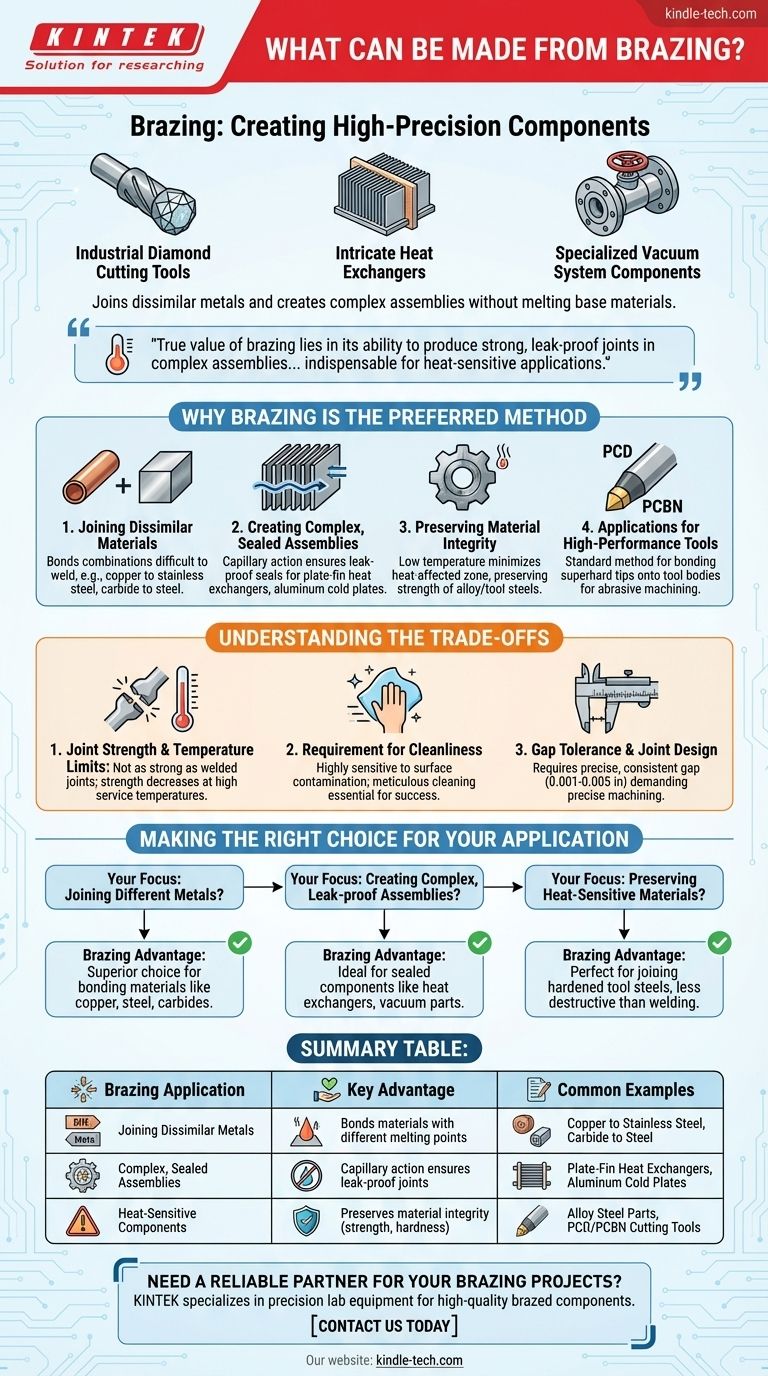
In short, brazing is used to create a vast range of high-precision components. This process excels at joining dissimilar metals and creating complex assemblies, making everything from industrial diamond cutting tools and intricate heat exchangers to specialized vacuum system components. Common examples include bonding copper to stainless steel, carbide tips to tool steel, and assembling aluminum cold plates.
The true value of brazing lies in its ability to produce strong, leak-proof joints in complex assemblies without melting the base materials, making it indispensable for heat-sensitive applications and joining dissimilar metals.

Why Brazing is the Preferred Method
Brazing is a joining process where a filler metal is melted and drawn into a joint between two base materials. The key is that the filler metal's melting point is lower than that of the base materials, so the parts themselves are never melted. This fundamental principle gives brazing its unique advantages.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Brazing is one of the most effective methods for joining materials with different properties and melting points.
Because the base materials do not melt, you can successfully join combinations that are difficult or impossible to weld, such as copper to stainless steel or a carbide cutting tip to a steel shank.
Creating Complex, Sealed Assemblies
The process relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the tight-fitting joint, ensuring complete coverage even in complex geometries.
This makes it ideal for manufacturing parts like plate-fin heat exchangers, aluminum cold plates, and other components that require a continuous, leak-proof seal across a large surface area.
Preserving Material Integrity
High-strength alloys, tool steels, and heat-treated components can lose their carefully engineered properties if melted.
Since brazing occurs at a lower temperature than welding and doesn't melt the base metal, it minimizes the heat-affected zone. This preserves the material's original strength, hardness, and other characteristics, which is critical for alloy steel and tool steel components.
Applications for High-Performance Tools
The manufacturing of superhard cutting tools relies heavily on brazing.
It is the standard method for bonding Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) and Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN) tips onto tool bodies, creating robust tools for machining abrasive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Joint Strength and Temperature Limits
A brazed joint is typically not as strong as a properly welded joint, which fuses the base metals together.
Additionally, the strength of a brazed joint decreases as the service temperature approaches the melting point of the filler metal, limiting its use in very high-temperature applications.
Requirement for Cleanliness
Brazing is highly sensitive to surface contamination. The base materials must be meticulously cleaned of oils, oxides, and other residues for the capillary action to work.
Any failure in preparation can lead to voids, incomplete joints, and a significant reduction in strength.
Gap Tolerance and Joint Design
The process requires a very specific, consistent gap between the parts to be joined (typically 0.001 to 0.005 inches).
This demands precise machining and fixturing, which can add complexity and cost to the manufacturing process compared to other joining methods that are more forgiving of poor fit-up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting brazing depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and materials.
- If your primary focus is joining different metals: Brazing is often the superior choice, allowing you to reliably bond materials like copper, steel, and carbides.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, leak-proof assemblies: The capillary action of brazing is ideal for manufacturing sealed components like heat exchangers and vacuum parts.
- If your primary focus is preserving the properties of heat-sensitive materials: Brazing is far less destructive than welding, making it perfect for joining hardened tool steels and other treated alloys.
Ultimately, brazing enables the creation of sophisticated components that would be impractical or impossible to produce with other methods.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Application | Key Advantage | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Joining Dissimilar Metals | Bonds materials with different melting points | Copper to Stainless Steel, Carbide to Steel |
| Complex, Sealed Assemblies | Capillary action ensures leak-proof joints | Plate-Fin Heat Exchangers, Aluminum Cold Plates |
| Heat-Sensitive Components | Preserves material integrity (strength, hardness) | Alloy Steel Parts, PCD/PCBN Cutting Tools |
Need a reliable partner for your brazing projects? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that require high-quality brazed components for demanding applications. Our expertise ensures strong, leak-proof joints in complex assemblies, perfect for your heat exchangers, cutting tools, and vacuum systems. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















