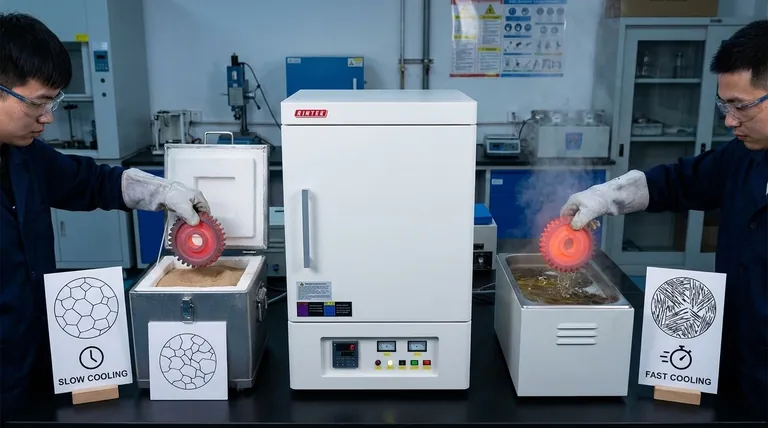
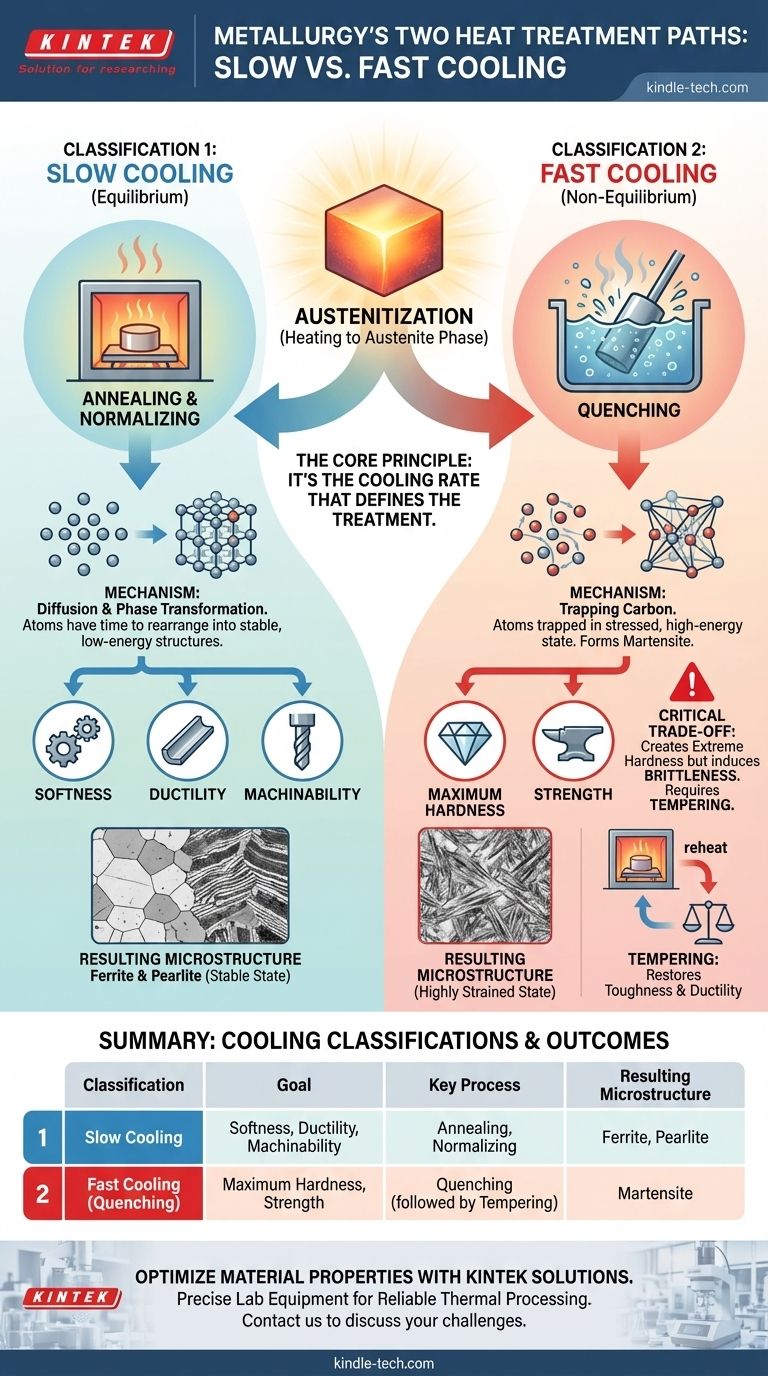
In metallurgy, all heat treatments fall into two primary classifications based on their cooling rate from a high temperature. These are slow cooling processes (like annealing) and fast cooling processes (known as quenching). The first category aims to create a soft, ductile material by allowing the metal's internal structure to form in a stable, low-energy state. The second category intentionally freezes the structure in an unstable, high-energy state to achieve maximum hardness and strength.
