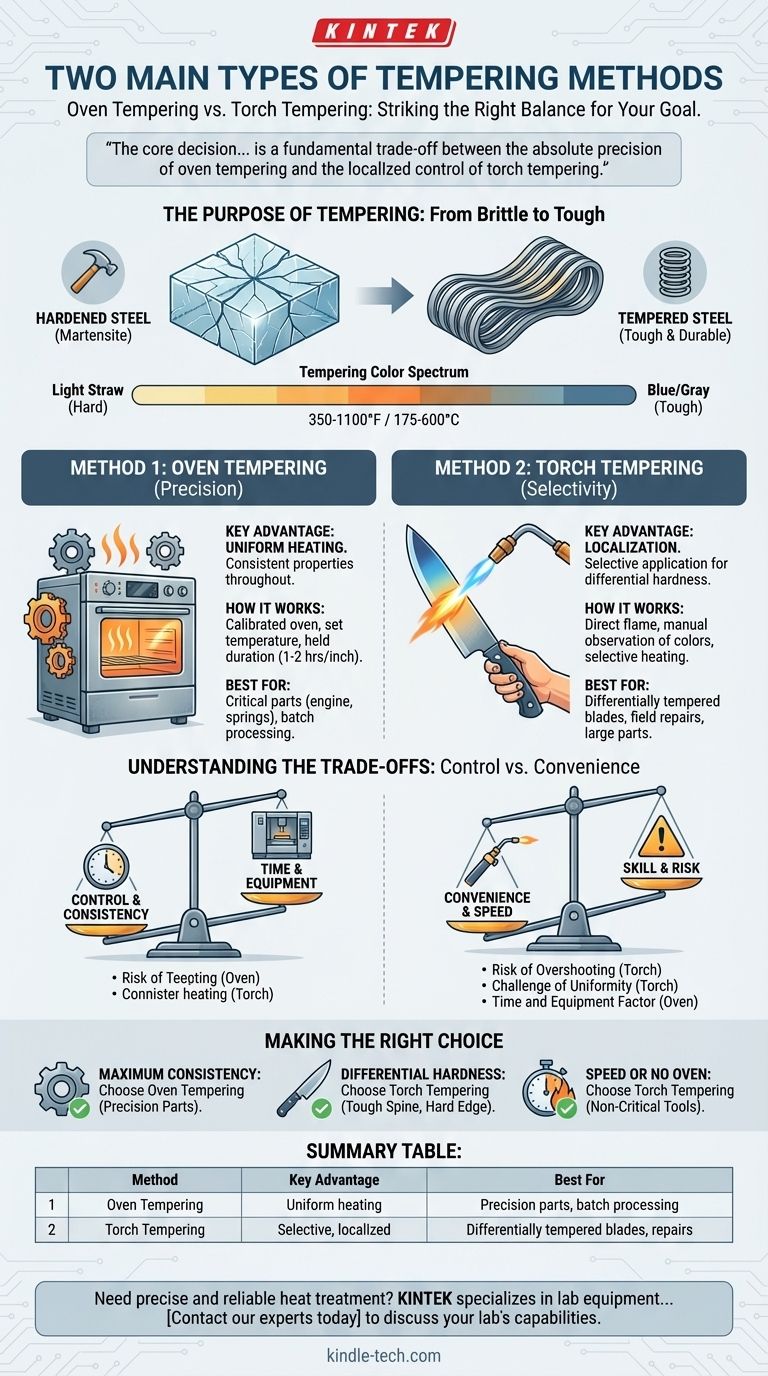
In professional heat treatment, the two principal methods for tempering steel are oven tempering and torch tempering. Oven tempering provides uniform heat in a highly controlled environment, making it ideal for precision and consistency. In contrast, torch tempering uses a direct flame for localized heat application, valued for its speed and ability to create differential hardness within a single workpiece.
The core decision between tempering methods is not about which is "better," but which offers the right balance for your goal. It is a fundamental trade-off between the absolute precision of oven tempering and the localized control of torch tempering.

The Purpose of Tempering: From Brittle to Tough
Tempering is a critical heat-treatment process that follows hardening (quenching). Without it, most hardened steel is too brittle for practical use.
From "Glass-Hard" to Useful
After quenching, steel is in its hardest possible state, known as martensite. While extremely hard and wear-resistant, it is also incredibly brittle, like glass, and filled with internal stresses from the rapid cooling. A sharp impact could cause it to shatter.
