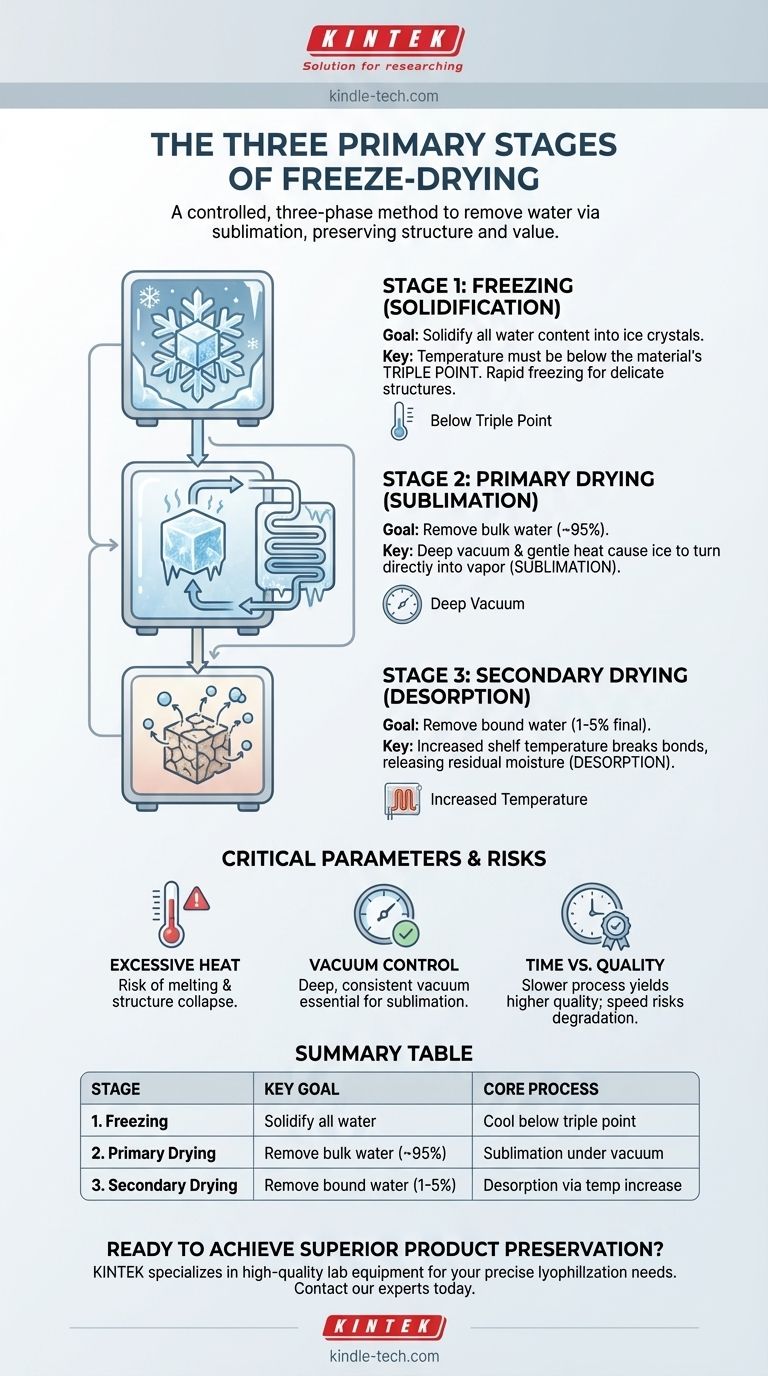
At its core, the freeze-drying process consists of three distinct stages: Freezing, Primary Drying, and Secondary Drying. This controlled, three-phase method removes water from a product by first freezing it, then converting the ice directly into vapor under a deep vacuum, and finally removing any remaining bound moisture. The result is a perfectly preserved product with its original structure, color, and nutritional value intact.
Freeze-drying is not simply dehydration; it is a precise manipulation of temperature and pressure to bypass the liquid state of water. This process of sublimation—turning solid ice directly into vapor—is the key to preserving a material's delicate structure without damage.

