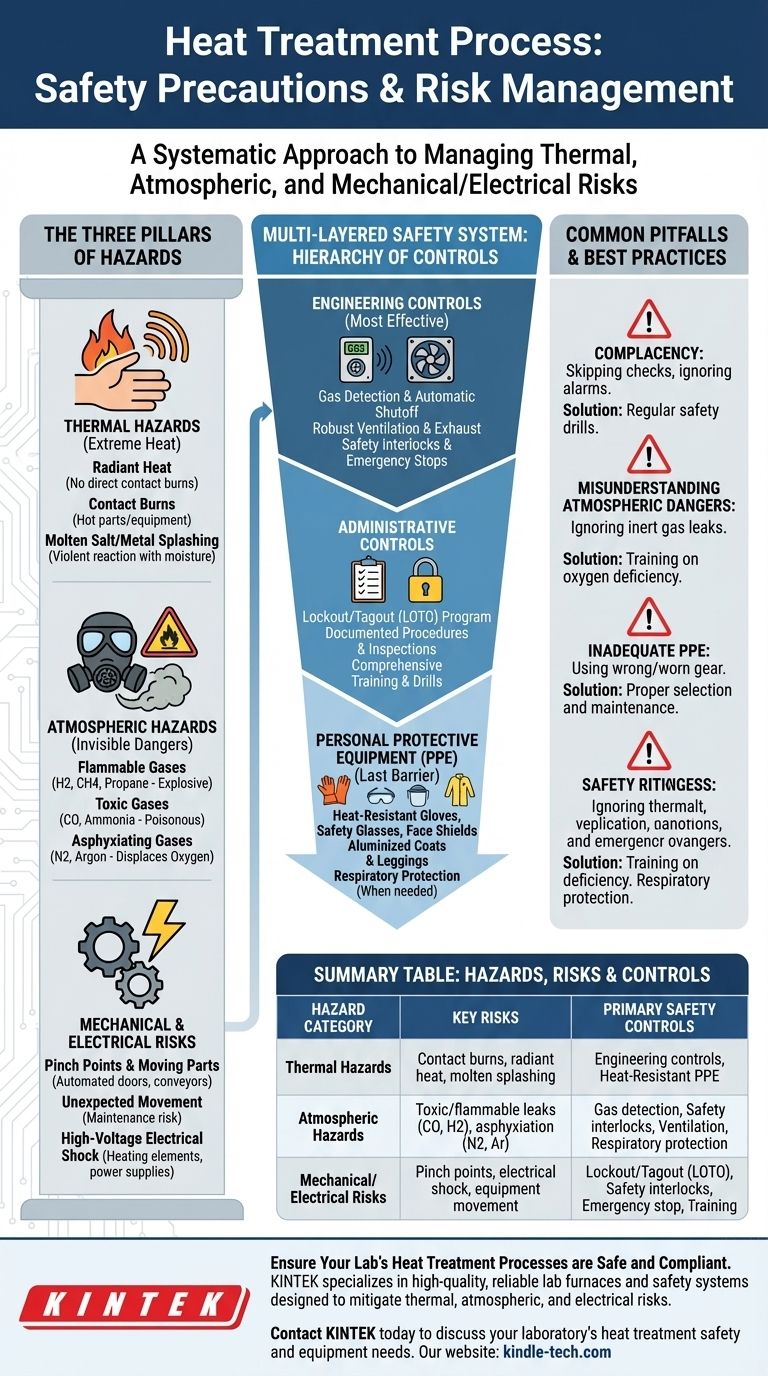
At its core, ensuring safety in heat treatment requires a systematic approach to managing three distinct categories of risk. These include severe thermal hazards from high temperatures, atmospheric hazards from the gases used to control the process, and mechanical or electrical dangers from the equipment itself. A comprehensive safety plan must address all three areas to prevent injury and operational failure.
The most critical insight for heat treatment safety is that the most dangerous risks—such as toxic gas exposure or asphyxiation from inert gases—are often invisible. A successful safety program prioritizes engineering controls to manage these atmospheric dangers, rather than relying solely on personal protective equipment for burn prevention.
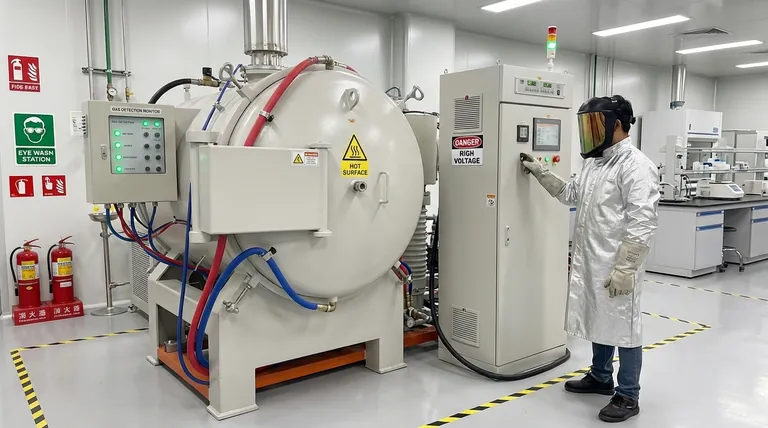

The Three Pillars of Heat Treatment Hazards
Understanding the full spectrum of risk is the first step toward mitigating it. Hazards in a heat treatment environment are not limited to the furnace's high temperature.
