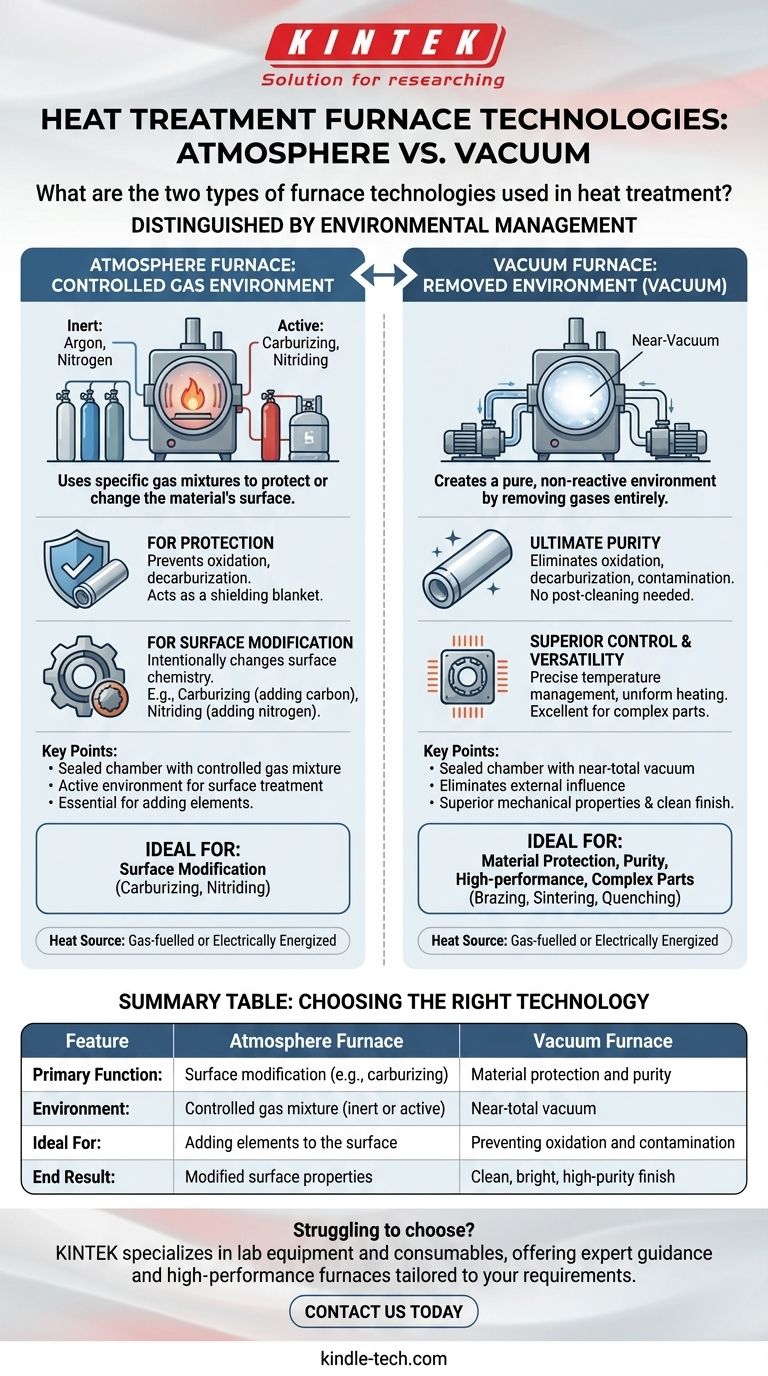
At its core, the two primary furnace technologies used in heat treatment are distinguished by how they manage the environment surrounding the material. The fundamental choice is between using a controlled gas environment, known as an Atmosphere Furnace, or removing the environment entirely, which is done in a Vacuum Furnace. The selection between these two is determined by the specific surface chemistry and material properties required for the final product.
The critical distinction is not just how the furnace is heated, but what happens inside. Atmosphere furnaces actively use gases to protect or change a material's surface, while vacuum furnaces create a pure, non-reactive environment by removing those gases altogether.
