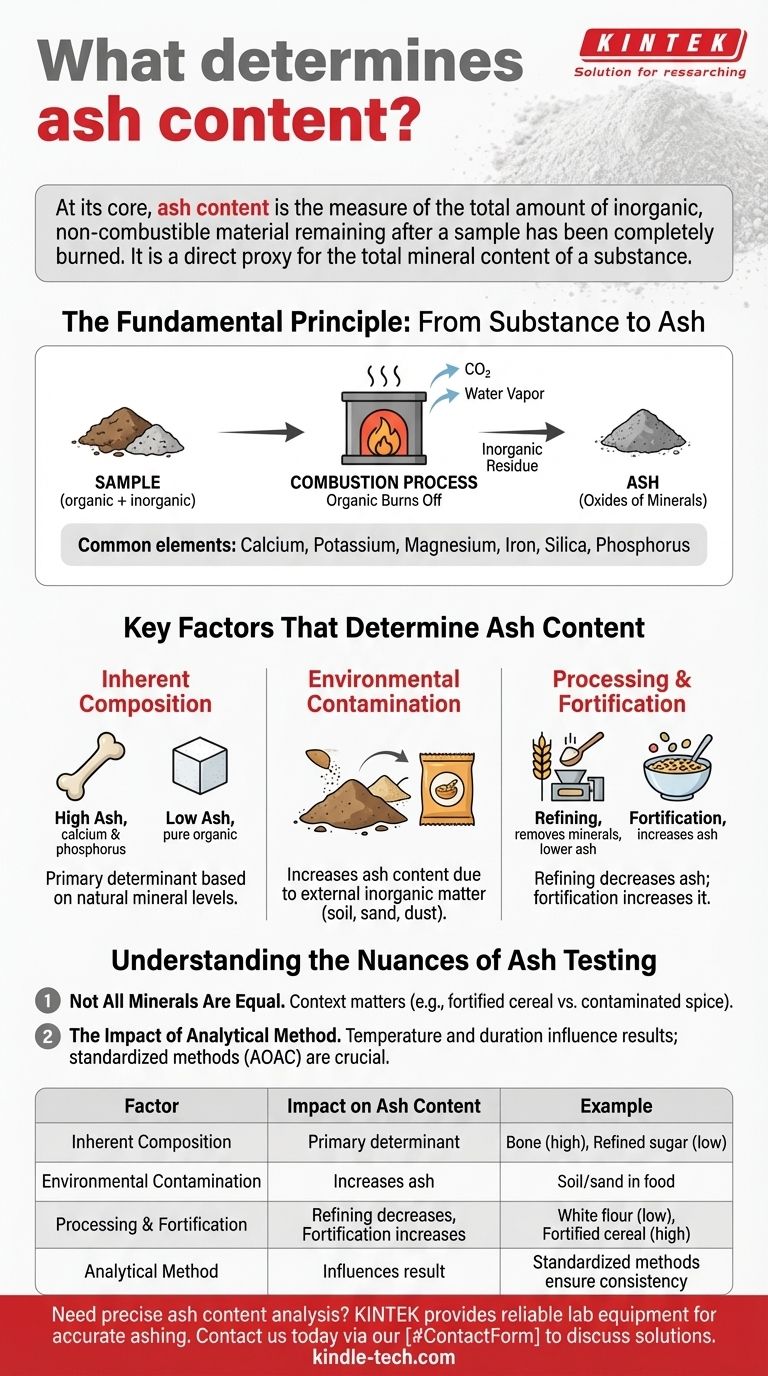
At its core, ash content is the measure of the total amount of inorganic, non-combustible material remaining after a sample has been completely burned. This residue consists of the minerals inherent to the original substance, which convert to oxides and other stable compounds during the high-temperature combustion process.
Ash content is not a measure of burnt material; it is a direct proxy for the total mineral content of a substance. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately assessing a material's quality, nutritional value, and purity.