The Physics of Preservation: A Stage-by-Stage Breakdown
To truly understand freeze-drying, you must understand the goal of each stage and the physical principles at play. It is a sequence designed to gently remove water without the destructive forces of liquid-phase evaporation.
Stage 1: The Freezing Phase (Solidification)
The first step is to completely freeze the material. The goal is to solidify all water content into ice crystals, preparing it for the sublimation phase.
The temperature must be lowered below the material’s triple point—the unique temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist as a solid, liquid, and gas simultaneously. Getting the product colder than this point ensures that when pressure is later reduced, the ice will turn into vapor rather than melt into liquid.
The rate of freezing is also a critical parameter. Rapid freezing creates small ice crystals, which is ideal for preserving delicate biological structures. Slower freezing creates larger, less-uniform crystals that can damage cell walls but may speed up the subsequent drying process.
Stage 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
This is the longest and most energy-intensive stage, where the bulk of the water is removed. With the material frozen solid, two things happen: a deep vacuum is applied, and a small, controlled amount of heat is introduced.
This combination of low pressure and gentle heat gives the frozen water molecules enough energy to break free and transition directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (water vapor). This process is called sublimation.
The water vapor is then drawn away from the product and collected on a condenser, a surface within the freeze-dryer that is kept at an even colder temperature. Here, the vapor instantly turns back into ice, effectively trapping it and preventing it from re-contaminating the product. This phase removes approximately 95% of the water.
Stage 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
After primary drying, a small amount of water remains, tightly bound to the material's molecules through a process called adsorption. The final stage, secondary drying, is designed to remove this residual moisture.
During this phase, the vacuum is maintained while the shelf temperature is gradually increased, sometimes above 0°C. This extra energy breaks the bonds between the water molecules and the material, a process known as desorption.
Removing this bound water is crucial for ensuring the final product is shelf-stable and will not degrade over time. Completing this stage results in a final water content of just 1-5%.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
Achieving a perfect result with freeze-drying requires balancing competing factors. Mismanagement of key variables can compromise or ruin the product.
The Risk of Excessive Heat
The most common failure point is applying too much heat during primary drying. If the product temperature rises above its critical collapse point, the ice matrix will melt instead of sublimating. This causes the product's structure to collapse, resulting in shrinkage, poor rehydration properties, and a loss of quality.
The Importance of Vacuum Control
A deep and consistent vacuum is non-negotiable for sublimation. If the vacuum level is not low enough, the pressure will be too high for sublimation to occur at a low temperature. Just like with excessive heat, this will cause the ice to melt, defeating the entire purpose of the process.
The Balance of Time vs. Quality
While a slower, more methodical process yields the highest quality results, it is also more time-consuming and expensive. In commercial settings, there is often pressure to speed up the cycle. This can be done by using larger ice crystals (from slower freezing) or by pushing the temperature limits during drying, but both carry the risk of slightly degrading the final product's quality.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which stage and parameters you need to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is preserving delicate biological structures (e.g., pharmaceuticals, bacteria): Your priority is a very rapid freezing rate and meticulous temperature control during primary drying to prevent collapse.
- If your primary focus is bulk food preservation with good quality: Your priority is optimizing the primary drying stage for efficiency without crossing the product's collapse temperature.
- If your primary focus is maximum long-term shelf stability: Your priority is ensuring the secondary drying stage is run to completion to remove all bound water molecules.
By controlling the transition of water through its physical states, you can achieve a level of preservation that other drying methods cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Goal | Core Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Freezing | Solidify all water content | Cool material below its triple point |
| 2. Primary Drying | Remove bulk water (~95%) | Sublimation (ice to vapor) under vacuum |
| 3. Secondary Drying | Remove bound water (1-5% final) | Desorption via increased temperature |
Ready to achieve superior product preservation with a freeze-drying process tailored to your specific needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for laboratories. Whether you are preserving delicate biological samples, optimizing food quality, or ensuring maximum shelf stability, our expertise and reliable equipment are designed to support your precise lyophilization requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your freeze-drying process and achieve perfect results every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP



