Thermal Hazards: Beyond the Obvious Burn
The most apparent risk is the extreme heat. This manifests in several ways, including radiant heat from furnace walls, which can cause severe burns without direct contact, and contact burns from handling hot parts or touching equipment.
Specialized processes involving molten salt or metal baths introduce the additional risk of violent splashing and severe, deep-tissue burns if moisture is introduced.
Atmospheric Hazards: The Invisible Dangers
Many heat treatment processes occur in a controlled atmosphere, which introduces significant, often overlooked, dangers.
- Flammable Gases: Processes like carburizing use atmospheres rich in hydrogen, methane, or propane. Leaks can create an explosive environment, requiring rigorous gas detection and ventilation.
- Toxic Gases: Atmospheres may contain carbon monoxide (CO), a byproduct of combustion, or ammonia, used in nitriding. Both are highly toxic even at low concentrations and require continuous monitoring.
- Asphyxiating Gases: Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are used to displace oxygen and prevent oxidation. While not toxic, they can displace breathable air in enclosed spaces, leading to rapid asphyxiation with little to no warning.
Mechanical and Electrical Risks
Furnaces are complex industrial machines. Dangers include pinch points from automated doors and conveyors, unexpected movement during maintenance, and the risk of high-voltage electrical shock from heating elements and power supplies.
Implementing a Multi-Layered Safety System
Effective safety is not a single action but a series of layered defenses, often described as the "Hierarchy of Controls."
Engineering Controls: The First Line of Defense
These are design-level solutions that remove the hazard at its source and are the most effective form of protection.
Key examples include gas detection systems interlocked with automatic shutoff valves, robust ventilation and exhaust systems to manage atmospheric hazards, and safety interlocks that prevent furnace doors from opening under dangerous conditions. Emergency stop buttons must be clearly marked and accessible.
Administrative Controls: Procedures and Training
These are the procedures and policies that dictate how work is performed safely. They require active participation from every team member.
The most critical administrative control is a robust Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) program to ensure equipment is de-energized before any maintenance. Other essential controls include documented safe work procedures, regular equipment inspections, and comprehensive training on normal operations, emergency shutdowns, and hazard recognition.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The Final Barrier
PPE is essential but should be considered the last line of defense after engineering and administrative controls have been implemented.
Standard PPE includes heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses or face shields, and durable footwear. For tasks with high radiant heat or splash risk, specialized aluminized coats and leggings are required. In situations where atmospheric hazards cannot be fully engineered away, respiratory protection may be necessary.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Even with systems in place, certain oversights can undermine a safety program.
The Risk of Complacency
The routine nature of heat treatment operations can lead to complacency. Operators may become accustomed to alarms or skip pre-use safety checks, creating a window for accidents. Regular safety drills and "what-if" scenario training can help combat this.
Misunderstanding Atmospheric Dangers
The deadliest risks are often misunderstood. A common and fatal mistake is treating an inert gas leak of nitrogen or argon with less urgency than a flammable gas leak. Workers may not realize that an oxygen-deficient atmosphere provides no sensory warning (like a smell or irritation) before causing unconsciousness.
Inadequate PPE Selection and Maintenance
Using the wrong type of glove or worn-out equipment provides a false sense of security. A leather glove rated for 400°F offers no protection when handling a part at 1200°F. PPE must be selected for the specific task and temperature, inspected regularly, and replaced when damaged.
Building a Robust Safety Program
To apply these principles effectively, align your safety priorities with your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize comprehensive training on atmospheric hazards and conduct frequent drills for emergency scenarios like gas leaks or power failure.
- If your primary focus is facility compliance: Implement and document a rigorous inspection schedule for all engineering controls, especially gas detectors, ventilation fans, and safety interlocks.
- If your primary focus is preventing downtime: Integrate Lockout/Tagout procedures seamlessly into all maintenance workflows to prevent the catastrophic accidents that lead to the most significant operational and financial losses.
Ultimately, safety in heat treatment is an active, continuous process of identifying and controlling risk, not a static checklist.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Primary Safety Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Hazards | Contact burns, radiant heat, molten salt splashing | Engineering controls (ventilation), Heat-Resistant PPE (gloves, face shields) |
| Atmospheric Hazards | Toxic/flammable gas leaks (CO, H2), asphyxiation (N2, Ar) | Gas detection systems, Safety interlocks, Ventilation, Respiratory protection |
| Mechanical/Electrical Risks | Pinch points, electrical shock, equipment movement | Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), Safety interlocks, Emergency stop buttons, Training |
Ensure your lab's heat treatment processes are safe and compliant. The right equipment is fundamental to a robust safety program. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, reliable lab furnaces and safety systems designed to mitigate thermal, atmospheric, and electrical risks. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and understand the critical safety features needed for your specific applications.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your laboratory's heat treatment safety and equipment needs. Let us help you protect your team and your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does arc melting equipment facilitate the preparation of refractory multi-principal element alloys (RMPEAs)?
- What role do high-temperature furnaces play in RAFM steel pretreatment? Achieve Precise Microstructural Stability
- What is a sintering process? A Guide to Fusing Powders into High-Performance Parts
- Can aluminum be brazed? Mastering the Oxide Layer for Strong Joints
- How does the cooling rate control of a furnace influence slow-cooled solid-state electrolytes? Achieve Crystal Perfection
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum annealing furnace play in Zircaloy post-treatment? Enhance Oxide Stability
- What is the safety factor of a vacuum chamber? Ensuring Structural Integrity Against Implosion



















