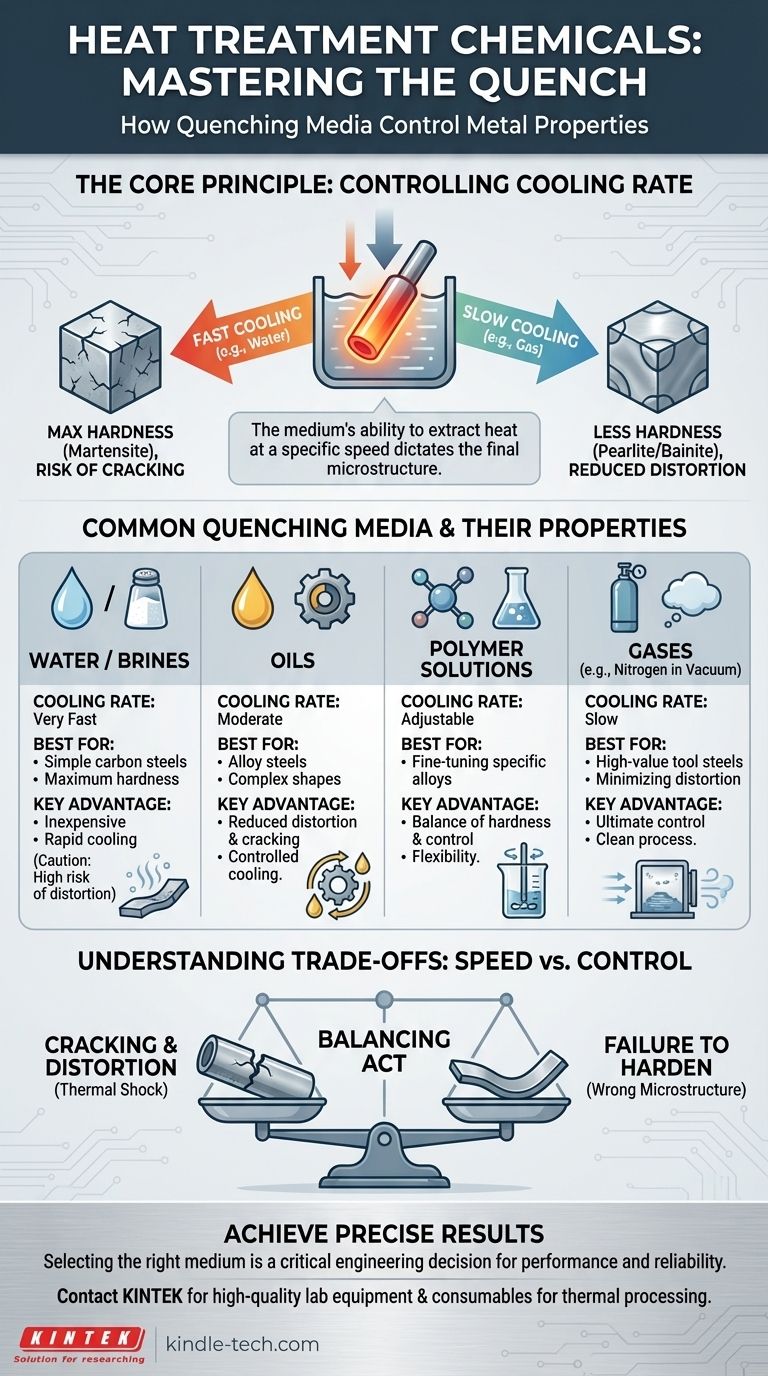
In heat treatment, the term "chemicals" primarily refers to the quenching media used to rapidly cool a metal part after it has been heated. The most common of these are water, oils, and specialized polymer solutions, each chosen to control the cooling rate and, therefore, the final properties of the metal, such as its hardness and ductility.
The core principle is not about the chemical itself, but its ability to extract heat at a specific speed. The choice of quenching medium is the most critical factor in controlling this cooling rate, which directly dictates whether the final metal component will be hard and brittle or softer and more ductile.

