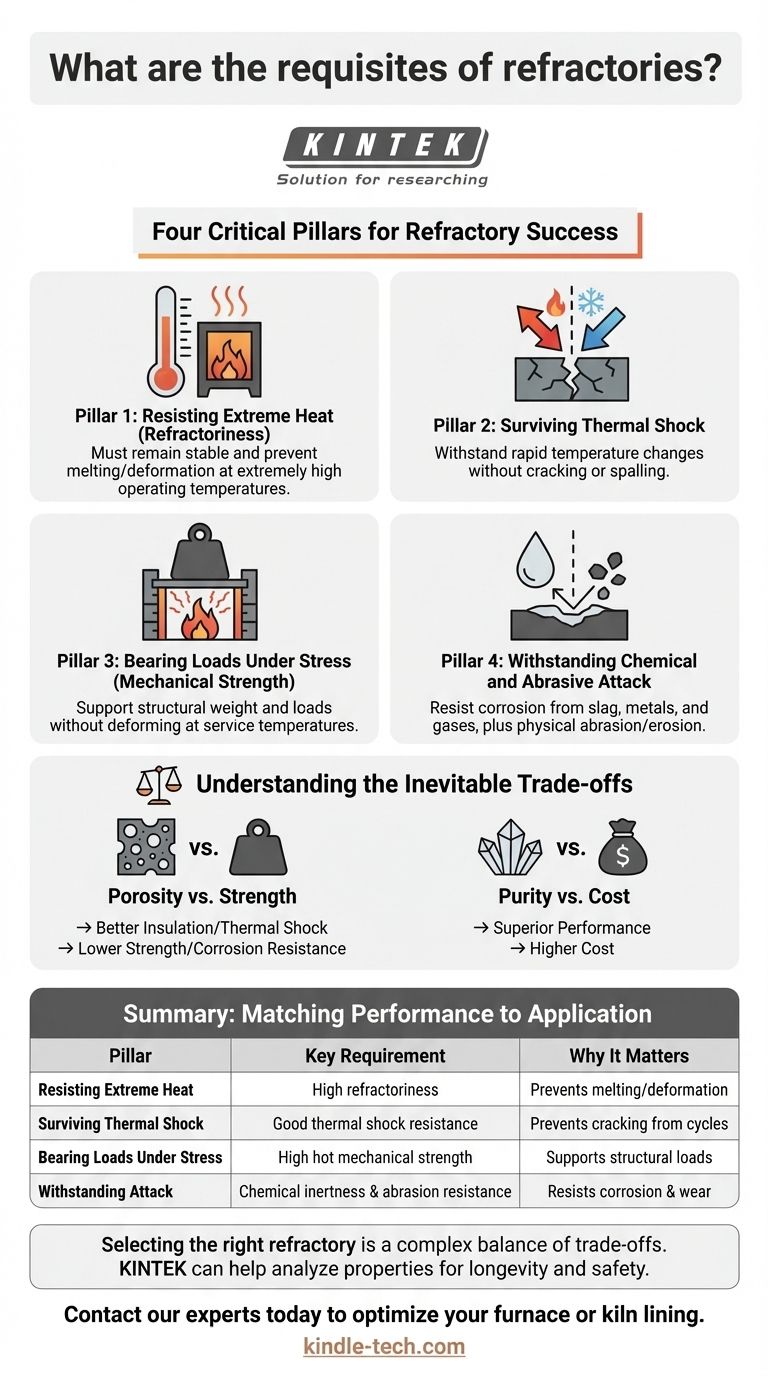
At its core, a refractory must succeed in four critical areas. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures, survive sudden changes in those temperatures, bear structural loads while hot, and resist attack from chemical corrosion and physical abrasion. These qualities ensure it can reliably contain heat and protect the surrounding structure in demanding industrial environments.
The true measure of a refractory is not just its ability to resist heat, but its capacity to endure a simultaneous assault of thermal, mechanical, and chemical stress. The "best" refractory is always a compromise, a material engineered to meet the specific challenges of its intended application.
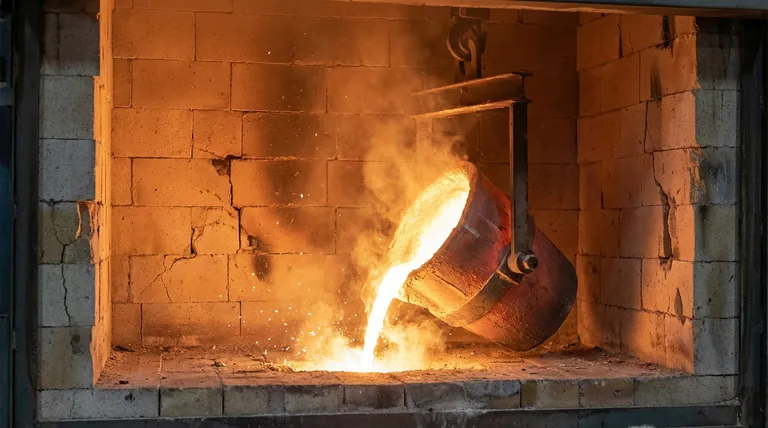

The Four Pillars of Refractory Performance
A refractory material is the barrier between a controlled, high-temperature process and the outside world. To function effectively, it must demonstrate excellence across four distinct but interconnected properties.
