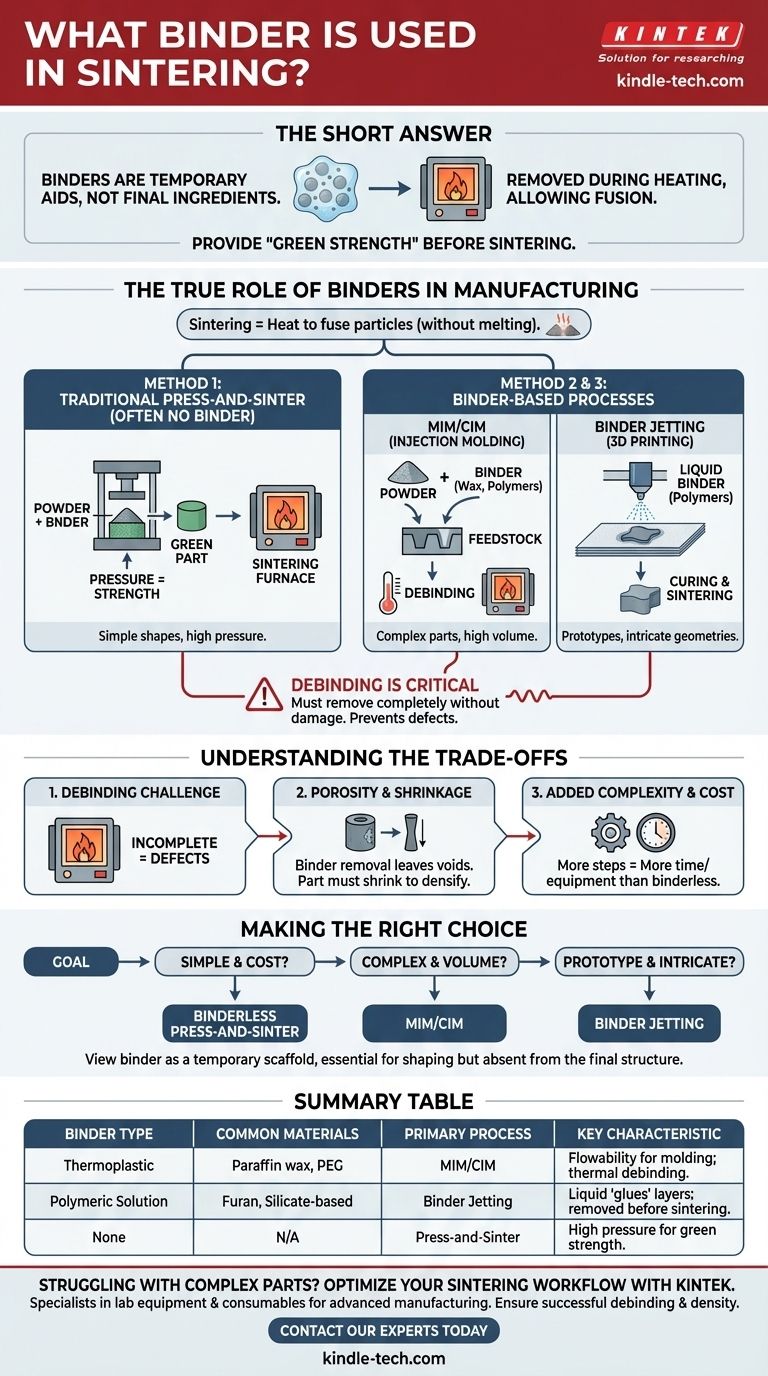
The short answer is that binders are not always required for sintering, but when they are, the most common types are temporary organic materials like polymers and waxes. These binders are used in specific manufacturing processes to hold metal or ceramic powder in a desired shape before the high-temperature sintering stage fuses the primary material together.
The critical distinction to understand is that a binder is a process aid, not a final ingredient. Its primary job is to provide temporary "green strength" to a part, after which it is completely removed during the heating process, allowing the base material particles to fuse permanently.