The Fundamental Principle: From Substance to Ash
To understand what determines ash content, you must first understand the process of combustion and what it leaves behind.
The Combustion Process
When a sample is subjected to high heat in the presence of oxygen, its organic components—primarily compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—are burned off. They are converted into gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, leaving the sample entirely.
What Remains: The Inorganic Residue
What does not burn is the inorganic fraction of the sample. These are the minerals, which are stable at high temperatures. This residue is what we call ash.
Common elements that constitute ash include calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron, silica, and phosphorus. They are left behind primarily as their respective oxides.
A Proxy for Total Minerals
Because the ash is the mineral portion of the sample, its weight provides a direct, quantitative measure of the total mineral content. This is why ash testing is a foundational analysis in fields ranging from food science to geology.
Key Factors That Determine Ash Content
The amount of ash produced is not random. It is determined by several critical factors related to the sample's origin and handling.
Inherent Composition of the Material
The primary determinant is the material itself. Different substances have vastly different natural mineral contents.
For example, a bone sample will have a very high ash content due to its high concentration of calcium and phosphorus. In contrast, a highly refined sugar will have a near-zero ash content because it is almost pure organic sucrose.
Environmental Contamination
External, inorganic materials introduced into the sample will increase its final ash content. This is a critical indicator of quality and purity.
Common contaminants include soil, sand (silica), or dust that may have been mixed with a food product during harvesting or processing.
Processing and Fortification
Human intervention can significantly alter ash content. Refining processes, such as milling wheat into white flour, remove the bran and germ, which are rich in minerals. This results in a lower ash content for the refined product.
Conversely, fortification—the process of adding minerals and vitamins to a food—will intentionally increase the ash content as a way to improve its nutritional profile.
Understanding the Nuances of Ash Testing
While ash content is a powerful metric, interpreting it correctly requires acknowledging its limitations. It provides a total quantity but does not identify the specific minerals present.
Not All Minerals Are Equal
A high ash content can be desirable or undesirable depending on the context. In fortified breakfast cereal, high ash indicates a successful addition of valuable minerals. In a sample of ground spice, high ash could indicate contamination with sand, a sign of poor quality.
The Impact of Analytical Method
The specific temperature and duration of the ashing procedure can influence the final result. Certain minerals may volatilize or partially decompose at extremely high temperatures, leading to an underestimation of the true mineral content.
Therefore, standardized methods (like those from AOAC INTERNATIONAL) are crucial for ensuring results are consistent and comparable across different labs and products.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your interpretation of ash content should be guided by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is nutritional analysis: Use ash content as the primary indicator of the total mineral load in a food or feed product.
- If your primary focus is quality control: View unexpectedly high ash content as a potential red flag for contamination with inorganic adulterants like soil or sand.
- If your primary focus is fuel efficiency: Recognize that high ash content in a fuel (like coal or biomass) signifies more non-combustible material, leading to lower energy output and higher disposal costs for the residual ash.
Ultimately, ash content serves as a fundamental quantitative tool for understanding the inorganic composition of any material.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Ash Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Inherent Composition | Primary determinant based on natural mineral levels. | Bone (high ash) vs. refined sugar (low ash). |
| Environmental Contamination | Increases ash content due to external inorganic matter. | Soil or sand mixed with a food product. |
| Processing & Fortification | Refining decreases ash; fortification increases it. | White flour (low ash) vs. fortified cereal (high ash). |
| Analytical Method | Temperature and duration can affect the final result. | Standardized methods ensure consistency. |
Need precise ash content analysis for your materials? The mineral composition of your samples directly impacts product quality, nutritional value, and purity. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for accurate ashing and sample preparation. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve consistent, reliable results for your quality control or nutritional analysis goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of a muffle furnace? Achieve Uncontaminated, High-Purity Heating
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil laboratory? Essential for Accurate Soil Organic Matter Analysis
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity with Precise High-Temp Analysis



