Pillar 1: Resisting Extreme Heat (Refractoriness)
This is the most fundamental requirement. A refractory must remain physically and chemically stable at very high operating temperatures, well beyond the melting point of most metals.
Its primary job is to contain heat within a furnace, kiln, or reactor, ensuring process efficiency and protecting the outer steel shell from damage. The material must not melt, soften, or deform under these thermal loads.
Pillar 2: Surviving Thermal Shock
Industrial processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. This creates immense internal stress within the refractory material, a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
A refractory must be able to withstand these sudden temperature changes without cracking, fracturing, or spalling (breaking off in layers). Good thermal shock resistance is critical for longevity in applications with intermittent operation.
Pillar 3: Bearing Loads Under Stress (Mechanical Strength)
Refractories are not just passive liners; they are structural components. They must support their own weight, the weight of the components above them, and often the weight of the material being processed.
This ability to withstand load at service conditions is crucial. A material that softens and deforms under pressure at high temperatures will lead to a catastrophic structural failure of the furnace lining. This property is often measured as hot crushing strength or refractoriness-under-load (RUL).
Pillar 4: Withstanding Chemical and Abrasive Attack
The internal environment of a furnace is incredibly hostile. Refractories are constantly exposed to corrosive substances like molten slag, metals, glass, and reactive gases.
They must be chemically inert to these substances to prevent being corroded or dissolved. Furthermore, in processes involving the movement of solid materials, the refractory must also resist physical abrasion and erosion.
Understanding the Inevitable Trade-offs
No single refractory material excels in all four pillars simultaneously. The selection of a refractory is always an exercise in balancing competing properties to find the optimal solution for a specific environment.
Porosity vs. Strength and Resistance
Higher porosity (more air gaps in the material) can significantly improve a refractory's insulating properties and its ability to resist thermal shock.
However, this same porosity creates pathways for corrosive slag to penetrate and reduces the material's overall mechanical strength and resistance to abrasion.
Purity vs. Cost
Refractories made from higher-purity raw materials, like high-alumina or magnesia-carbon bricks, generally offer superior performance at extreme temperatures and better chemical resistance.
This enhanced performance comes at a significantly higher cost. The goal is to select a material that meets the demands of the application without being excessively over-engineered and expensive.
Selecting the Right Refractory for Your Application
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of which performance pillar is most critical for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is containing molten metal or glass: Prioritize superior chemical resistance to slag and high hot mechanical strength to prevent deformation.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Emphasize excellent thermal shock resistance, even if it requires a more porous material with slightly lower strength.
- If your primary focus is pure insulation in a clean environment: Choose a lightweight, highly porous material with low thermal conductivity, as chemical and abrasive resistance are less critical.
Ultimately, selecting the right refractory is about matching the material's unique profile of strengths and weaknesses to the specific challenges of its industrial environment.
Summary Table:
| Pillar | Key Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Resisting Extreme Heat | High refractoriness | Prevents melting/deformation at high temperatures |
| Surviving Thermal Shock | Good thermal shock resistance | Prevents cracking from rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Bearing Loads Under Stress | High hot mechanical strength | Supports structural loads at operating temperatures |
| Withstanding Attack | Chemical inertness & abrasion resistance | Resists corrosion from slag, metals, and physical wear |
Struggling to find the right refractory for your demanding application? The selection process is a complex balance of performance trade-offs. KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables to help you test and select the ideal refractory materials. Our solutions can help you analyze thermal properties, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance to ensure longevity and safety in your high-temperature processes. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and let us help you optimize your furnace or kiln lining for maximum efficiency and durability. Get in touch via our contact form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are cross-shaped magnetic stirrers used in micro-CSTRs for solid particles? Boost Mixing & Prevent Clogging
- Why is a high-purity quartz tube necessary for CO2 and methane separation? Key Role in Plasma DBD Stability
- Why is a mechanical stirring system considered essential hardware for the epoxidation reaction of polyols?
- Why must electrode holders in CGDE be coated with high-temp resin? Ensure Accurate Isolation & Data Integrity
- What are the benefits of using zirconia (ZrO2) grinding jars and balls when milling sulfide-based solid electrolytes?
- What is the necessity of using high-alumina ceramic balls as grinding media? Ensure Purity in Graphite Experiments
- What is the role of a Mass Flow Controller (MFC) in HMDSO deposition? Ensure Process Stability and Film Consistency
- What role do SiC sandpaper and alumina polishing suspension play in steel pretreatment? Achieve Optimal Coating Adhesion



