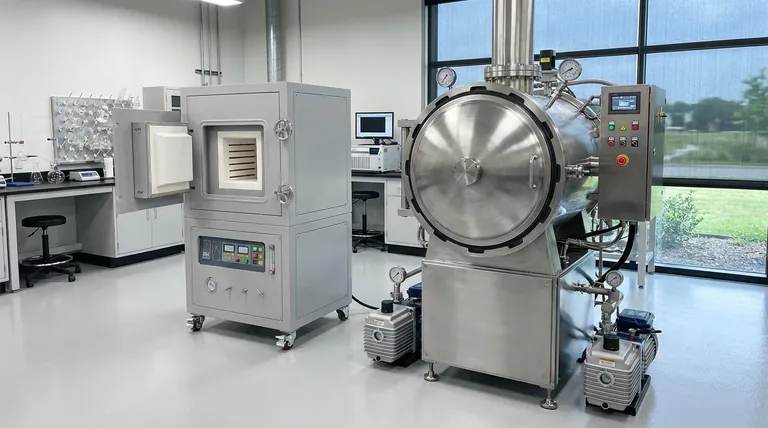

Understanding Atmosphere Furnaces
Atmosphere furnaces are sealed chambers where the air is replaced with a specific, carefully controlled mixture of gases. This "atmosphere" is a critical part of the heat treatment process itself.
The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
The primary goal is to control the surface chemistry of the component being treated. Simply heating a metal in air would cause it to react with oxygen, leading to unwanted scaling and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel).
Using Atmospheres for Protection
An inert atmosphere, using gases like argon or nitrogen, prevents these undesirable reactions. It acts as a protective blanket, shielding the material from oxygen and other reactive elements during the high-temperature cycle.
Using Atmospheres for Surface Modification
An active atmosphere is used to intentionally change the surface of the material. By introducing specific chemical species, you can achieve unique properties. This includes processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen) to harden the surface of a steel component.
The Alternative: Vacuum Furnaces
A vacuum furnace operates on the opposite principle. Instead of introducing a specific gas, it uses powerful pumps to remove nearly all of the air and gas from the sealed chamber, creating a near-vacuum.
The Core Advantage: Ultimate Purity
By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum furnace eliminates the risk of oxidation, decarburization, and contamination. This results in a clean, bright, and high-purity end product without the need for post-treatment cleaning.
Superior Process Control
The vacuum environment allows for extremely precise temperature management and highly uniform heating. With no atmosphere to interfere, heat is transferred efficiently and evenly, which is critical for complex parts and sensitive materials.
High Versatility of Processes
This controlled environment is ideal for a wide range of advanced processes. Vacuum furnaces are frequently used for high-demand applications like vacuum brazing, sintering, and quenching, where component integrity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between an atmosphere and vacuum furnace is driven by the desired outcome, cost, and the material being processed. Neither is universally superior; they are tools for different jobs.
When to Choose an Atmosphere Furnace
Atmosphere furnaces are the standard for processes that require adding elements to a material's surface. If your goal is carburizing or nitriding, an active atmosphere is not just an option—it's a fundamental requirement of the process.
When to Choose a Vacuum Furnace
Vacuum furnaces excel when the primary goal is to protect the material from any external influence. They produce components with superior mechanical properties and a clean finish, making them ideal for high-performance, critical applications where purity is non-negotiable.
The Heat Source: Gas vs. Electric
It is also important to note that both atmosphere and vacuum furnaces require a heat source. This is typically either gas-fuelled or electrically energized. The choice of heat source often depends on operational costs, required temperature precision, and the specific furnace design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be based entirely on the metallurgical outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is surface modification (adding elements): An Atmosphere Furnace is the essential tool for processes like carburizing and nitriding.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface reaction or contamination: A Vacuum Furnace provides the purest, most controlled environment for achieving superior material properties.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive or complex parts: A Vacuum Furnace offers unmatched uniformity and precision in heating and cooling.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace technology means choosing the ideal environment to produce the exact material characteristics your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Atmosphere Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Surface modification (e.g., carburizing, nitriding) | Material protection and purity |
| Environment | Controlled gas mixture (inert or active) | Near-total vacuum |
| Ideal For | Adding elements to the surface | Preventing oxidation and contamination |
| End Result | Modified surface properties | Clean, bright, high-purity finish |
Struggling to choose the right furnace technology for your specific heat treatment needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and high-performance furnaces tailored to your laboratory's requirements. Whether you need precise surface modification with an atmosphere furnace or ultimate material purity with a vacuum furnace, we have the solution. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process



















