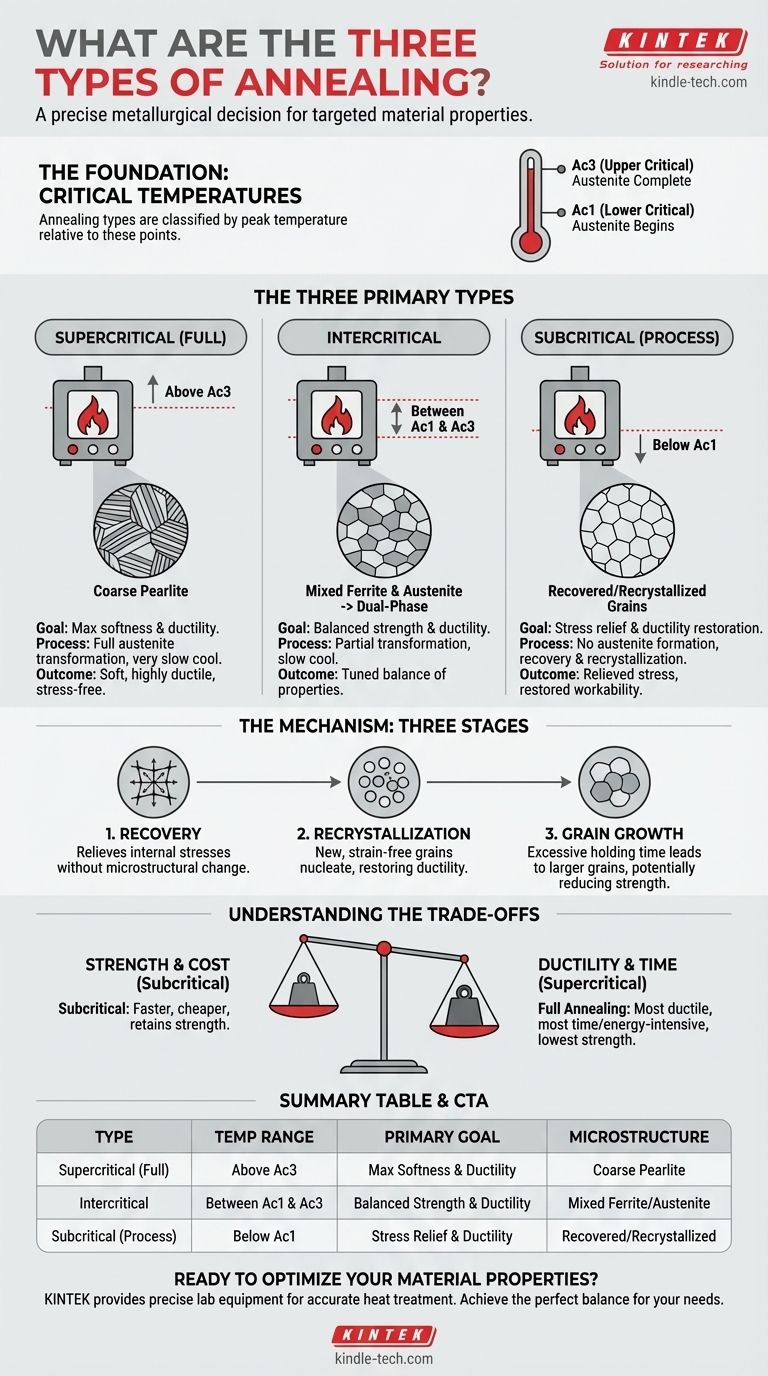
At its core, annealing is a heat treatment process defined by heating a material to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it slowly. The three primary types of annealing, distinguished by the temperature used relative to the material's critical transformation points, are supercritical (full) annealing, intercritical annealing, and subcritical annealing. These processes are used to alter the microstructure of a material, primarily to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable.
The specific type of annealing chosen is not arbitrary; it is a precise metallurgical decision. The goal is to achieve a target microstructure and its corresponding mechanical properties by carefully controlling temperature relative to the material's critical phase transformation points.

Understanding the Foundation: Critical Temperatures
To understand the different types of annealing, you must first understand the critical transformation temperatures in steel, which are points on the iron-carbon phase diagram.
The Ac1 Temperature (Lower Critical)
Ac1 is the temperature at which a steel structure begins to transform into a phase called austenite upon heating. Below this temperature, no significant phase transformation occurs.
The Ac3 Temperature (Upper Critical)
Ac3 is the temperature at which the transformation of the steel's microstructure into austenite is complete. Heating above this point ensures the entire material has a uniform austenitic structure before cooling.