The True Role of Binders in Manufacturing
Sintering, at its core, is the process of using heat to fuse particles of a material—like metal, ceramic, or polymer—without melting it completely. The goal is to create a solid, dense object from a powder.
Binders are introduced only when the manufacturing method requires the powder to be shaped in a way that mechanical pressure alone cannot achieve.
Method 1: Traditional Press-and-Sinter (Often No Binder)
In the most common form of sintering, a fine powder of a material like stainless steel or iron is simply poured into a die and compacted under immense pressure.
This pressure is often sufficient to create a fragile, preliminary shape called a "green part." This part has enough structural integrity to be carefully handled and moved to a furnace for the final sintering. In this case, no binder is needed.
Method 2: Metal and Ceramic Injection Molding (MIM/CIM)
For creating small, highly complex parts in high volumes, injection molding is ideal. To make a metal or ceramic powder flow like a plastic, it must be mixed with a significant amount of binder.
This mixture, called feedstock, typically uses a multi-component binder system. Common binders here include paraffin wax, carnauba wax, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and other thermoplastics. The binder allows the material to be molded, and is then carefully removed in a subsequent debinding step before final sintering.
Method 3: Binder Jetting (Additive Manufacturing)
Binder jetting is a 3D printing process that builds objects layer by layer from a powder bed.
A liquid binding agent is selectively sprayed from a print head onto the powder, "gluing" the particles together according to the digital design. Common liquid binders for this process are proprietary but often involve aqueous solutions with polymers like furan or silicate-based agents. The completed "green part" is then cured and sintered to burn away the binder and densify the object.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Using Binders
While binders enable the creation of complex geometries, they introduce necessary compromises and additional process steps that are crucial to understand.
The Debinding Step is Critical
The most significant challenge is the debinding stage. The binder must be removed completely without disturbing the fragile arrangement of the powder particles.
This is typically done through thermal burnout or chemical solvents. Incomplete binder removal can lead to contamination, high porosity, and poor mechanical properties in the final part.
Impact on Porosity and Shrinkage
As the binder is removed, it leaves behind empty space, or porosity, between the material particles.
During the final sintering stage, the part must shrink significantly to close these voids and achieve high density. This shrinkage must be precisely predicted and controlled to meet dimensional tolerances.
Added Process Complexity and Cost
Incorporating binders and requiring a debinding step adds time, equipment cost, and complexity to the overall manufacturing workflow compared to simpler press-and-sinter methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a binder is dictated entirely by the desired part geometry and the manufacturing process chosen to achieve it.
- If your primary focus is simple shapes and cost-effective mass production: Binderless press-and-sinter is the most direct and efficient method.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex, small-to-medium sized parts: A binder-based process like Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is producing one-off prototypes or intricate custom geometries: Additive manufacturing methods like binder jetting are the ideal choice.
Ultimately, viewing the binder as a temporary scaffold—essential for certain construction methods but absent from the final structure—is the correct mental model.
Summary Table:
| Binder Type | Common Materials | Primary Manufacturing Process | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Paraffin wax, Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) | Metal/Ceramic Injection Molding (MIM/CIM) | Provides flowability for molding; removed via thermal debinding |
| Polymeric Solution | Furan, Silicate-based agents | Binder Jetting (Additive Manufacturing) | Liquid binder 'glues' powder layers; removed before sintering |
| None | Not applicable | Traditional Press-and-Sinter | Simple shapes; high pressure provides green strength without binder |
Struggling to choose the right sintering process for your complex parts? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing. Our expertise in sintering and binder technologies can help you optimize your workflow for superior part density and dimensional accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure successful debinding and sintering results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- Why only KBr is used in IR spectroscopy? The Truth About the Best Material for Your Sample
- How do you do the KBr pellet method? A Step-by-Step Guide to Perfect FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- How do you prepare KBr pellets for FTIR analysis? Master the Technique for High-Quality IR Spectra



















