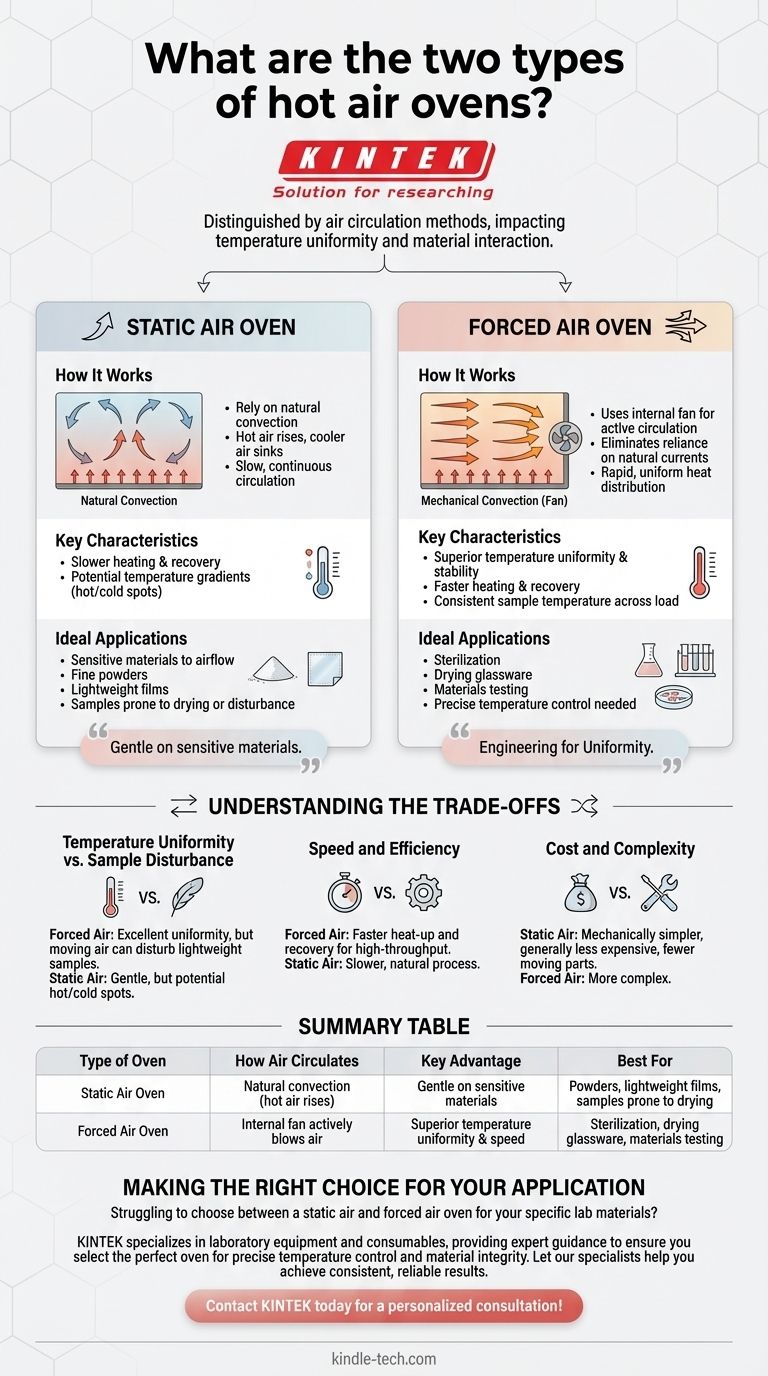
The two fundamental types of hot air ovens are distinguished by how they circulate air: the static air oven and the forced air oven. A static air oven relies on natural convection, where hot air rises and cooler air sinks on its own. A forced air oven, often considered more effective, uses an internal fan to actively circulate hot air, ensuring a more uniform temperature throughout the chamber.
Your choice between a static or forced air oven is a direct trade-off between temperature uniformity and air disturbance. Forced air provides superior heat consistency for most applications, while static air is essential for sensitive materials that cannot withstand air currents.

The Static Air Oven: Relying on Natural Convection
How It Works
In a static air oven, heating elements are typically located at the bottom of the chamber. As the air near these elements heats up, it becomes less dense and naturally rises. Upon reaching the top, it cools, becomes denser, and sinks, creating a slow, continuous circulation pattern.
Key Characteristics
This natural convection process results in slower heating times and recovery after a door opening. More importantly, it can create temperature gradients, meaning "cold spots" and "hot spots" can exist within the oven chamber at the same time.
Ideal Applications
Static air ovens are best suited for processing materials that are sensitive to airflow. This includes fine powders, lightweight films, or any sample that could be disturbed or dried out by a fan.
The Forced Air Oven: Engineering for Uniformity
How It Works
A forced air oven, also known as a mechanical convection oven, adds a fan to the heating system. This fan actively blows the heated air throughout the chamber, eliminating the reliance on natural air currents.
Key Characteristics
The primary benefit is superior temperature uniformity and stability. This design heats up much faster and recovers its target temperature more quickly after the door is opened. It ensures that all samples, regardless of their position, experience the same temperature.
Ideal Applications
This is the standard for most laboratory and industrial applications. It is critical for processes like sterilization, drying glassware, and materials testing where precise and consistent temperature across the entire sample load is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Uniformity vs. Sample Disturbance
A forced air oven provides excellent temperature uniformity, which is critical for repeatable results in sterilization or testing. However, the moving air can be a significant problem for powders or lightweight samples, potentially blowing them around the chamber.
Speed and Efficiency
Forced air ovens are far more efficient for high-throughput work. Their rapid heat-up and temperature recovery times mean less waiting and more consistent processing cycles compared to the slower, natural process of a static oven.
Cost and Complexity
Static air ovens are mechanically simpler, containing no fans or motors for circulation. This generally makes them less expensive to purchase and maintain, as there is one less component that can fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The correct oven depends entirely on the nature of what you are heating.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature uniformity and speed: Choose a forced air oven for reliable sterilization, materials testing, or drying applications.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: Choose a static air oven for powders, lightweight items, or samples prone to drying out from direct airflow.
- If you need to minimize cross-contamination: A static air oven may be preferable as a fan can potentially circulate airborne particulates from one sample to another.
Ultimately, matching the oven's air circulation method to the physical requirements of your material is the key to achieving successful and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Type of Oven | How Air Circulates | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static Air Oven | Natural convection (hot air rises) | Gentle on sensitive materials | Powders, lightweight films, samples prone to drying |
| Forced Air Oven | Internal fan actively blows air | Superior temperature uniformity & speed | Sterilization, drying glassware, materials testing |
Struggling to choose between a static air and forced air oven for your specific lab materials? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to ensure you select the perfect oven for precise temperature control and material integrity. Let our specialists help you achieve consistent, reliable results. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
