The Role of Temperature
Tempering is a low-temperature heating process (typically 350-1100°F or 175-600°C) that relieves these internal stresses. It allows some of the trapped carbon atoms to precipitate out, which reduces hardness slightly but dramatically increases the steel's toughness—its ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
The Tempering Color Spectrum
As steel heats, a thin layer of oxide forms on its surface. The thickness of this layer corresponds to the temperature, creating a predictable spectrum of colors, from a light straw yellow (lower temperature, higher hardness) to blue and gray (higher temperature, lower hardness, higher toughness). This visual guide is essential for manual tempering.
Method 1: Oven Tempering for Precision
Oven tempering is the industrial standard for components where consistency and predictable performance are non-negotiable.
How It Works
The hardened steel part is placed in a calibrated heat-treating oven or a domestic oven (for some applications). The oven is set to a precise temperature that corresponds to the desired final hardness and is held there for a specific duration, typically one to two hours per inch of thickness.
The Key Advantage: Uniformity
The primary benefit is uniform heating. The entire component is brought to the target temperature evenly, ensuring that the final mechanical properties—hardness and toughness—are consistent throughout the entire part.
When to Use an Oven
This method is the only choice for critical parts like engine components, precision dies, and springs. It is also ideal when treating batches of identical parts to ensure they all have the same performance characteristics.
Method 2: Torch Tempering for Selectivity
Torch tempering is a more manual, skill-based technique favored by bladesmiths, blacksmiths, and for field repairs.
How It Works
This method involves applying heat directly to the steel using a torch, such as oxy-acetylene or propane. The operator carefully watches the temper colors travel across the polished surface of the steel, removing the heat once the desired color is reached in a specific area.
The Key Advantage: Localization
Torch tempering's unique strength is selective application. You can temper one part of a tool while leaving another part harder. A classic example is a knife, where the spine is tempered to a soft blue (for toughness) while the cutting edge is kept at a light straw (for hardness and edge retention).
When to Use a Torch
This is the go-to method for creating a differentially tempered blade. It is also useful for large parts that will not fit in an oven or for quick repairs on tools where absolute precision is secondary to getting the job done.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Control vs. Convenience
Choosing a method requires acknowledging the inherent compromises of each approach.
The Risk of "Overshooting"
Torch tempering is highly dependent on operator skill. It is very easy to apply too much heat too quickly, "overshooting" the target temperature and making the steel too soft. This mistake is often irreversible without re-hardening the entire piece.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving a perfectly even temper across a large, flat surface with a torch is extremely difficult. Hot spots are common, leading to inconsistent hardness and potential weak points in the material.
The Time and Equipment Factor
Oven tempering is "set it and forget it." While the process takes longer, it requires less active skill and is highly repeatable. The primary barrier is the need for a calibrated oven, whereas a torch is a more common and portable tool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the intended function of the steel component.
- If your primary focus is maximum consistency and repeatability: Choose oven tempering for its unparalleled temperature control and uniform results, essential for critical components.
- If your primary focus is differential hardness on a single part: Choose torch tempering for its unique ability to apply heat selectively, creating a tough spine and a hard edge on tools like knives and axes.
- If your primary focus is speed or you lack a calibrated oven: Torch tempering is an effective and efficient method for non-critical tools, provided you develop the skill to read the temper colors accurately.
Understanding the principles behind each method allows you to select the right process to transform brittle steel into a durable, reliable tool.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Oven Tempering | Uniform heating for consistent hardness | Precision parts, batch processing, critical components |
| Torch Tempering | Selective, localized heat application | Differentially tempered blades, field repairs, large parts |
Need precise and reliable heat treatment for your laboratory components?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise for consistent, high-quality results. Whether you require the uniform heating of an industrial oven or specialized tools for detailed work, we have the solutions to meet your laboratory's specific tempering and heat treatment needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure your materials meet the highest standards of performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace for ash determination? Key Insights for Accurate Results
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- Is a muffle furnace used for ash determination? Discover Its Critical Role in Accurate Analysis
- What are the safety precautions for using a muffle furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- What is the process of dry ashing of sample treatment? A Guide to High-Temperature Mineral Analysis



