The Three Primary Annealing Processes
The classification of the main annealing types is based entirely on where the peak temperature of the process falls in relation to these two critical points.
Supercritical (Full) Annealing
This process involves heating the steel to a temperature above the upper critical (Ac3) point.
This ensures the entire microstructure is transformed into austenite. The material is then cooled very slowly, resulting in a coarse pearlite structure that is soft, highly ductile, and free of internal stresses. When the term "annealing" is used without any other qualifier, it typically implies a full anneal.
Intercritical Annealing
In this process, the steel is heated to a temperature between the lower (Ac1) and upper (Ac3) critical points.
This causes only a partial transformation, resulting in a mixed microstructure of the original phase (ferrite) and the newly formed austenite. Slow cooling then transforms the austenite, creating a dual-phase material with a specific balance of strength and ductility.
Subcritical Annealing
Also known as process annealing, this involves heating the steel to a temperature just below the lower critical (Ac1) point.
Since the temperature never reaches the transformation point, no austenite is formed. The primary purpose is to relieve internal stresses and induce recovery and recrystallization in materials that have been hardened by cold working, thereby restoring ductility without significantly altering the base microstructure or strength.
The Mechanism of Change: Three Stages of Annealing
While not "types" of processes, these three stages describe the metallurgical changes that happen within the material as it is heated.
Stage 1: Recovery
At lower temperatures, the first thing to occur is recovery. This process relieves internal stresses stored in the crystal lattice from processes like cold working, without any significant change to the material's grain structure.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature increases (especially during subcritical annealing), recrystallization begins. New, strain-free grains nucleate and grow, replacing the old, deformed grains. This is what restores ductility and reduces hardness.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
If the material is held at the annealing temperature for too long, the newly formed grains will continue to grow larger. Excessive grain growth is often undesirable as it can reduce the material's strength and toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an annealing process requires balancing desired outcomes with practical constraints.
Strength vs. Ductility
This is the primary trade-off. Full (supercritical) annealing produces the softest, most ductile state, but at the cost of the lowest strength. Subcritical annealing offers a compromise, restoring a good amount of ductility while retaining more of the material's original strength.
Time, Energy, and Cost
Full annealing requires heating to the highest temperatures and often involves the slowest cooling rates, making it the most time-consuming and energy-intensive process. Subcritical annealing is faster and cheaper because it operates at lower temperatures.
The Problem of Naming Conventions
You will encounter many other names for annealing, such as "bright annealing," "box annealing," or "spheroidizing." These terms do not typically describe new metallurgical types. Instead, they usually refer to the equipment used (box furnace), the resulting surface finish (bright, oxide-free), or a very specific microstructure goal (spheroidite), but the underlying process is still one of the three primary types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of annealing process should be directly tied to your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and workability: Use supercritical (full) annealing to completely reset the microstructure and achieve the highest possible ductility.
- If your primary focus is to relieve stress from cold working: Use subcritical (process) annealing to restore ductility for further forming operations without a major loss in strength.
- If your primary focus is to develop a specific dual-phase structure: Use intercritical annealing to precisely control the phase mixture for a targeted balance of properties.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heat treatment is about understanding the properties you need and knowing which thermal process will create the microstructure to deliver them.
Summary Table:
| Type of Annealing | Temperature Range | Primary Goal | Resulting Microstructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supercritical (Full) | Above Ac3 | Maximum softness and ductility | Coarse pearlite |
| Intercritical | Between Ac1 and Ac3 | Balanced strength and ductility | Mixed ferrite and austenite |
| Subcritical (Process) | Below Ac1 | Stress relief and ductility restoration | Recovered/recrystallized grains |
Ready to Optimize Your Material Properties?
Choosing the right annealing process is critical for achieving your desired material performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise laboratory equipment and consumables needed for accurate heat treatment processes. Whether you're working with metals in R&D or production, our solutions ensure you can achieve the perfect balance of strength, ductility, and microstructure.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your annealing needs. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main source of biochar? Unlock the Power of Sustainable Feedstocks
- Can you extract THC without heat? Yes, and here’s how to preserve terpenes and potency.
- Is biomass a sustainable energy option? Unlocking a Truly Sustainable Energy Future
- What role does an ultrasonic homogenizer play in the preparation of nickel nanoparticle colloids? Enhance Dispersion
- What are the two structures of molds? Understanding Hyphae and Mycelium
- Why is heating rate control essential for LOCA simulation tests? Ensure Precision in Nuclear Safety Research
- What are the properties of isotropic graphite? A Guide to Its Uniform Strength & Thermal Performance
- Where is soldering commonly used? From Everyday Electronics to Industrial Applications



