The Principle: Controlling the Cooling Rate
Heat treatment is a process of manipulating a metal's microscopic structure. By heating a steel part, for example, its crystalline structure changes. The goal of quenching is to "freeze" a desirable high-temperature structure, like austenite, by cooling it so quickly that it transforms into a very hard structure called martensite.
Why the Cooling Rate is Everything
The speed of cooling determines the final microstructure. A very fast cool creates maximum hardness but also introduces internal stresses that can cause warping or cracking.
A slower cool reduces these risks but may fail to achieve the required hardness. The quenching medium is the tool used to dial in the perfect cooling rate for a specific metal and part geometry.
Common Types of Quenching Media
Different media extract heat at vastly different speeds. The choice depends on the type of metal, the part's thickness and complexity, and the desired final properties.
Water
Water provides the fastest cooling rate among common liquid quenchants. It is inexpensive and readily available.
Because of its rapid and sometimes uneven cooling (due to the formation of a vapor blanket), it is typically used for simple shapes and carbon steels that require extreme hardness and are less prone to cracking.
Brines (Salt Water)
Adding salt (typically sodium chloride) to water accelerates the cooling rate even further.
The salt helps to disrupt the insulating vapor blanket that forms around the part, allowing for a more uniform and aggressive quench. This is used when the absolute maximum cooling speed is required.
Oils
Oils provide a much slower and more controlled cooling rate compared to water. This makes them ideal for alloy steels, complex shapes, or parts with varying thicknesses.
The slower quench significantly reduces the risk of distortion and cracking, making oil a very common choice for high-precision components like gears and bearings.
Polymer Solutions
Polymers mixed with water offer a unique advantage: their cooling rate is adjustable. By changing the concentration of the polymer, you can achieve cooling speeds that fall between water and oil.
This flexibility allows metallurgists to fine-tune the quenching process for specific alloys and components, providing a balance of hardness and reduced distortion.
Gases
Gases like nitrogen, helium, or argon are used in vacuum furnaces for a process called gas quenching. This provides the slowest and most controlled cooling process.
It is reserved for highly sensitive, high-value alloy steels (like tool steels) where preventing distortion is the absolute top priority. The pressure of the gas can be adjusted to control the cooling rate precisely.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Control
The choice of a quenching medium is always a balance between achieving the desired metallurgical properties and maintaining the physical integrity of the part.
The Risk of Cooling Too Fast
An overly aggressive quench, such as using water for a complex alloy steel part, is the leading cause of problems.
The extreme thermal shock creates high internal stresses. This can lead to visible cracking or microscopic distortion, rendering the component useless.
The Risk of Cooling Too Slow
Choosing a medium that cools too slowly, like using a slow oil for a low-alloy carbon steel, will fail to produce the desired hardness.
The metal's microstructure will transform into softer structures (like pearlite and bainite) instead of the hard martensite, defeating the purpose of the heat treatment.
Selecting the Right Medium for the Job
The ideal quenching medium is one that cools the steel just fast enough to achieve the desired hardness, and no faster.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on simple carbon steels: Use water or brine, but be aware of the high risk of distortion.
- If your primary focus is a balance of hardness and toughness in alloy steels: Use quenching oils, which offer a safer, more controlled cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is fine-tuning the properties or handling complex shapes: Use polymer quenchants for their adjustable cooling rates.
- If your primary focus is minimal distortion on high-value tool steels: Use high-pressure gas quenching in a vacuum furnace for ultimate control.
Ultimately, selecting the right medium is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the performance and reliability of the final component.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Medium | Typical Cooling Rate | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water / Brine | Very Fast | Simple carbon steel shapes | Maximum hardness |
| Oils | Moderate | Alloy steels, complex shapes | Reduced distortion and cracking |
| Polymer Solutions | Adjustable | Fine-tuning for specific alloys | Balance of hardness and control |
| Gases (e.g., Nitrogen) | Slow | High-value tool steels in vacuum furnaces | Minimal distortion, ultimate control |
Achieve precise and reliable results in your heat treatment processes. The right quenching medium is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and dimensional stability in your metal components.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal processing needs. Whether you are working with simple carbon steels or advanced alloys, our expertise can help you select the optimal materials and methods for your specific application.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success and ensure your heat treatment operations are efficient and effective.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