The core principle is simple: it's not the heating that defines the treatment, but the cooling. Slow cooling allows atoms to move into stable, soft arrangements, while rapid cooling traps them in a stressed, hard configuration. Your choice between these two paths dictates the final balance of strength and ductility in the metal.

The Foundation: Why We Heat Treat Metal
Heat treatment is the controlled heating and cooling of metals to manipulate their properties. It's not about changing the chemical composition, but about rearranging the internal crystal structure, or microstructure.
The Critical First Step: Austenitization
Nearly all hardening and softening heat treatments for steel begin with the same step: heating the metal into the austenite phase. Austenite is a specific crystal structure of iron that can dissolve a significant amount of carbon. This creates a uniform, solid solution, setting the stage for the transformation that occurs during cooling.
The Role of the Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram
This diagram is the roadmap for heat treating steel. It shows which microstructures (like ferrite, pearlite, or austenite) are stable at different temperatures and carbon concentrations. Understanding this map is key to predicting how a metal will respond to a given thermal cycle.
Classification 1: Slow Cooling (Equilibrium) Processes
This category involves cooling the metal slowly enough that the atoms have time to diffuse and rearrange themselves into the most stable, low-energy microstructures. These processes are sometimes called "equilibrium" treatments because the resulting structure is close to what the phase diagram predicts for a slow cool.
The Goal: Softness, Ductility, and Machinability
The primary purpose of slow cooling is to make the metal as soft and ductile as possible. This relieves internal stresses, improves machinability, and prepares the material for subsequent forming operations like bending or stamping.
The Mechanism: Diffusion and Phase Transformation
As the austenitic steel cools slowly, carbon atoms have ample time to move out of the iron crystal lattice. This controlled diffusion allows for the formation of soft microstructures like ferrite (pure iron) and pearlite (a layered structure of ferrite and iron carbide).
Common Examples: Annealing and Normalizing
Annealing is the quintessential slow-cooling process, involving cooling the part inside the furnace to produce the softest possible state. Normalizing involves cooling the part slightly faster, in still air, which refines the grain structure and produces a slightly stronger, yet still ductile, material.
Classification 2: Fast Cooling (Non-Equilibrium) Processes
This category involves cooling the metal so rapidly that the atoms do not have time to rearrange into their preferred stable state. This is a "non-equilibrium" process because it creates a microstructure that does not appear on the standard phase diagram.
The Goal: Maximum Hardness and Strength
The sole objective of fast cooling, or quenching, is to dramatically increase the hardness and strength of the steel. This is essential for applications requiring high wear resistance and load-bearing capacity, such as gears, bearings, and cutting tools.
The Mechanism: Trapping Carbon to Form Martensite
During a rapid quench (in water, oil, or air), the dissolved carbon atoms are trapped within the iron crystal lattice. They don't have time to diffuse out. This forces the structure to transform into a highly strained, needle-like microstructure called martensite. It is this immense internal strain that makes martensite exceptionally hard and strong, but also very brittle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment is never about getting "the best" properties; it's about achieving the right balance for a specific application.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
The formation of martensite through quenching creates extreme hardness, but at a significant cost: brittleness. A fully hardened, as-quenched steel part is often too brittle for practical use and can shatter like glass under impact.
Why Tempering Is Almost Always Required
To overcome this brittleness, quenched parts are almost always subjected to a secondary heat treatment called tempering. This involves reheating the part to a lower temperature, which relieves some of the internal stress and allows the martensite to transform slightly, regaining a crucial amount of toughness and ductility while sacrificing only a small amount of hardness.
The Impact of Alloying Elements
The specific cooling rate required to form martensite depends on the steel's alloy content. Plain carbon steels require a very fast quench, while steels with alloys like chromium or molybdenum (alloy steels) can be hardened with a much slower cooling rate, even in air. This is known as the steel's hardenability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment classification is dictated entirely by the desired end-state properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: You require a slow cooling process like full annealing to achieve the softest, most ductile state.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant, high-strength part: You must use a fast cooling process (quenching) to create martensite, followed immediately by tempering to restore toughness.
- If your primary focus is refining grain structure and relieving stress from prior work: You should use a normalizing process, which provides a good balance of strength and ductility.
By understanding these two fundamental cooling paths, you gain direct control over the final microstructure and performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Goal | Key Process | Resulting Microstructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Cooling | Softness, Ductility, Machinability | Annealing, Normalizing | Ferrite, Pearlite |
| Fast Cooling (Quenching) | Maximum Hardness, Strength | Quenching (followed by Tempering) | Martensite |
Need to optimize your material's properties? The right heat treatment is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable thermal processing. Whether you're annealing for softness or quenching for hardness, our solutions ensure accuracy and repeatability for your laboratory. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your heat treatment challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the precautions for heat in the laboratory? Essential Safety Rules to Prevent Burns and Fires
- In which industry is the muffle furnace used? Discover Its Role in Science and Industry
- What is the difference between oven and muffle furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Equipment
- What are the safety precautions for heat experiment? Essential Steps to Prevent Lab Burns and Accidents
- What happens after calcination? A Guide to Material Transformation and Next Steps



















